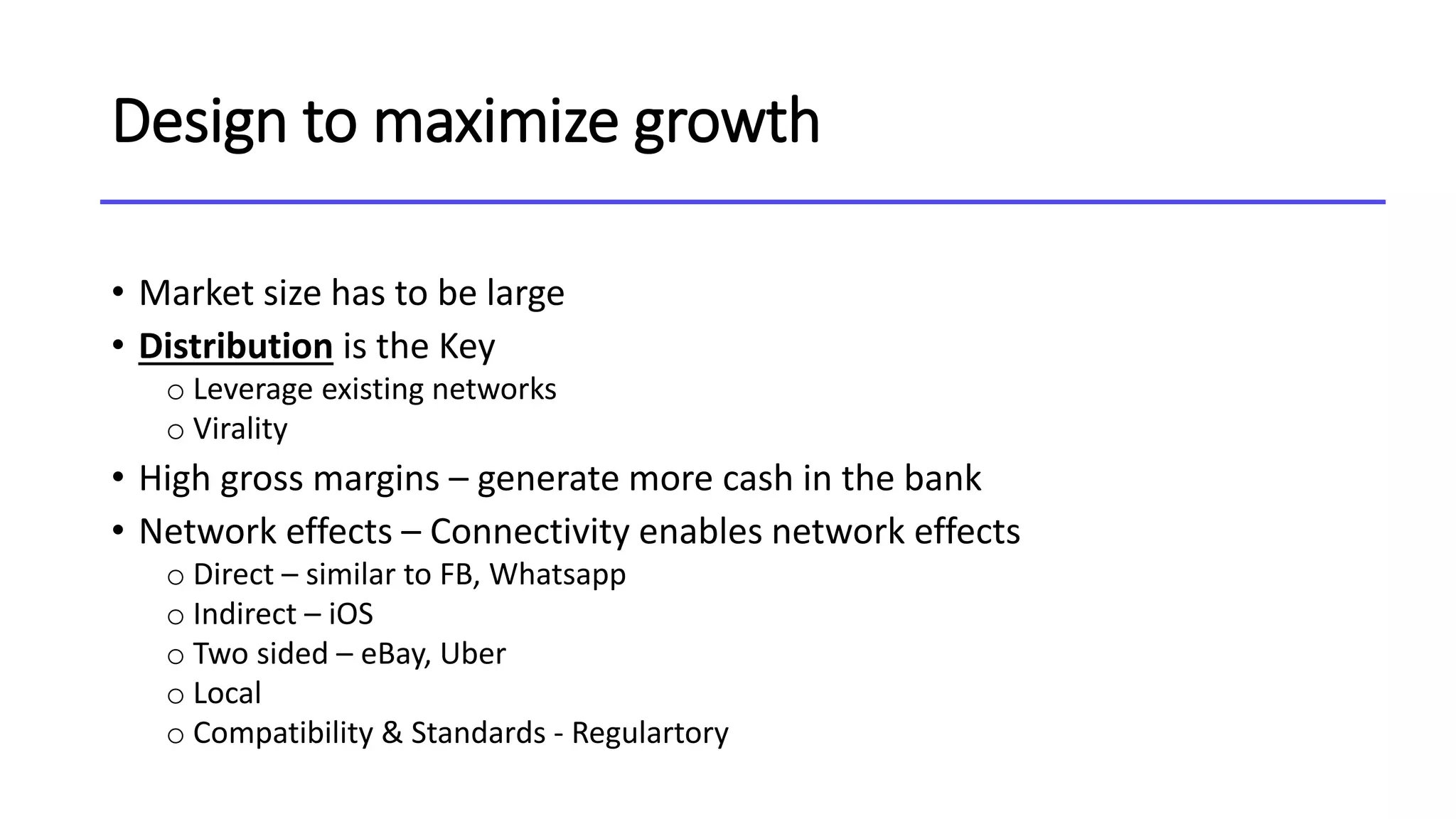
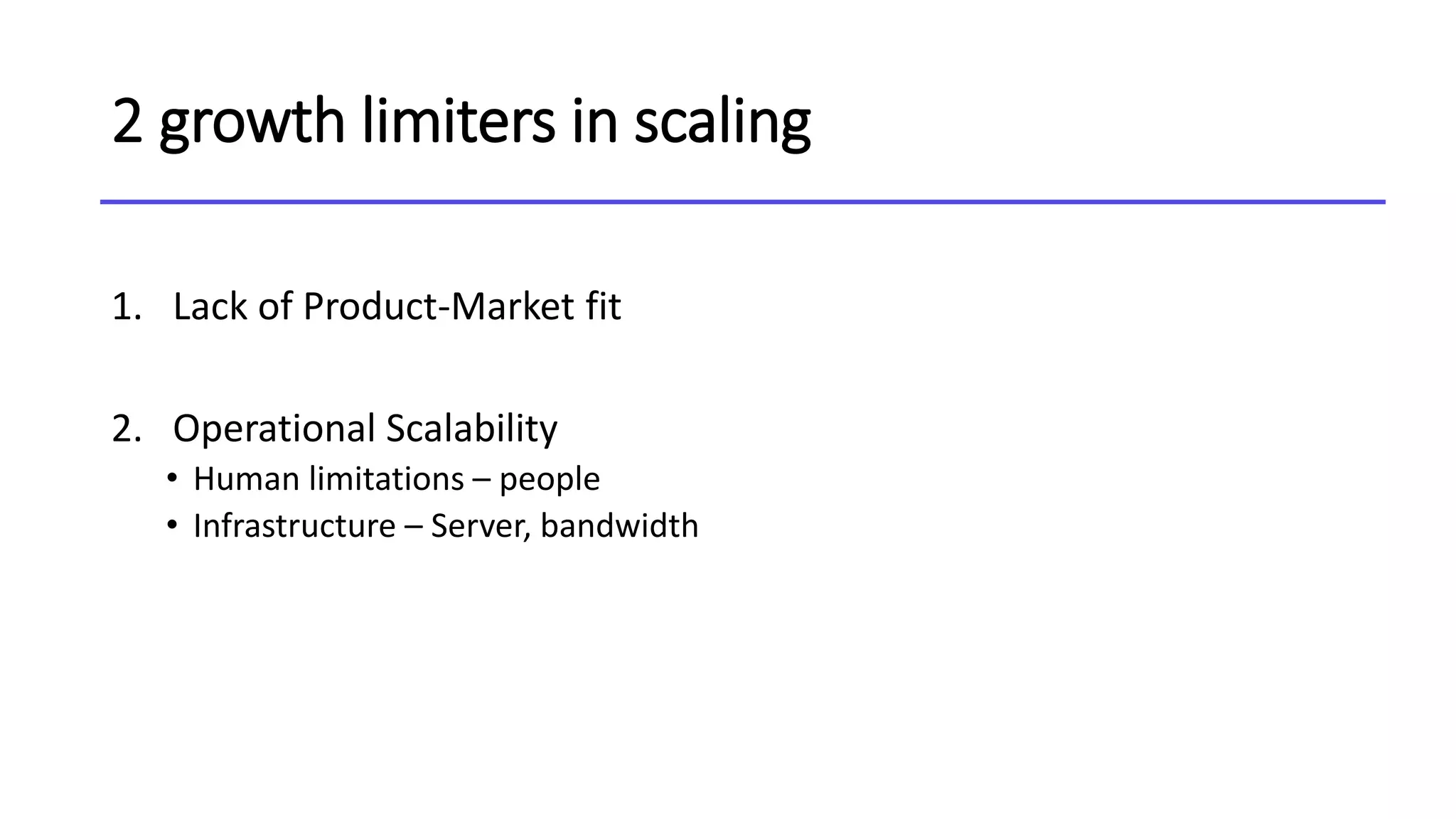
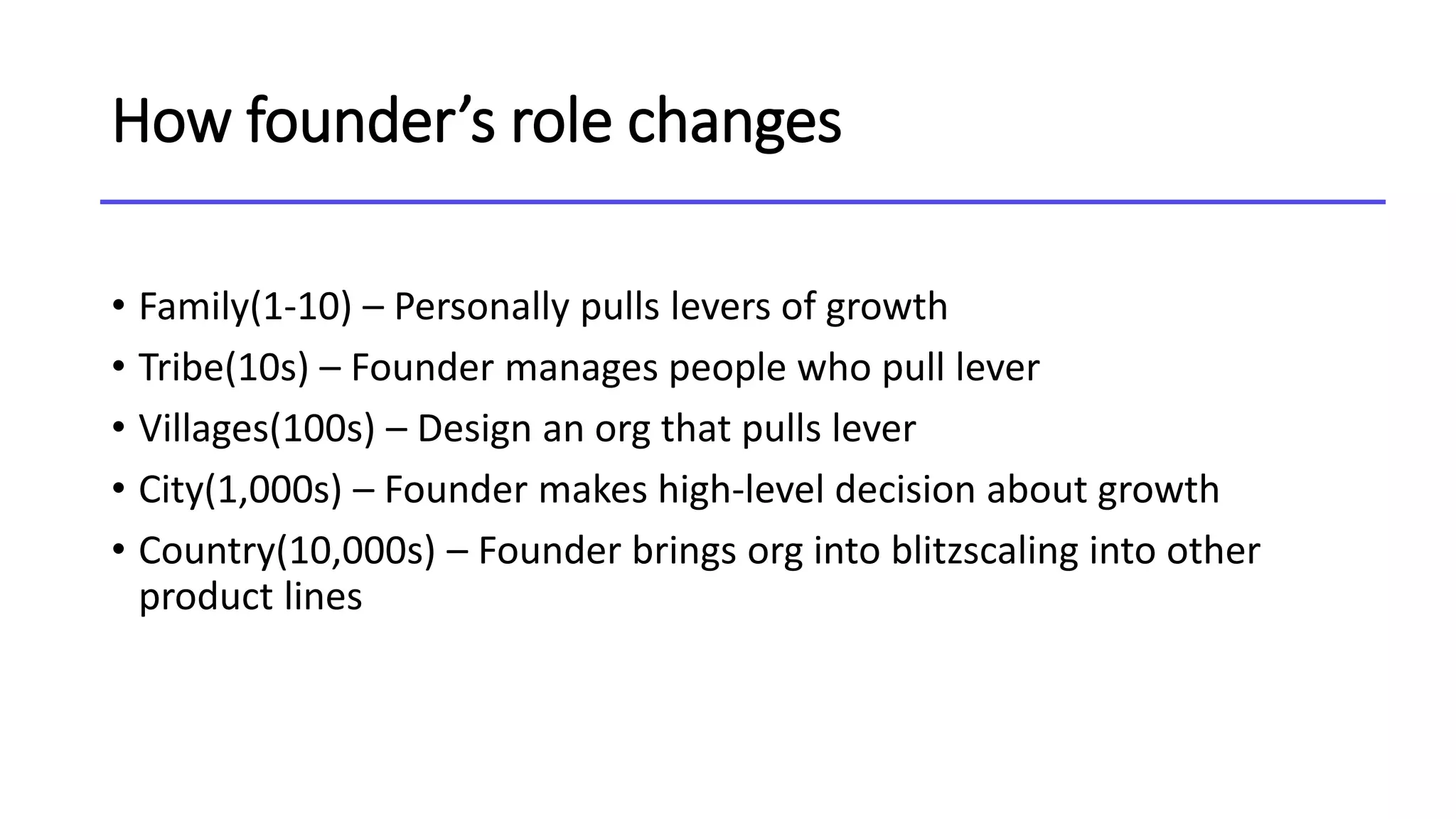
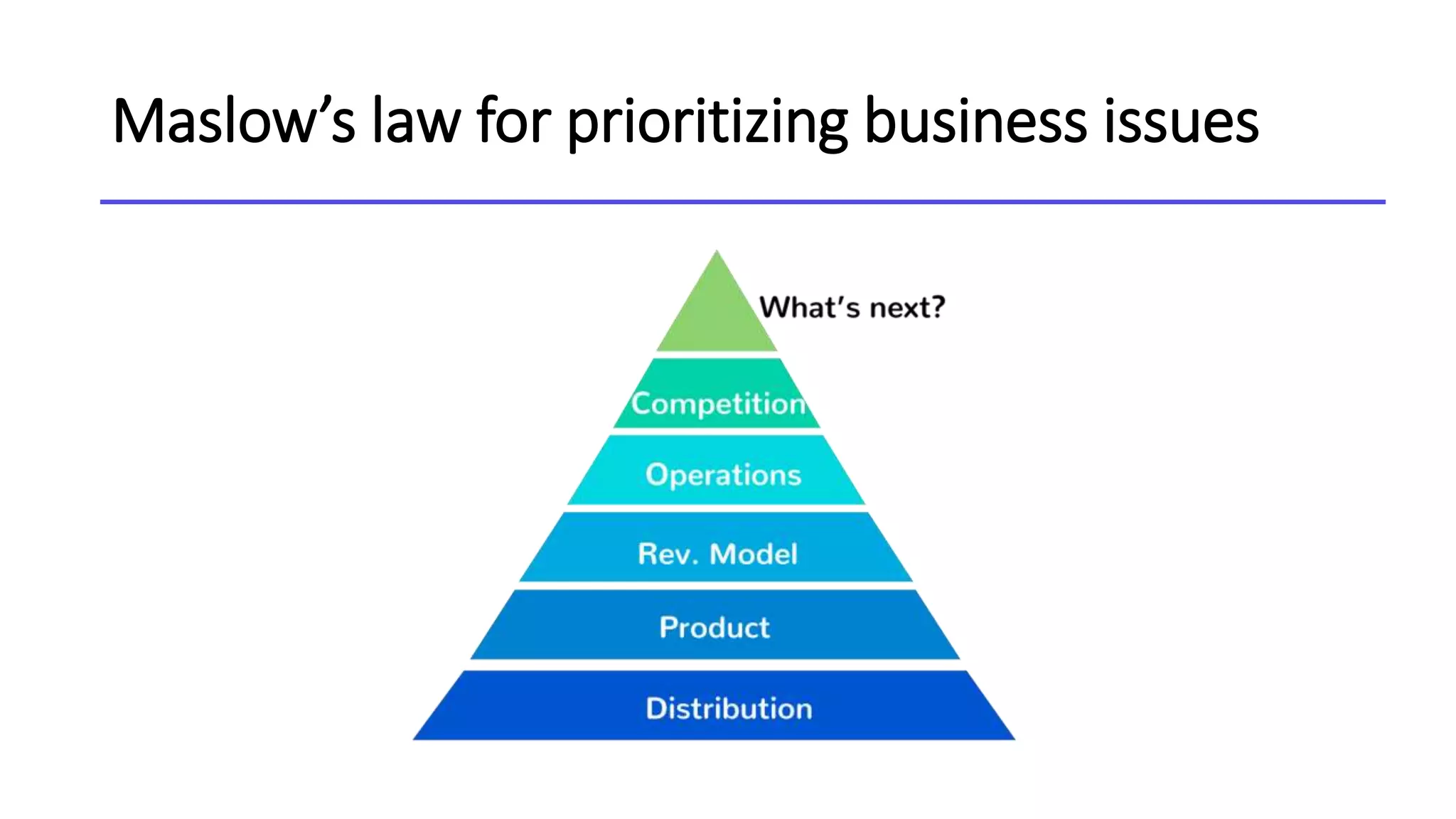
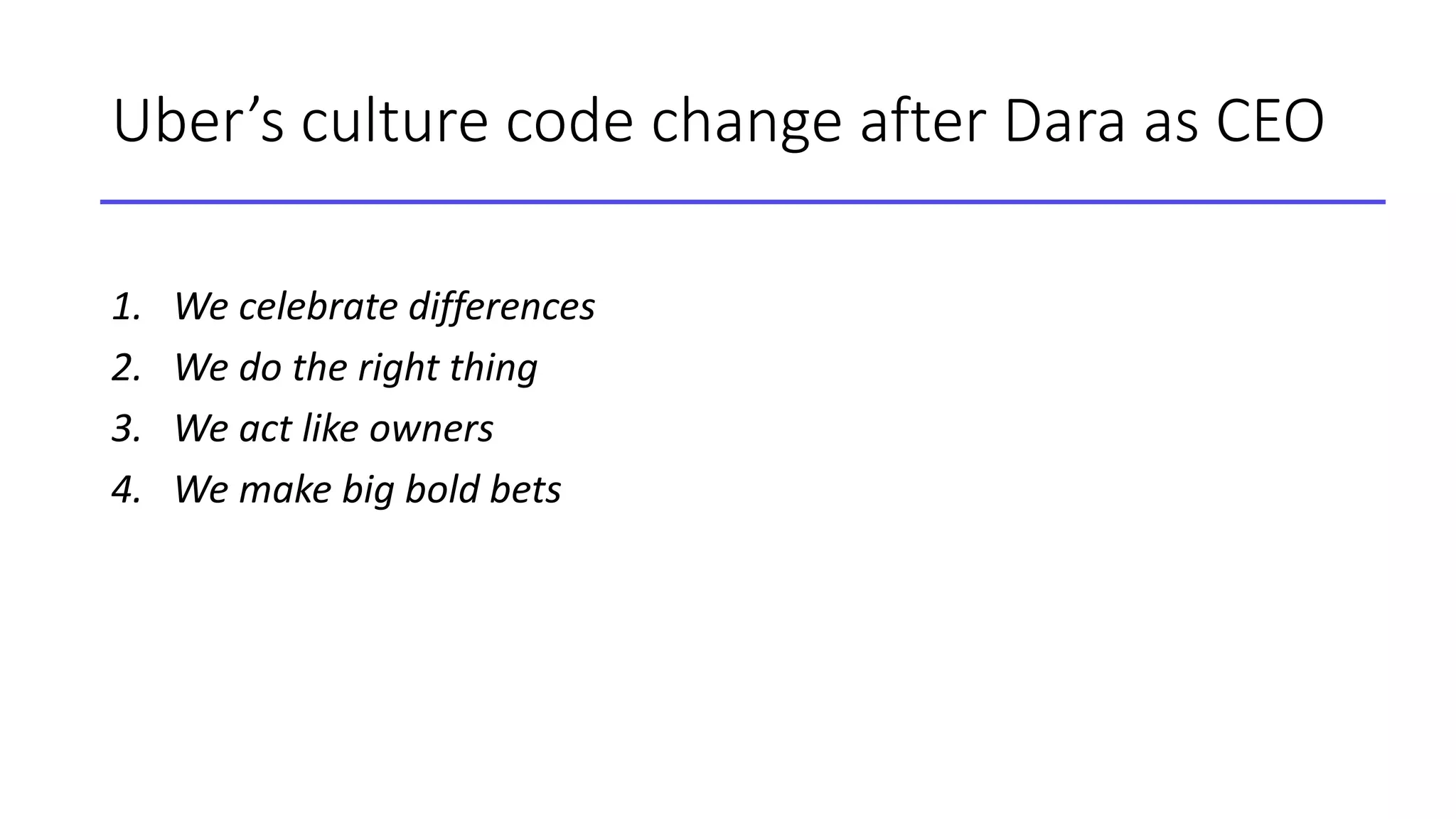
This document discusses the concept of blitzscaling, which refers to rapidly scaling a business in the face of uncertainty. It covers the basics of blitzscaling, including its defining characteristics and 5 stages of scaling a company. It also discusses techniques for blitzscaling like business model innovation, strategic innovation, and management innovation. Specific strategies covered include leveraging network effects, copying successful models, and determining when to stop blitzscaling. The document also outlines 8 key transitions companies face when scaling, such as shifting from generalists to specialists and from inspiration to data-driven decision making. Finally, it provides counterintuitive "rules" for blitzscaling and discusses developing an adaptive culture.