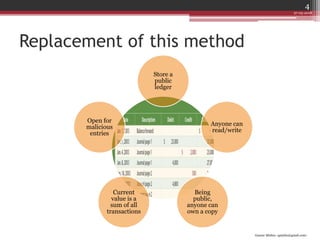
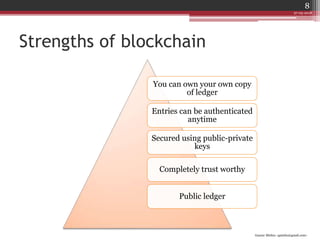
The document discusses blockchain and how it can be used as an alternative to the traditional banking system of transactions. In blockchain, a public ledger stores all transactions and anyone can own a copy of this ledger. Each transaction is authenticated using public-private key cryptography and blocks of transactions are hashed together and chained, making the records difficult to modify. This distributed and secured system allows for a trustworthy and transparent record of transactions without centralized control.