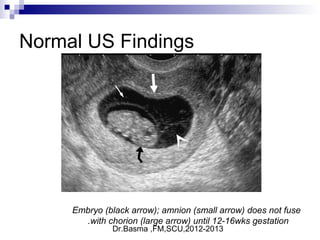
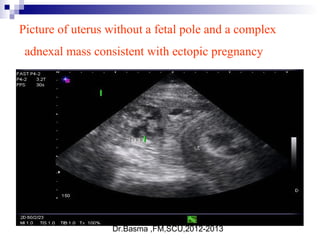
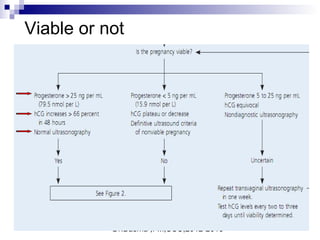
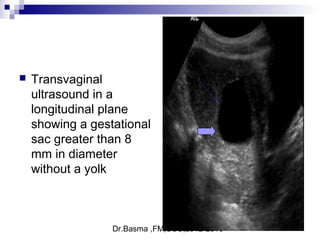
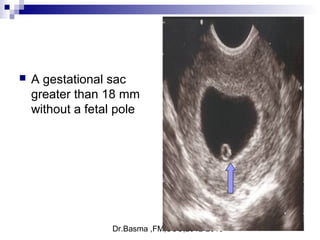
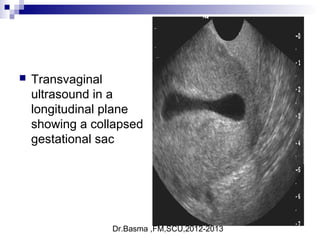
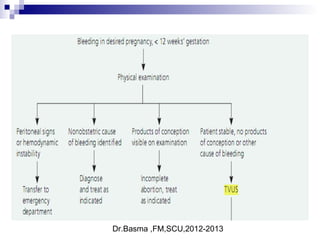
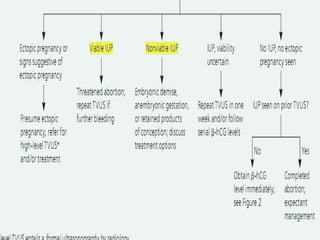
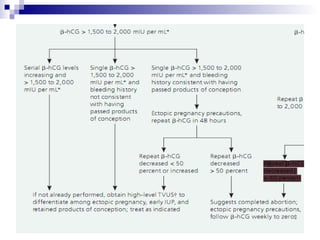
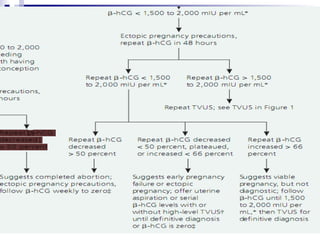
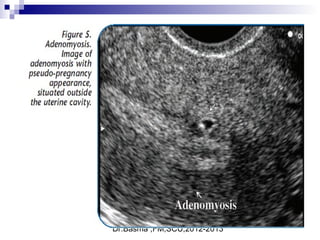
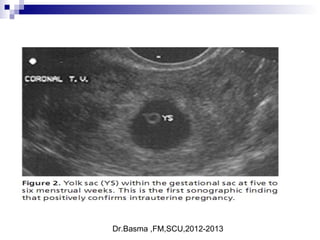
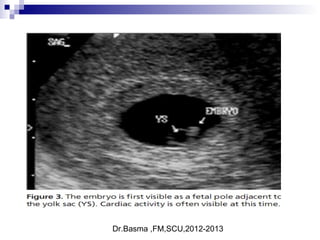
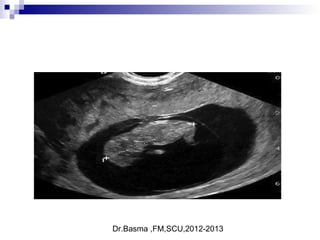
Vaginal bleeding in early pregnancy can be caused by abortion, ectopic pregnancy, or hydatidiform mole. For a 27-year old woman presenting with vaginal bleeding 1 day after a missed period, the doctor would check a beta hCG test and ultrasound to determine if she is pregnant and if the pregnancy is intrauterine or ectopic. If the pregnancy is not viable or located outside the uterus, management may involve expectant care, misoprostol, or uterine aspiration depending on the specific diagnosis and ultrasound findings.




















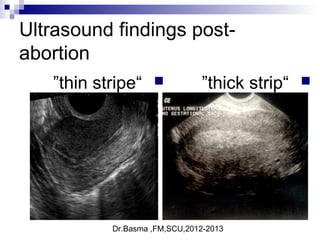
![Dr.Basma ,FM,SCU,2012-2013
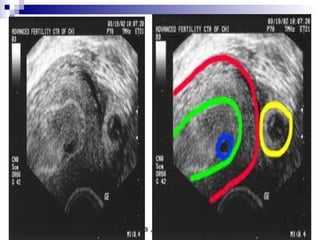
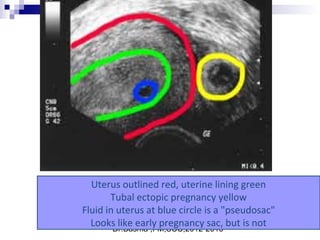
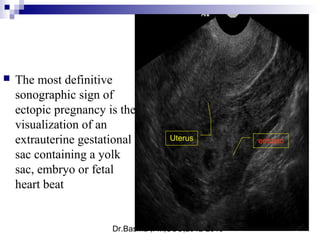
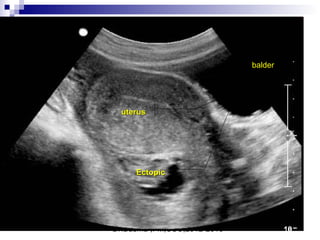
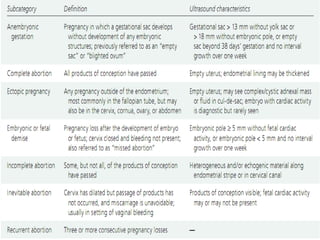
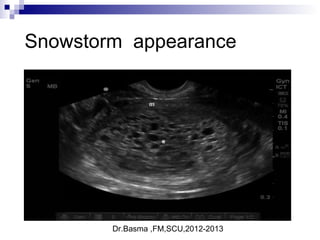
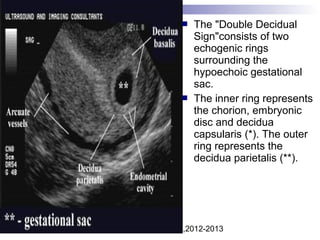
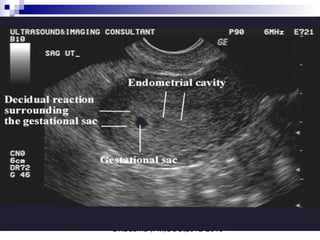
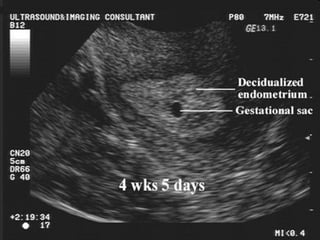
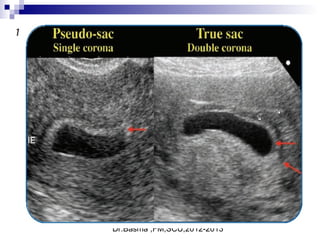
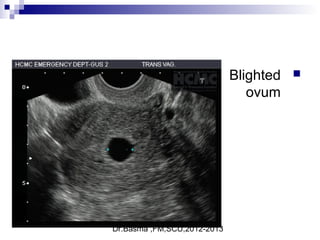
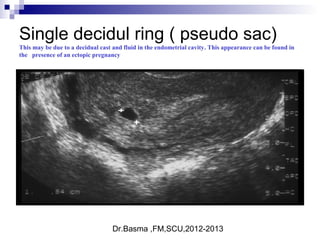
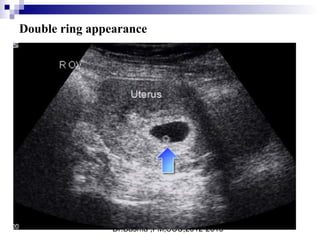
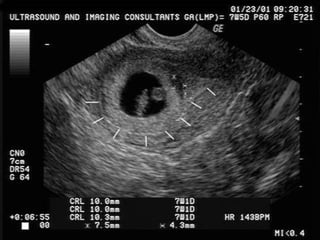
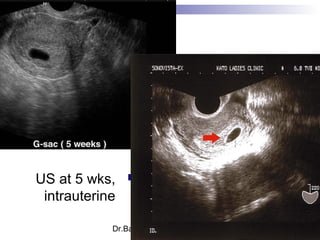
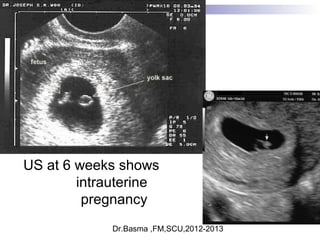
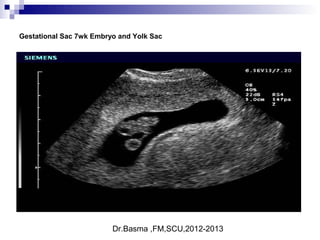
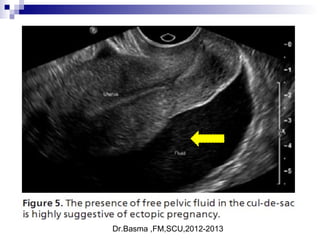
Ultrasound sign
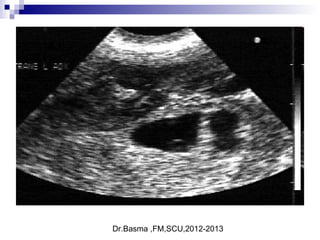
A tubal ring is a thick-walled cystic structure in the adnexa,
independent of the ovary and uterus, and is highly predictive
of ectopic pregnancy
It can sometimes be confused with a corpus luteum cyst when
the ovary is not well visualized.
The corpus luteum cyst wall tends to be thinner and less
echogenic than the endometrium, and the cyst tends to contain
clear fluid
When surrounded by free fluid, it can sometimes be confused
with a hemorrhagic ovarian cyst.[17]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bleeding2-170319045319/85/vaginal-bleeding-in-early-pregnancy-44-320.jpg)