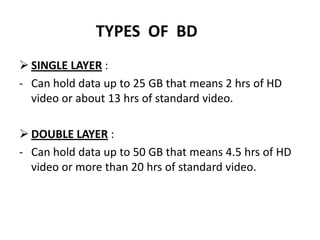
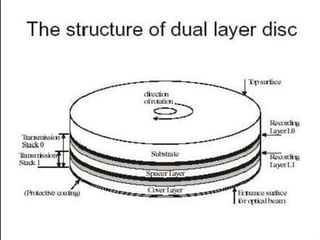
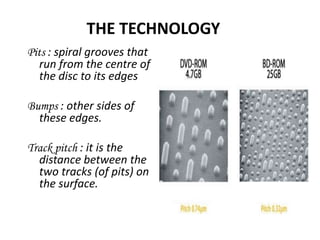
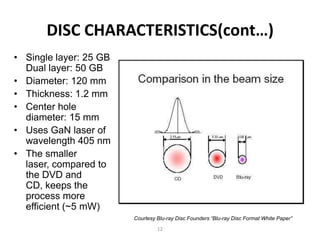
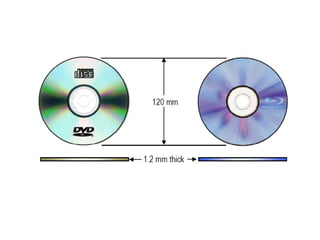
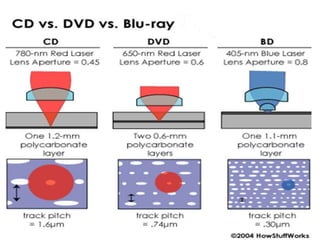
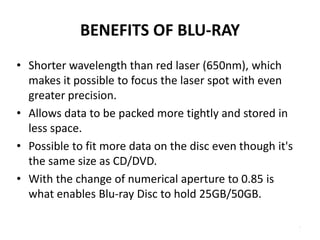
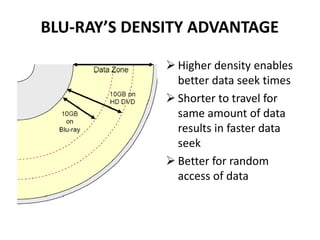
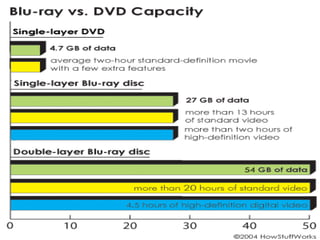
Blu-ray disc is a next-generation optical disc format that was developed to enable high-definition video recording and storage of large amounts of data. It uses a blue laser operating at a wavelength of 405 nm to read very small pits arranged in a continuous spiral track, allowing for 25 or 50 gigabytes of data storage on a single or double layer disc respectively. Blu-ray discs offer benefits over previous formats such as DVD including shorter wavelength for greater precision, higher data density, and increased durability. Ongoing developments aim to further increase storage capacity and compete with video on demand technologies.