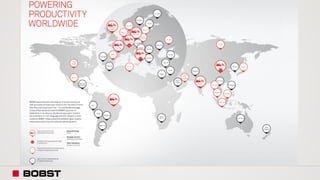
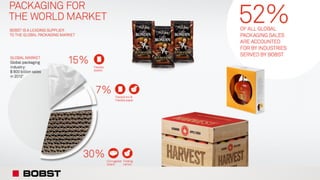
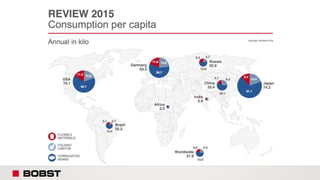
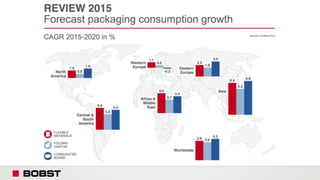
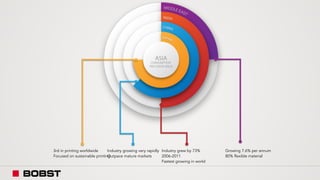
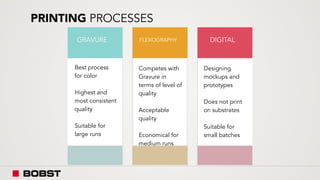
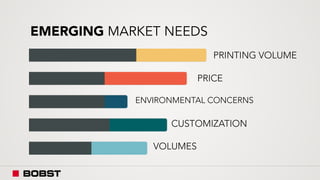
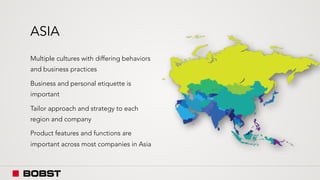
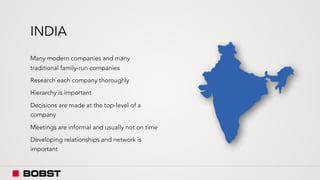
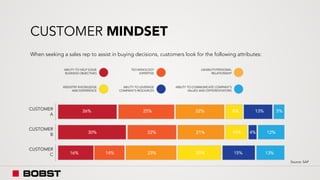
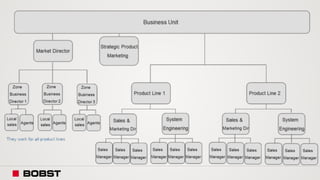
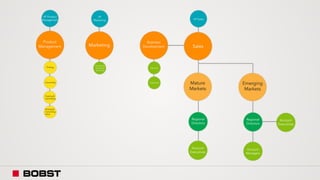
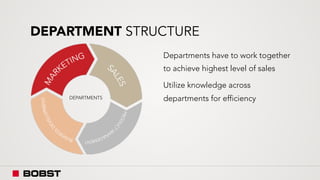
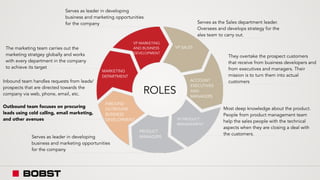
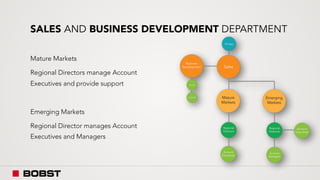
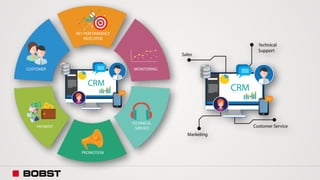
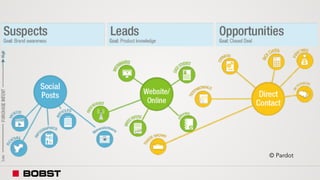
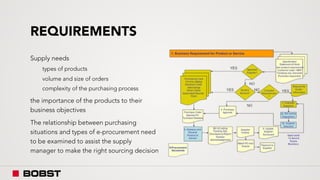
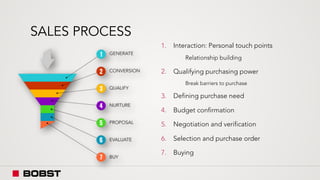
The proposal offers a new segmentation and organizational strategy to help the company adapt to changes in the packaging printing market. It proposes segmenting customers into Key and Prime categories based on their size, needs, and service expectations in both mature and emerging markets. The organizational structure would include dedicated product management and regional sales teams to better support the new segmentation strategy and growth in emerging markets. Implementing the changes would help reduce costs and allow the company to more effectively penetrate emerging market opportunities.