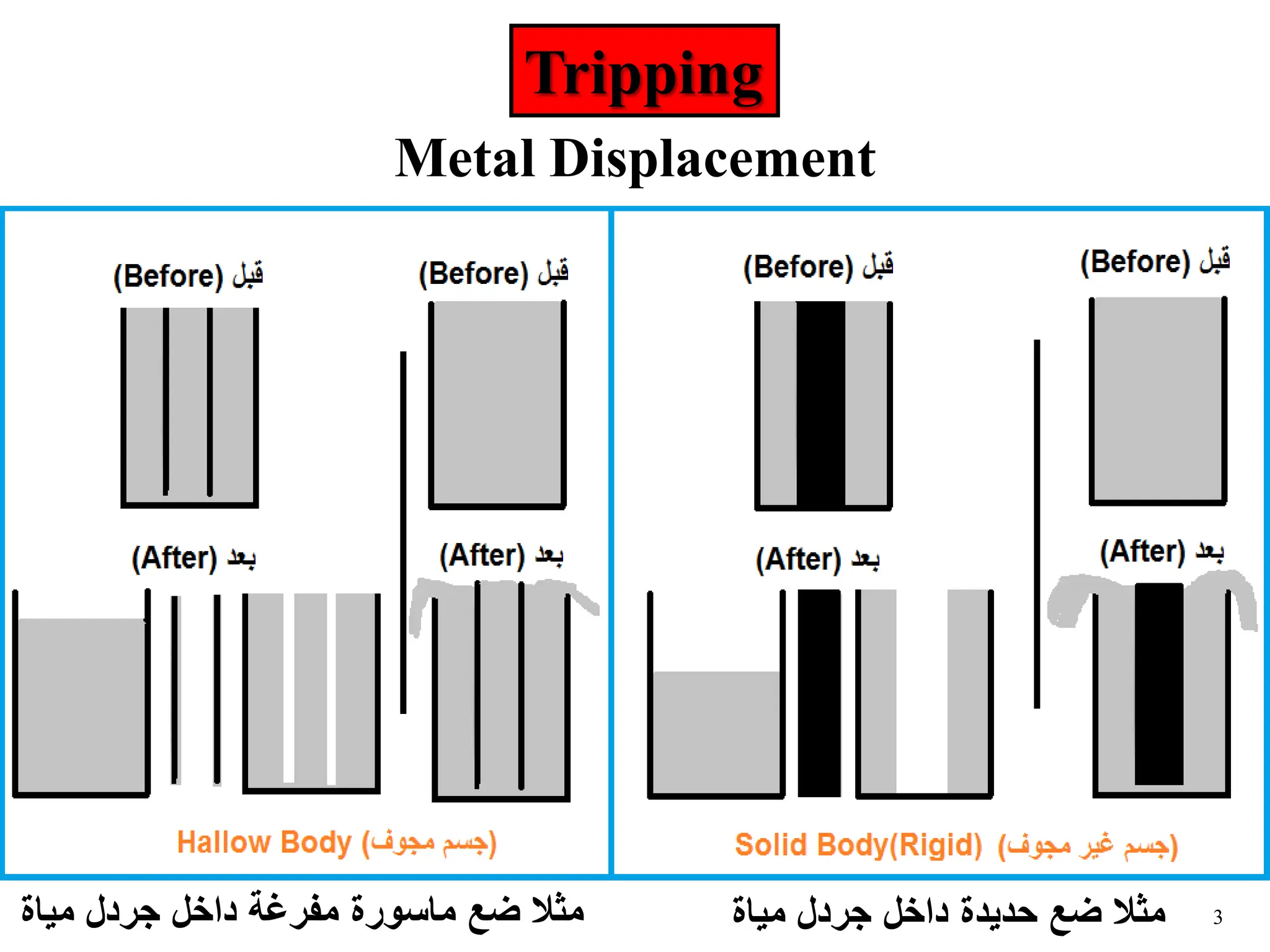
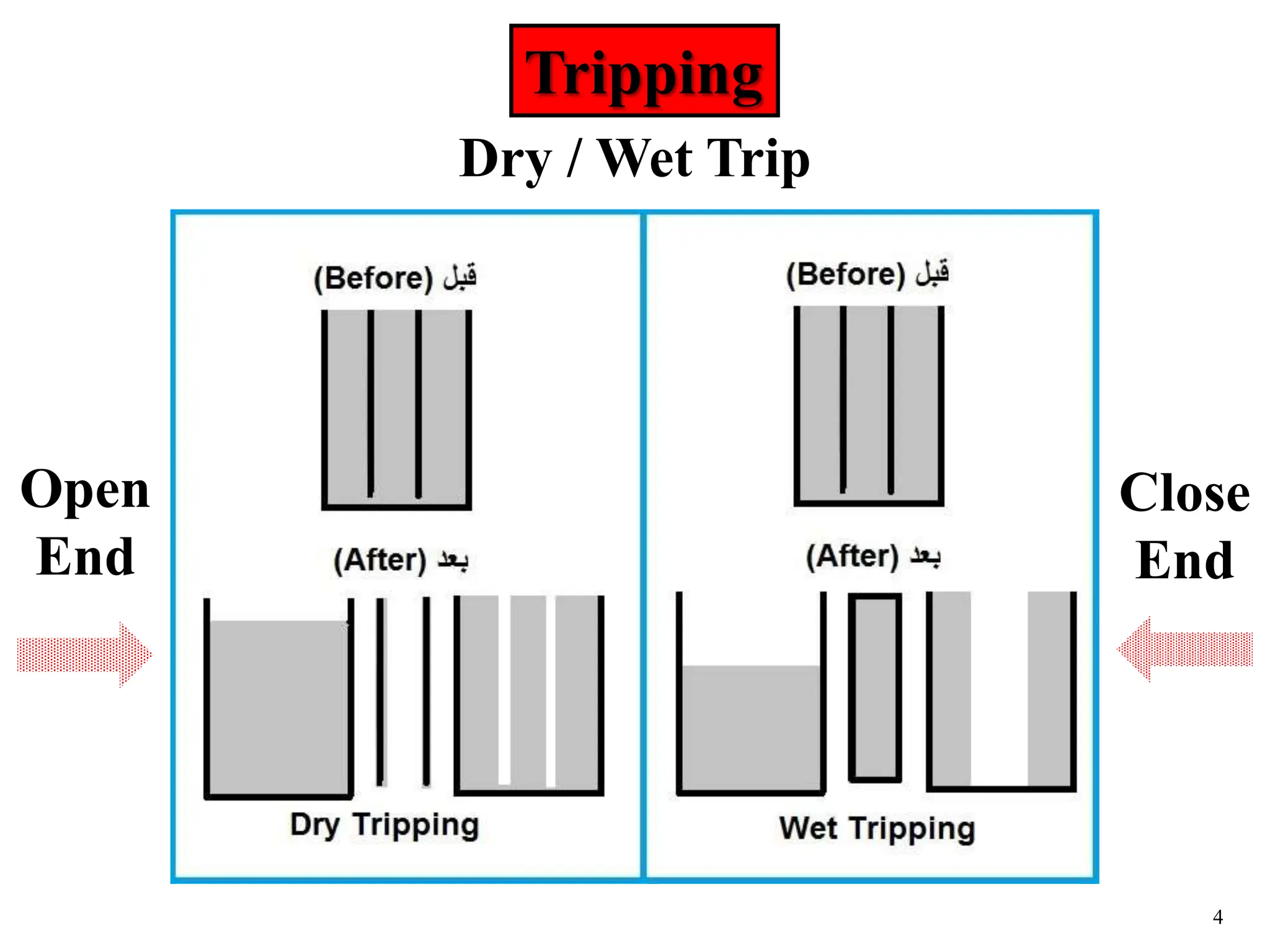
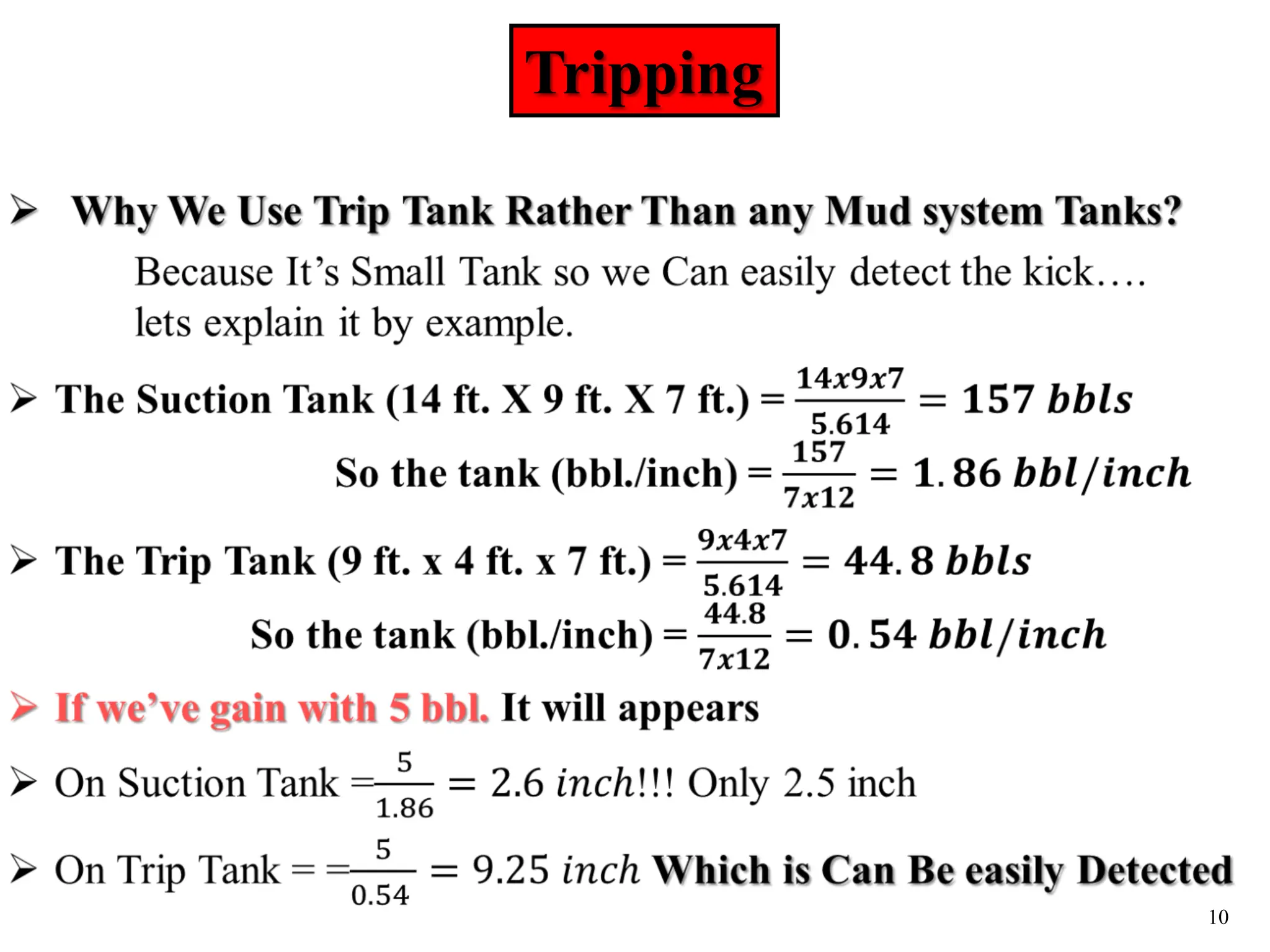
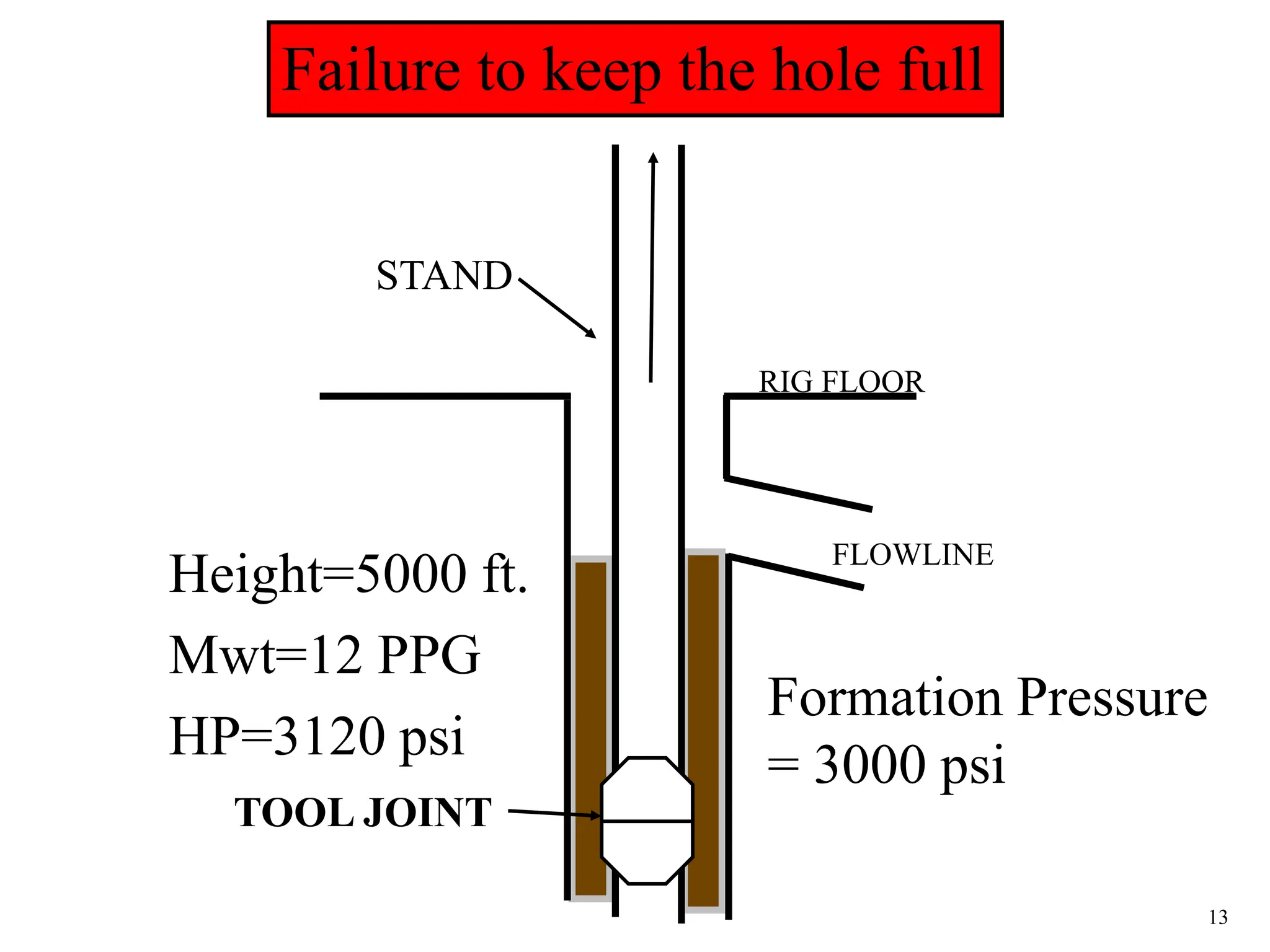
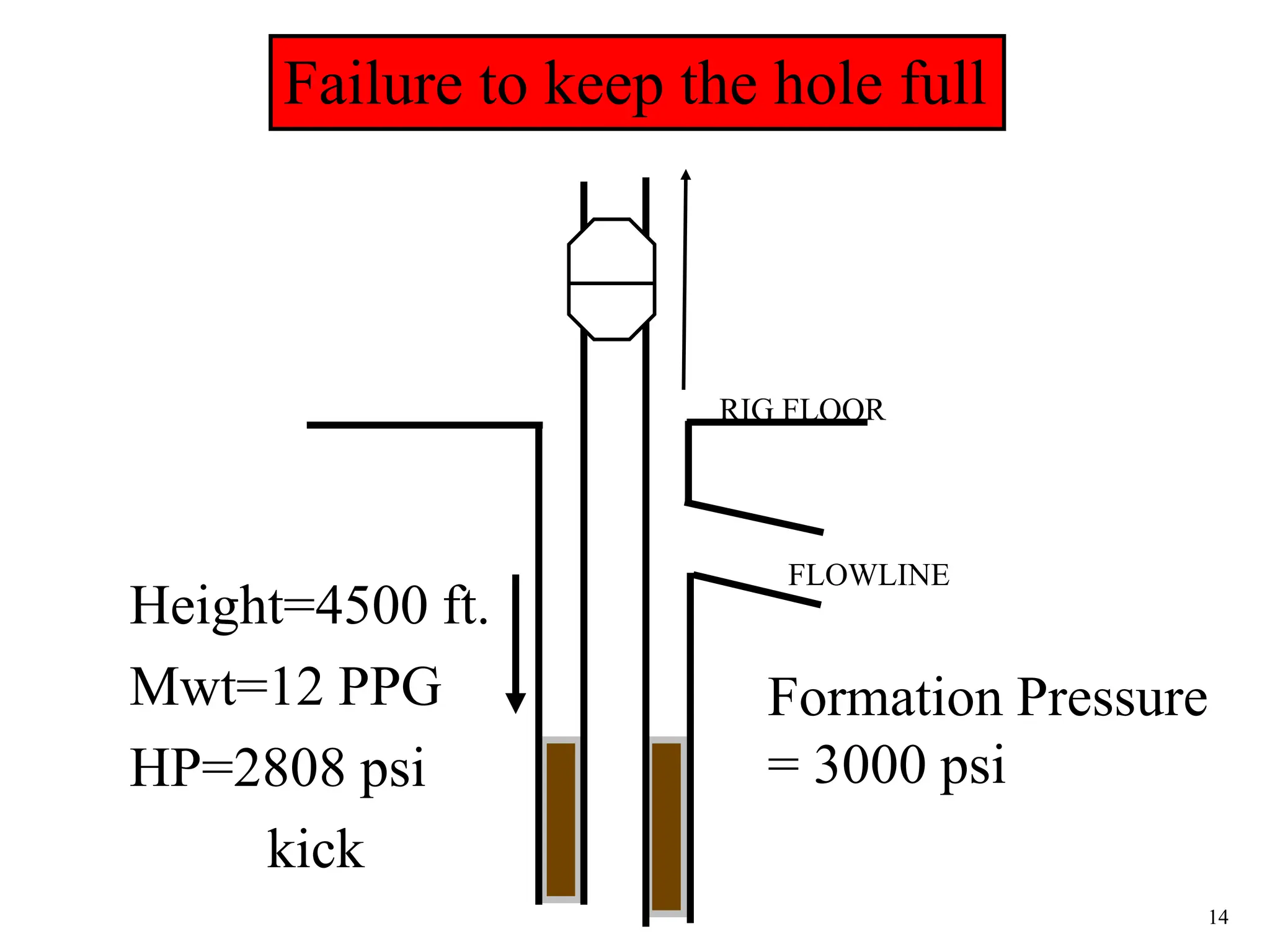
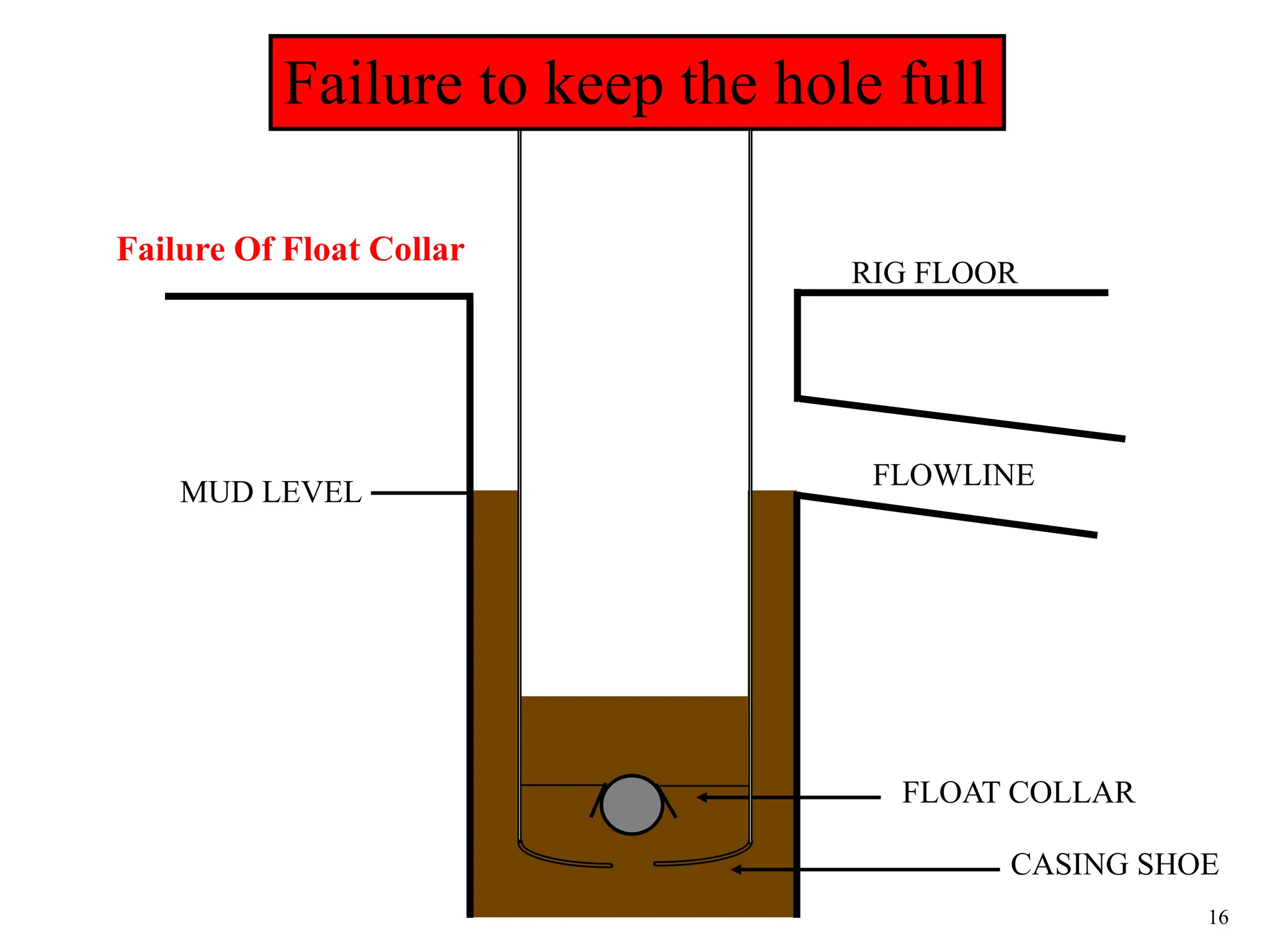
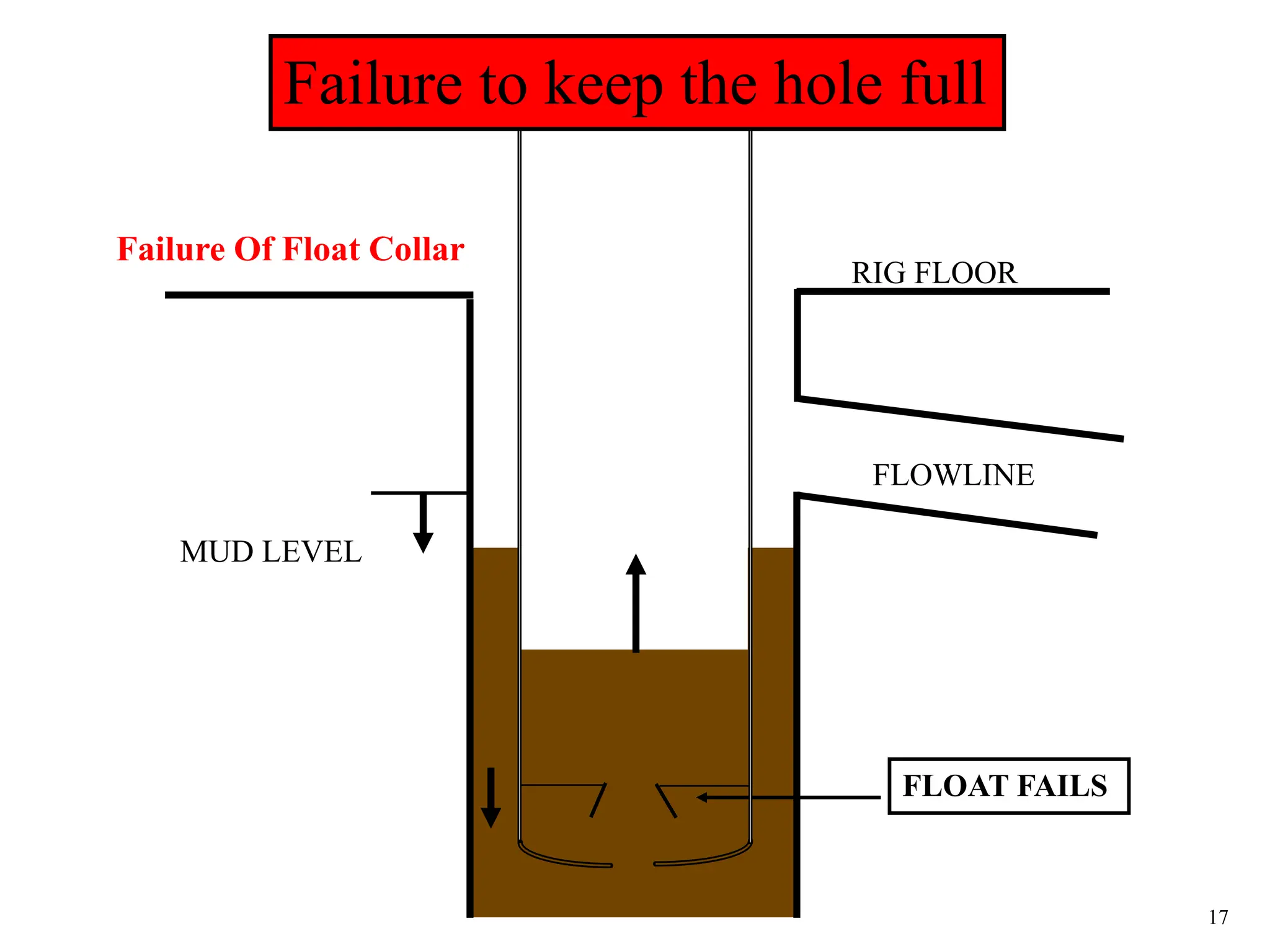
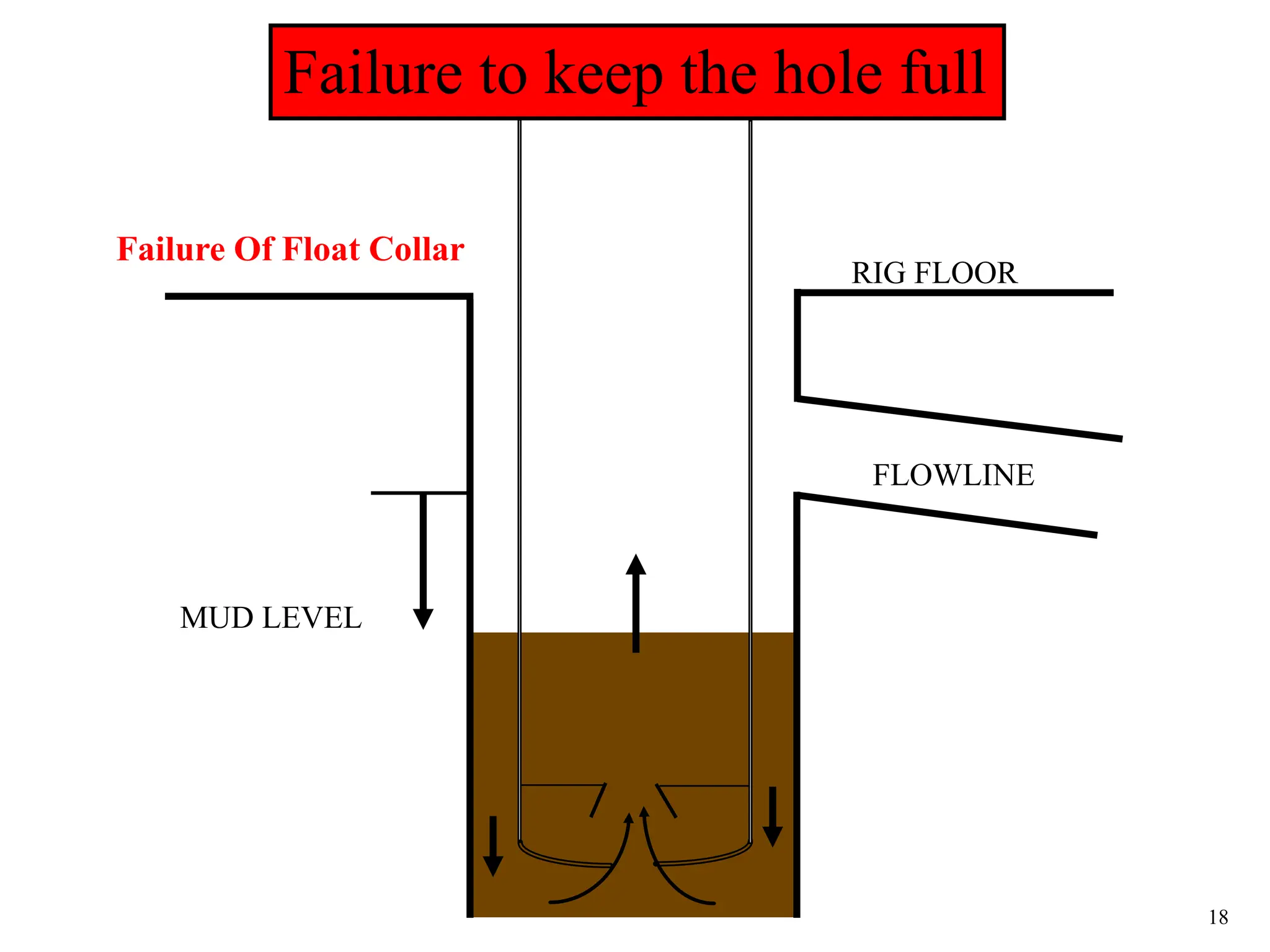
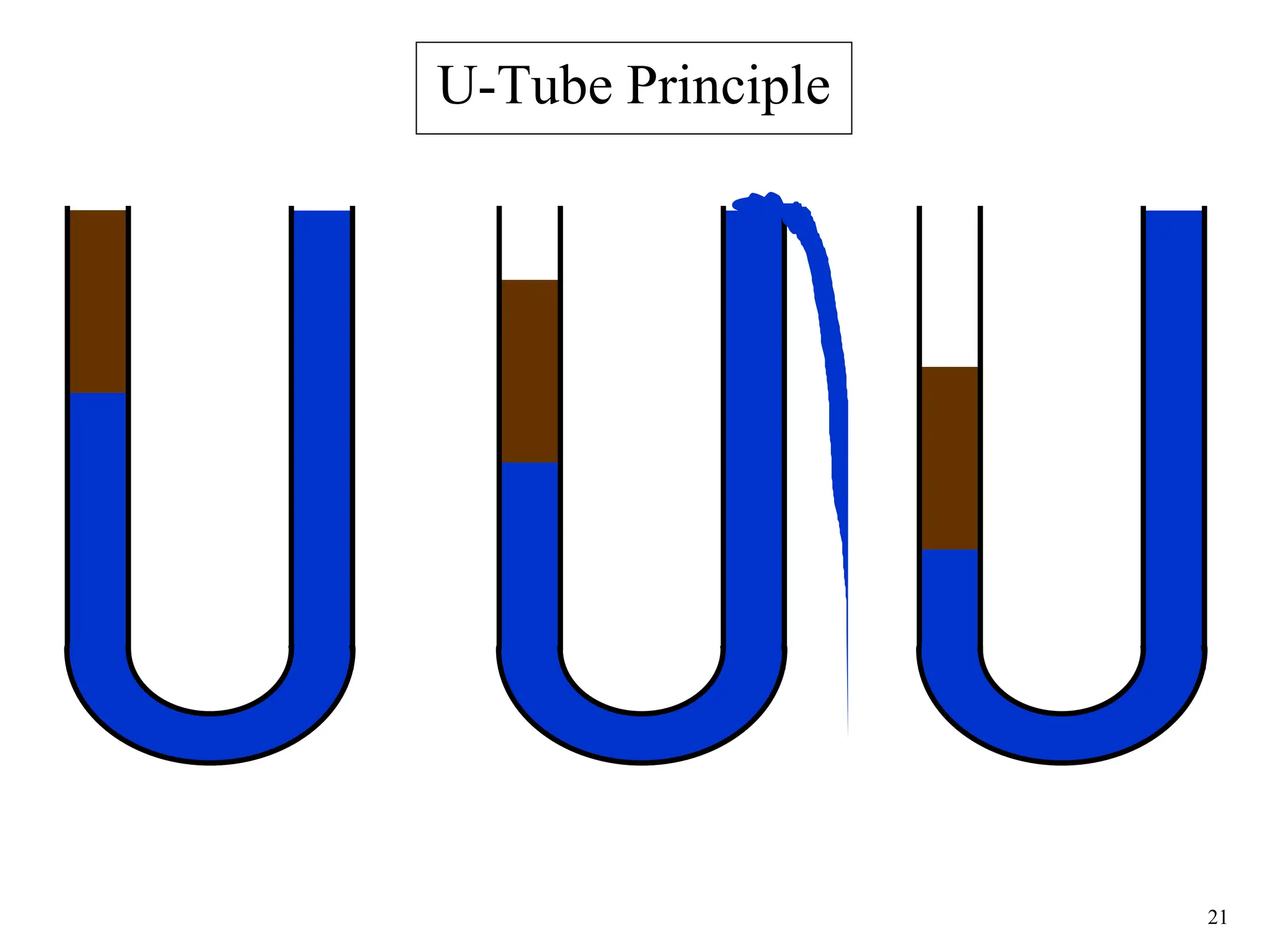
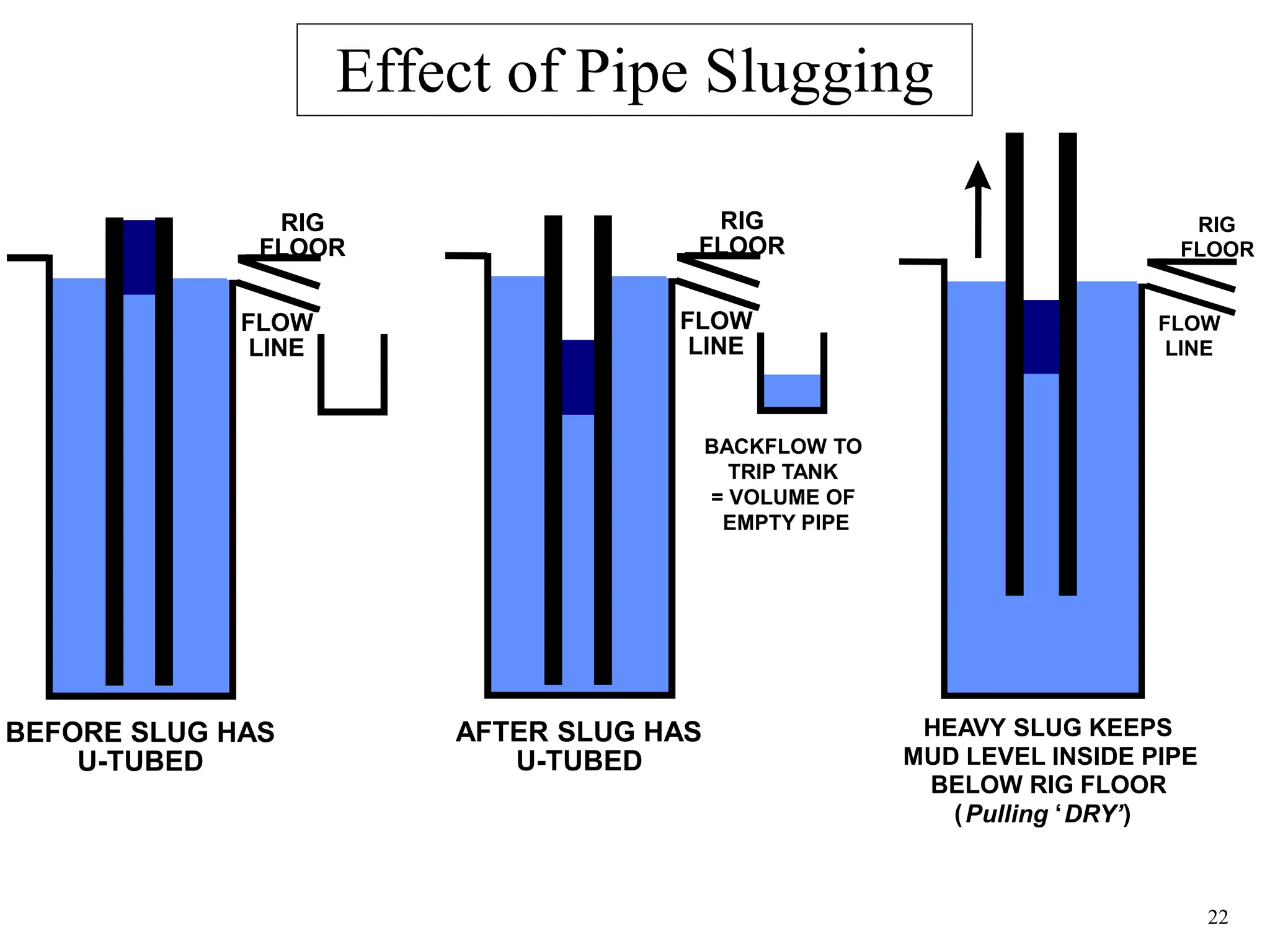
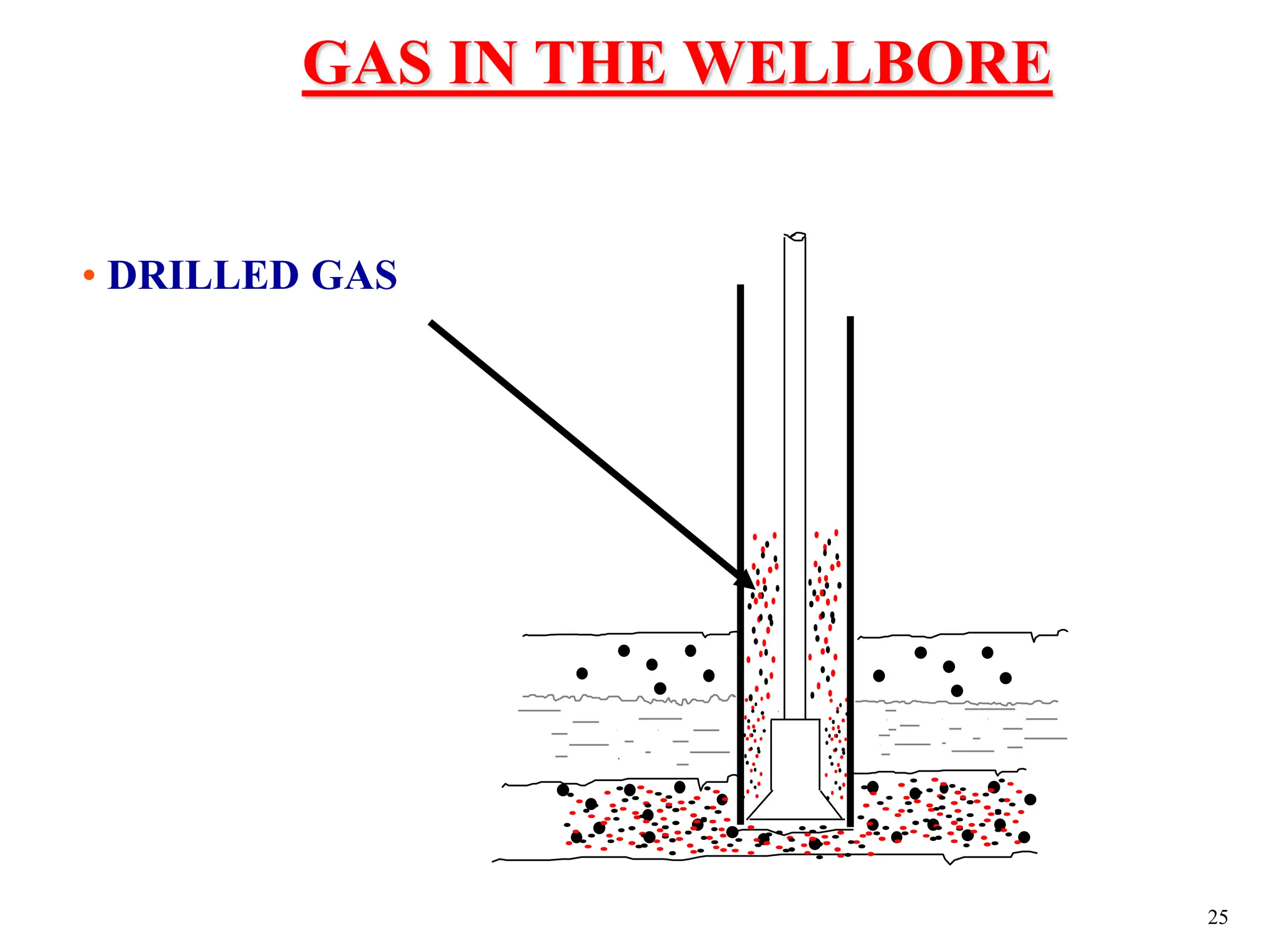
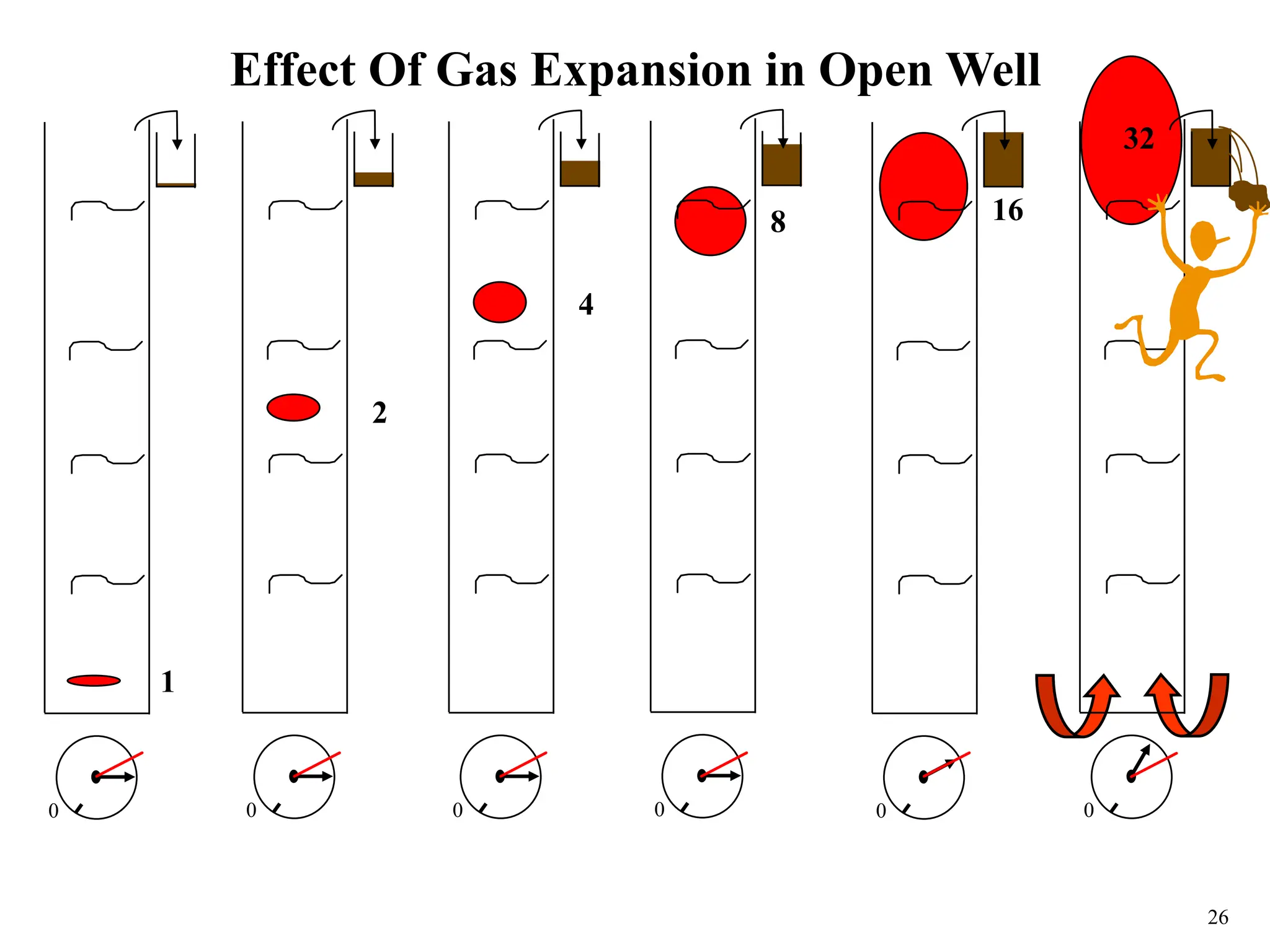
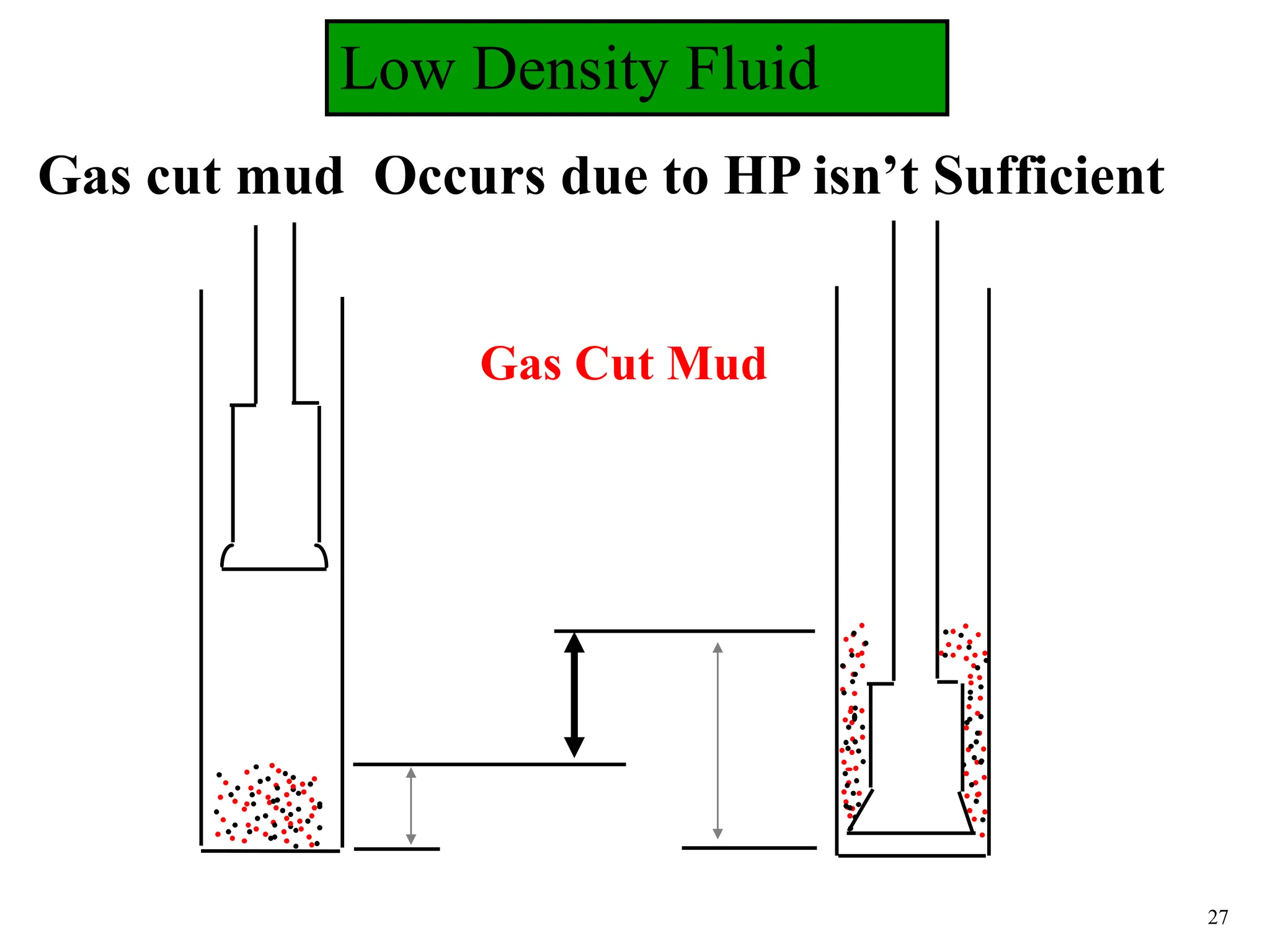
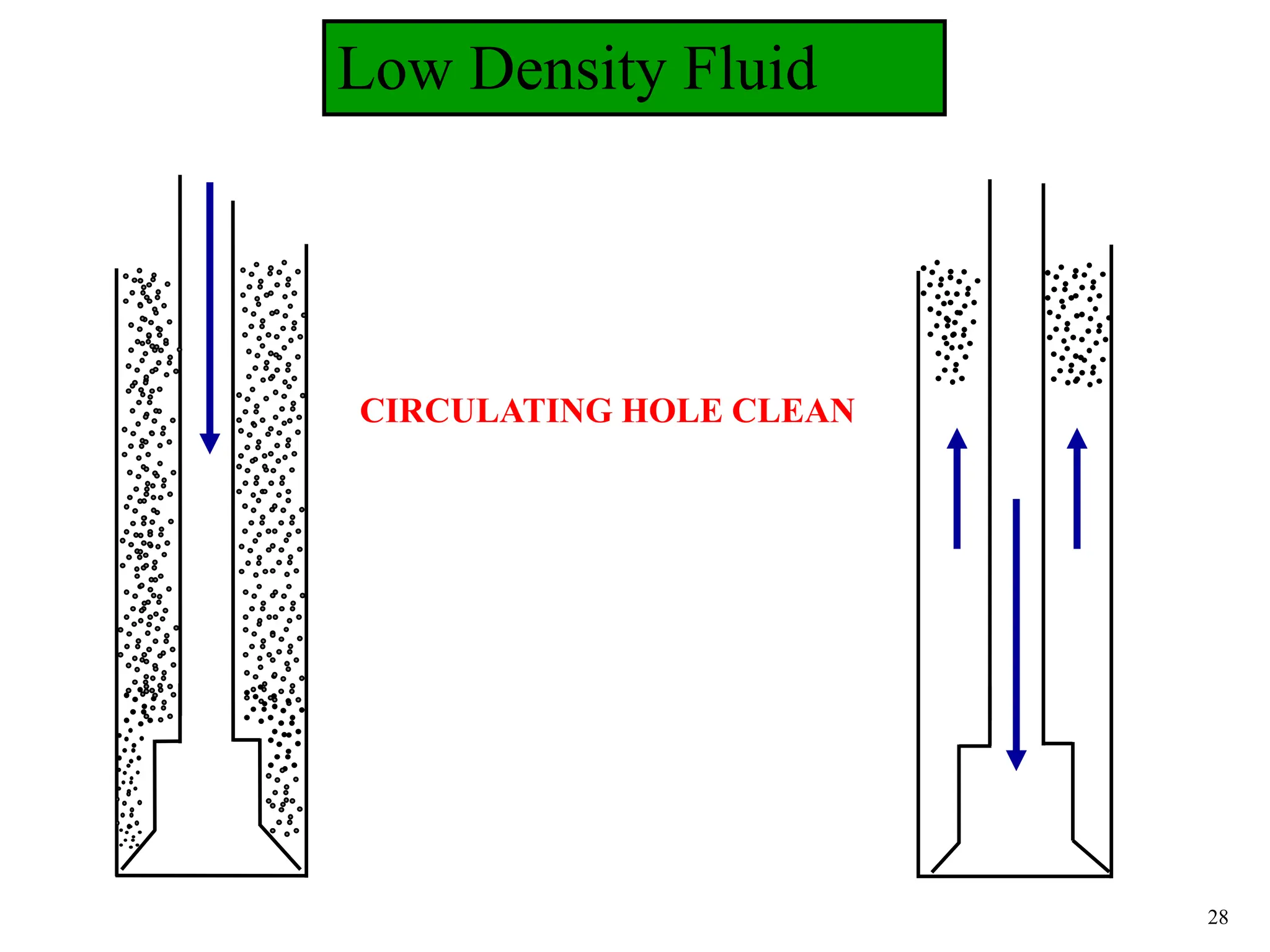
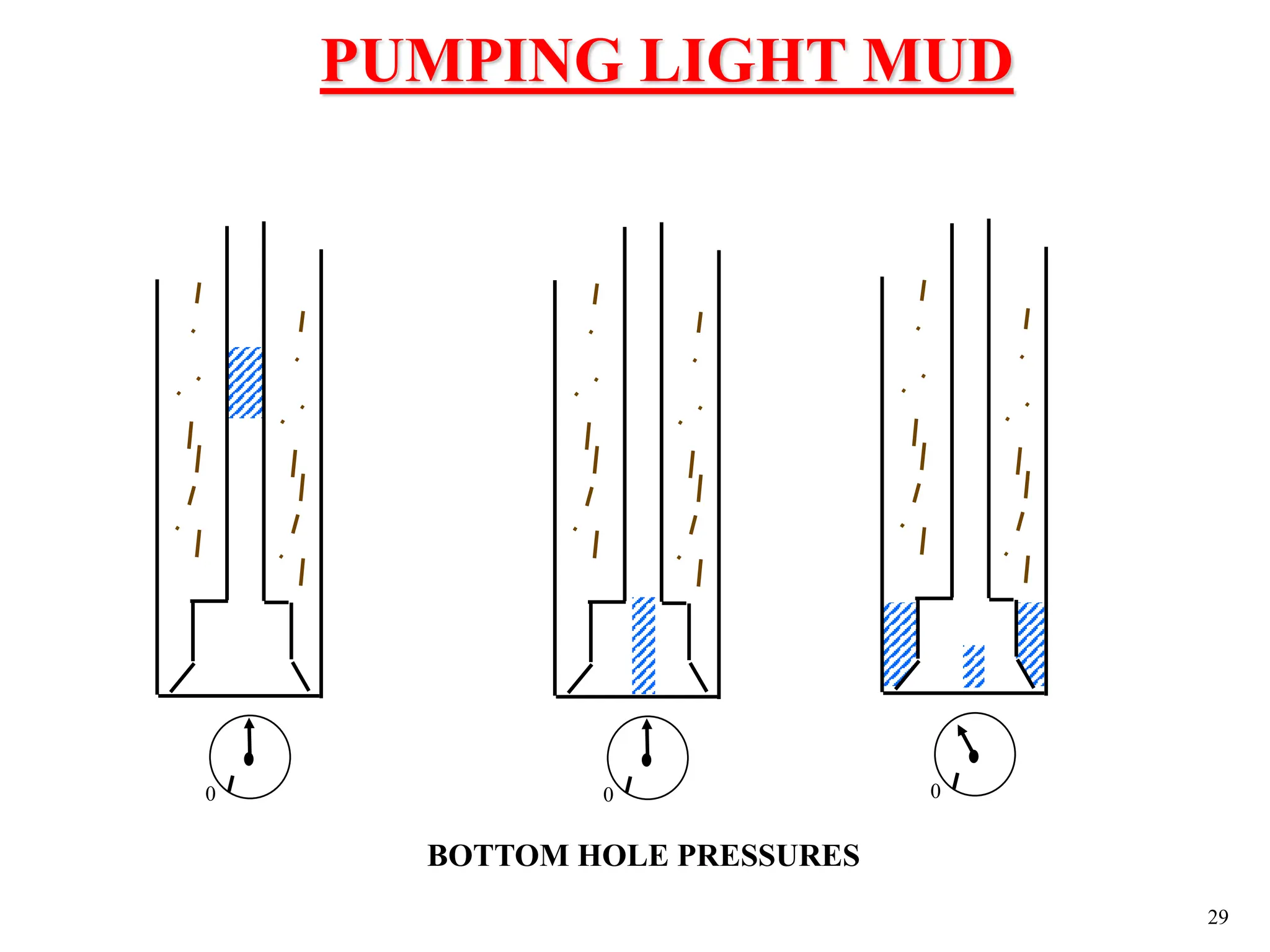
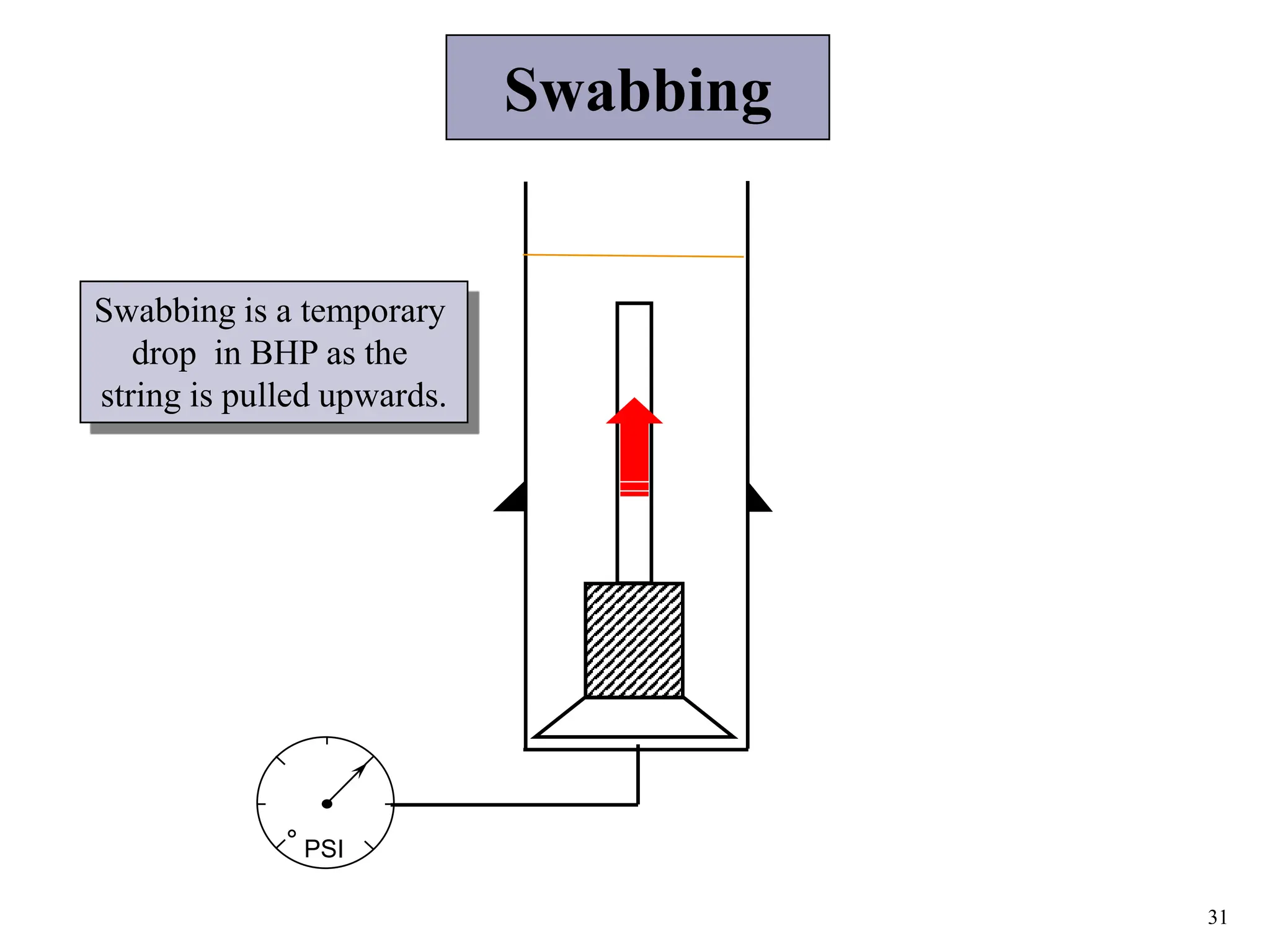
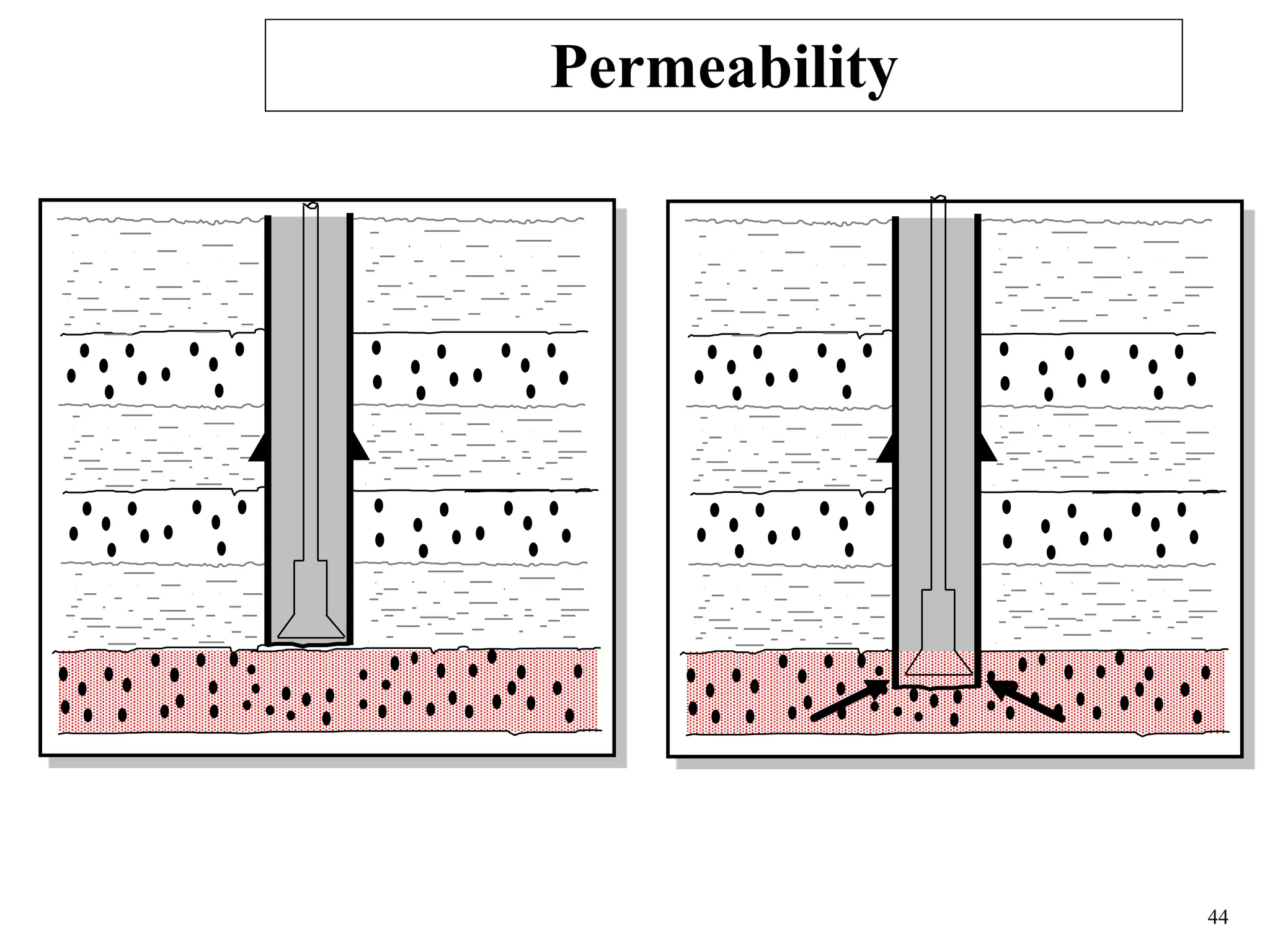
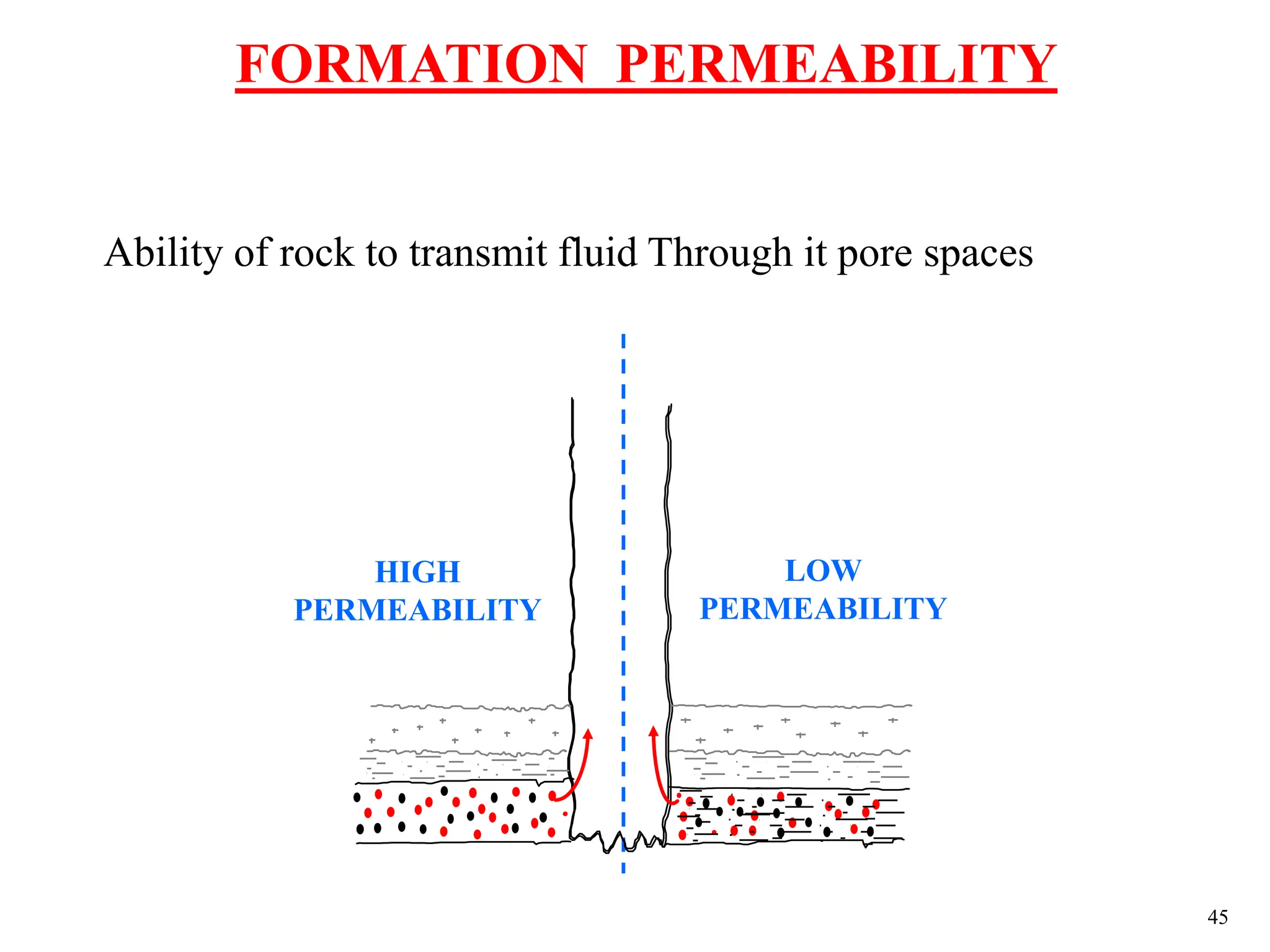
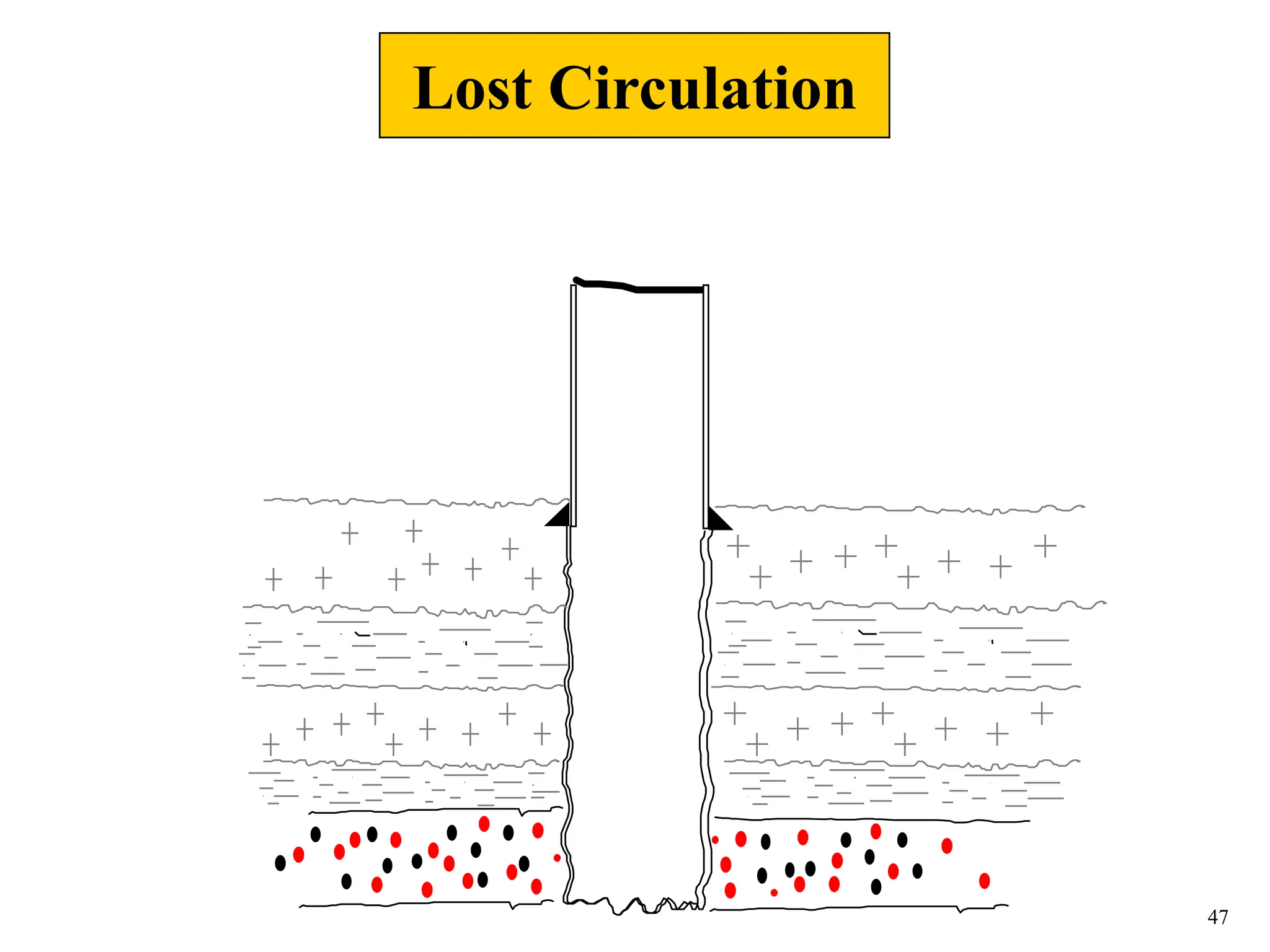
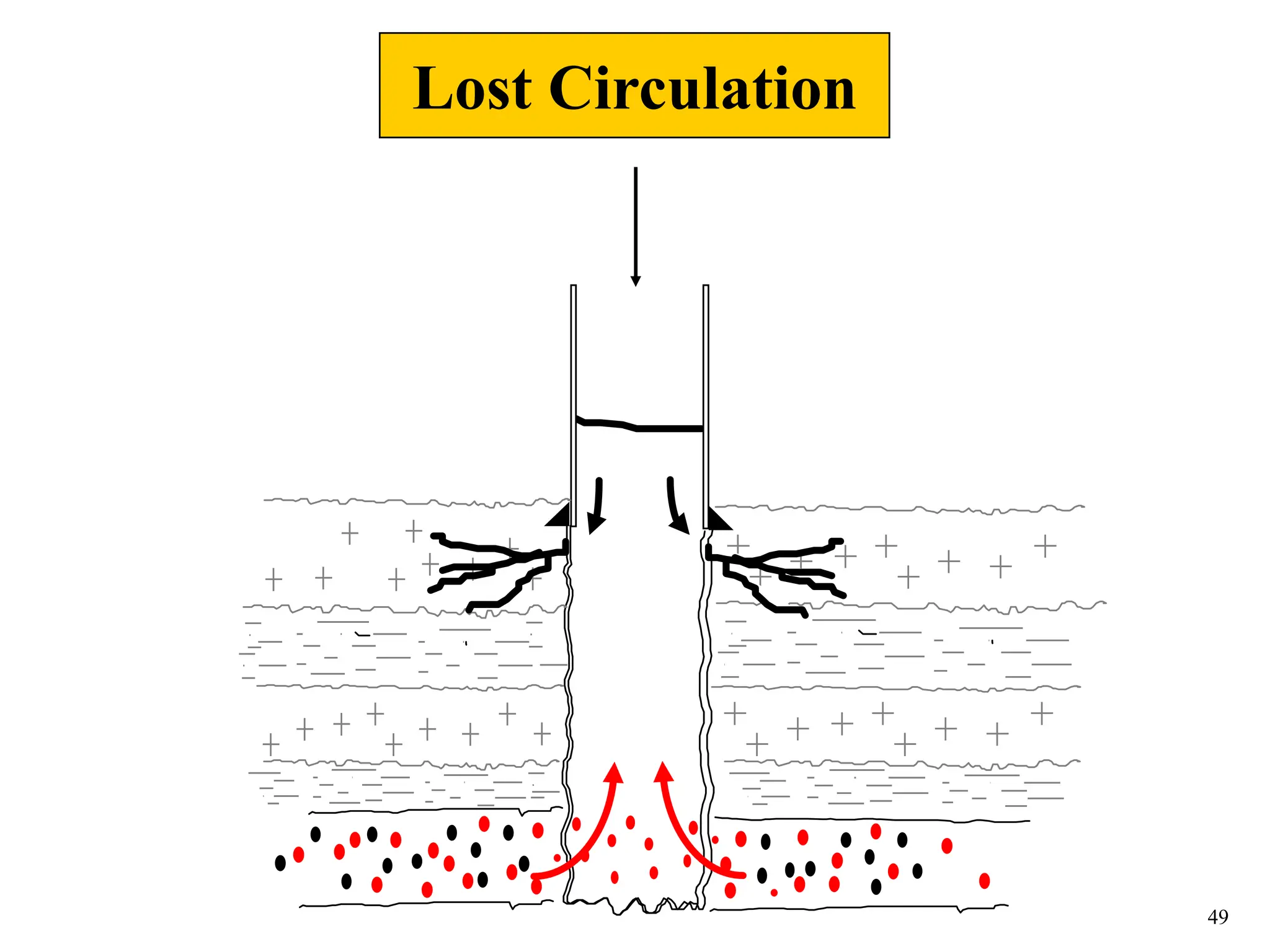
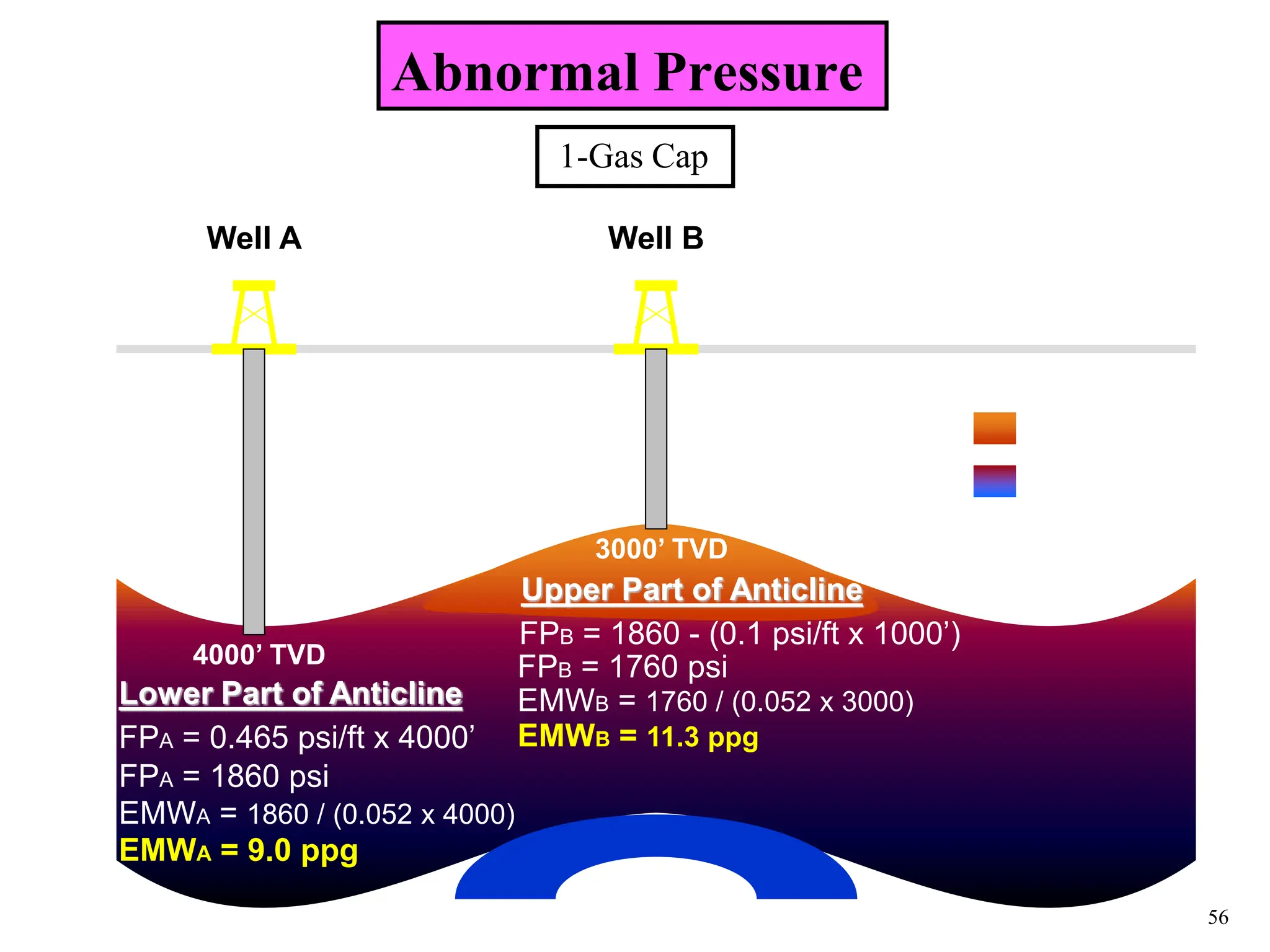
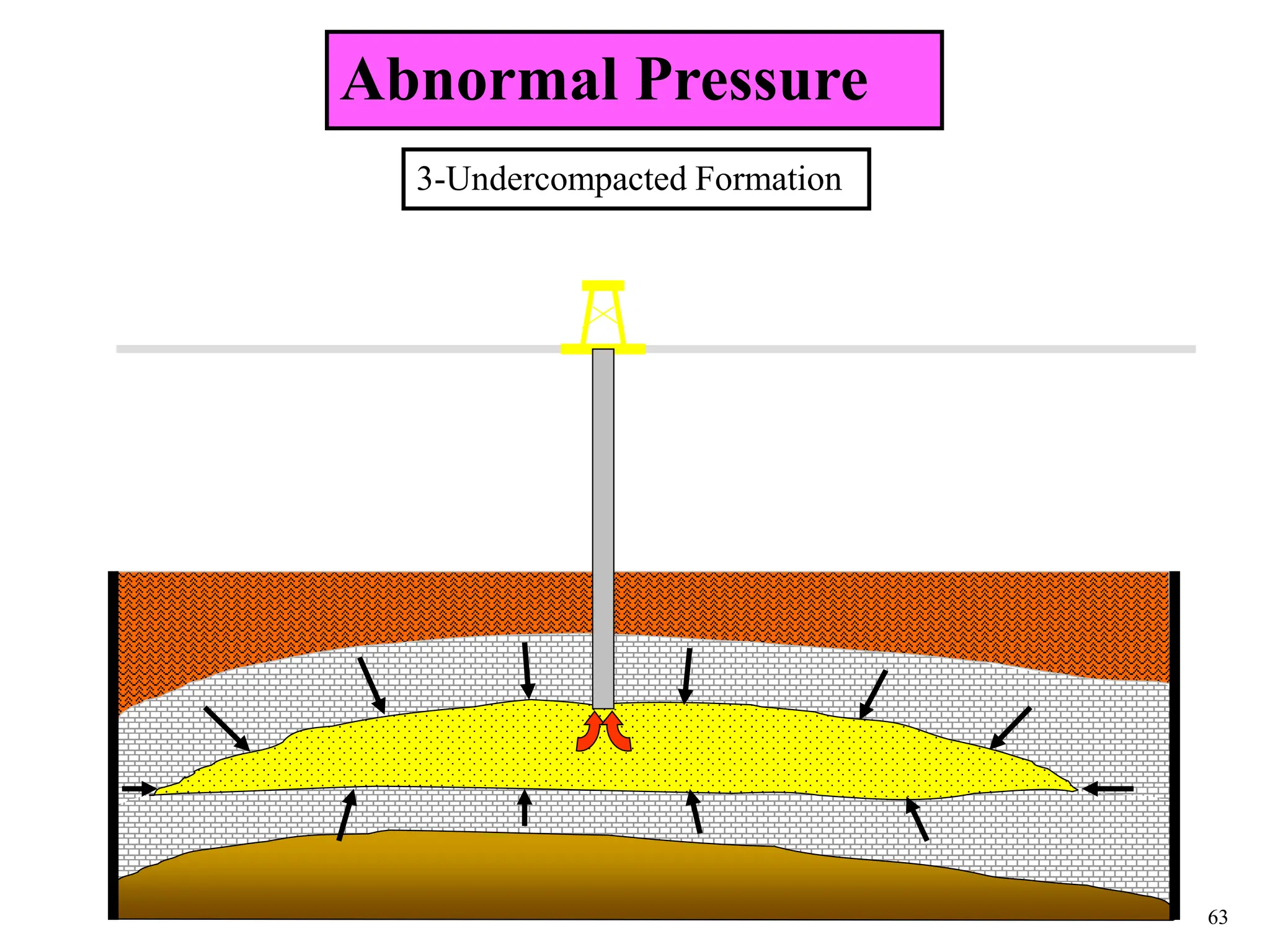
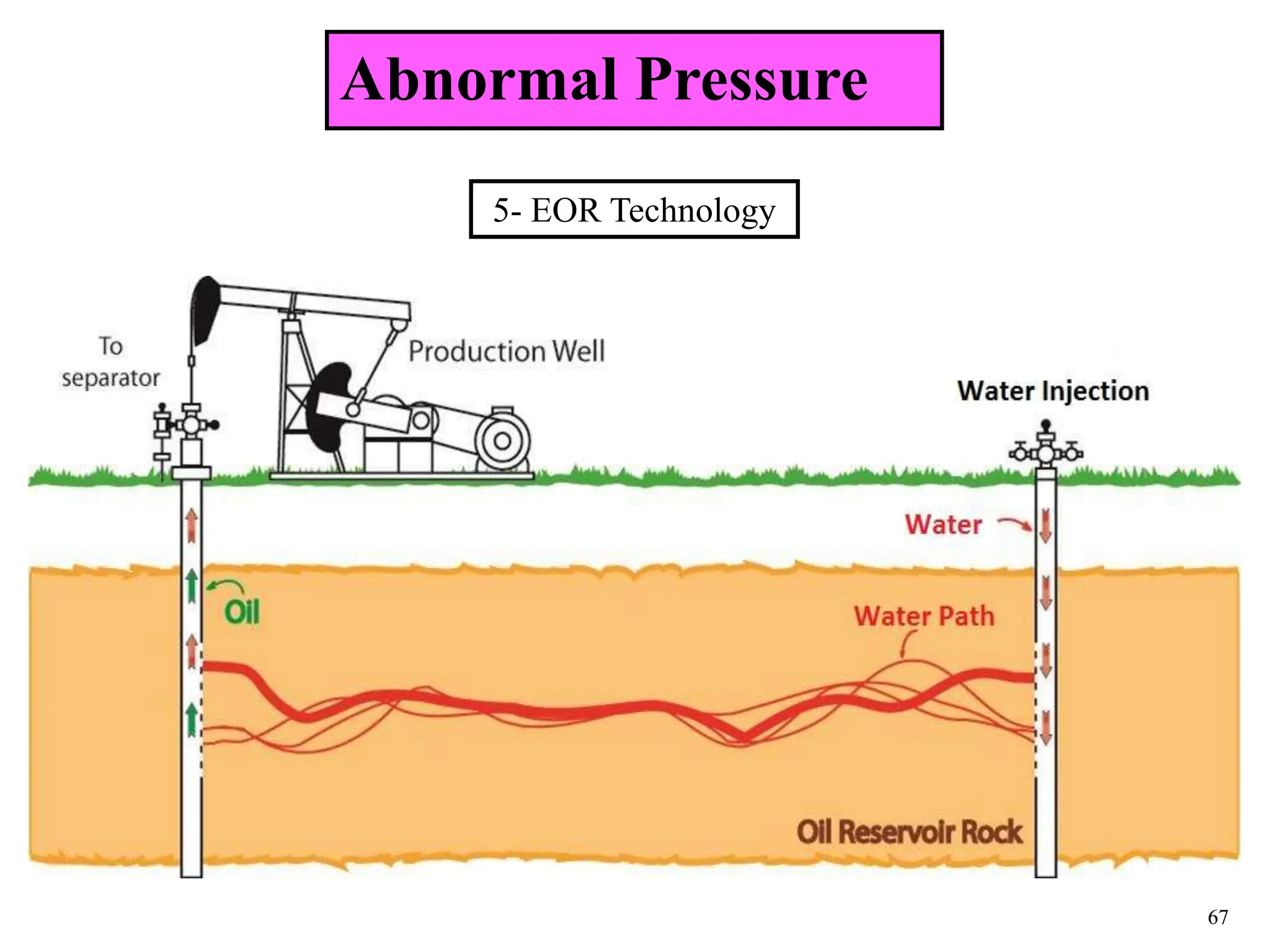
The document discusses various causes of kicks that can occur during tripping operations. It identifies failure to keep the hole full, low density drilling fluid, swabbing, surge, lost circulation, human error, and abnormal formation pressures as potential causes. Specific examples are given to illustrate how each cause can lead to a temporary loss of hydrostatic pressure and allow formation fluids to enter the wellbore. Close monitoring of tripping operations and maintaining an accurate trip tank are emphasized as ways to detect and prevent kicks.