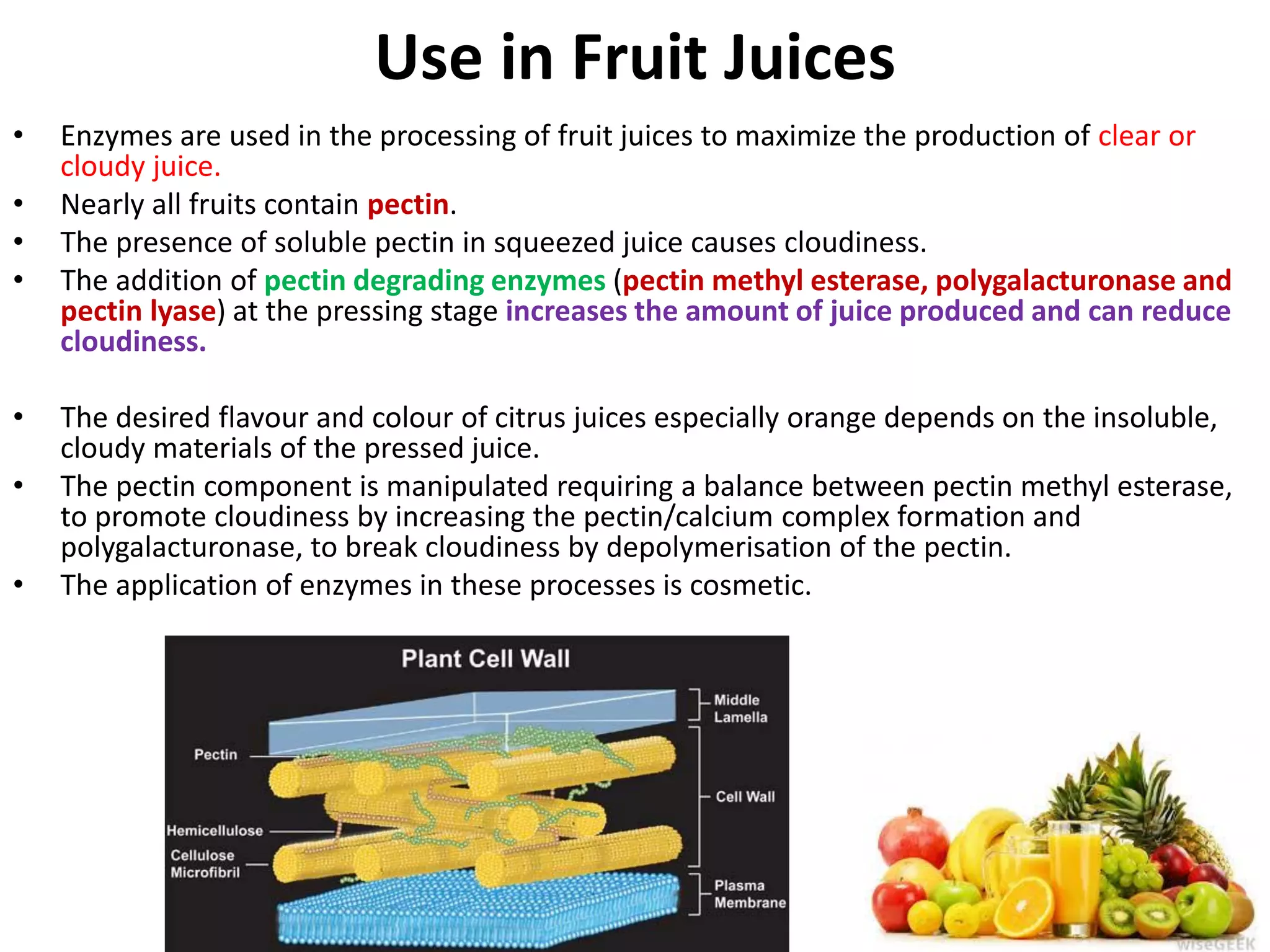
This document discusses several food and industrial applications of enzymes. It describes how enzymes are used in the alcohol industry, particularly for beer brewing, to convert starches and sugars and produce alcohol and carbon dioxide. It also explains how enzymes are used to process fruit juices by degrading pectin and manipulating cloudiness. Additionally, the document outlines the use of enzymes like proteases, lipases and amylases in washing powders and dishwasher detergents to remove various stains and food particles. Finally, it mentions how enzymes are utilized in the textile industry for processes like de-hairing animal hides, de-greasing, and bio-polishing and bio-stoning of fabrics.