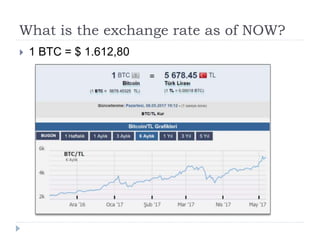
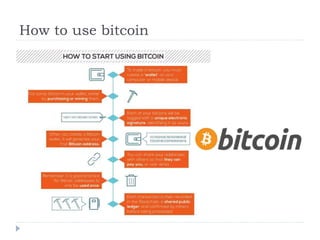
The document discusses Bitcoin and blockchain technology. It begins by outlining how a small number of large institutions control much of the world's financial assets, phone calls, insurance policies, and media. It then asks if decentralization could provide alternatives to these centralized systems. The document goes on to discuss how blockchain technology allows data to be stored across thousands of computers worldwide, preventing disruption. It also examines how blockchain could eliminate the need for middlemen like banks and insurance companies through decentralization.