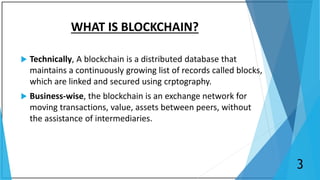
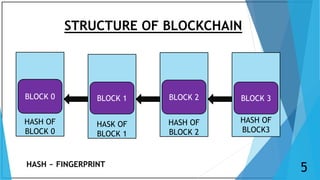
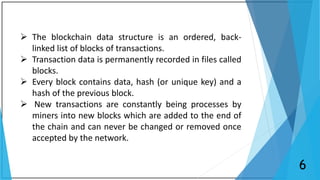
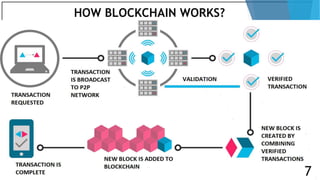
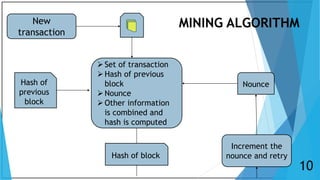
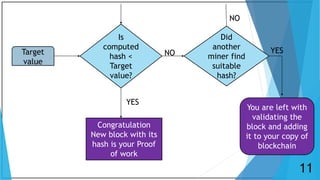
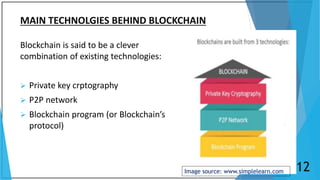
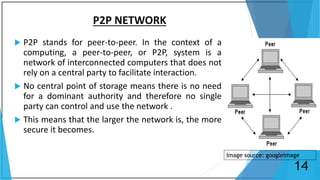
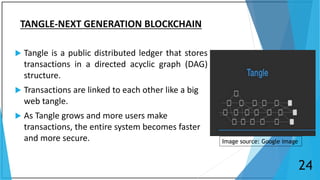
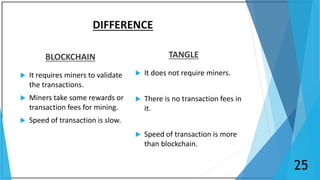
Blockchain is a distributed database that maintains a growing list of transaction records called blocks. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, transaction data, and a timestamp. This forms a chain where blocks are linked in a linear chronological order. New transactions are broadcast to the peer-to-peer network, validated by nodes, and grouped into blocks that are then added to the blockchain through a process called mining which solves a complex math problem. The blockchain is maintained across the decentralized network and no single entity controls it, providing security, transparency, and decentralization.