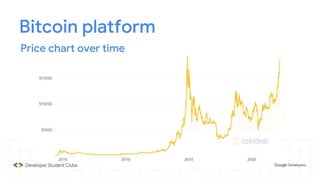
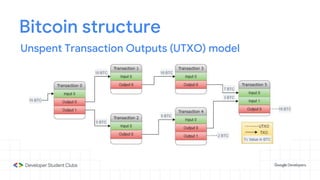
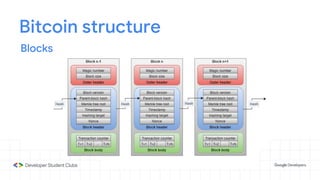
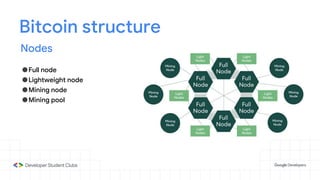
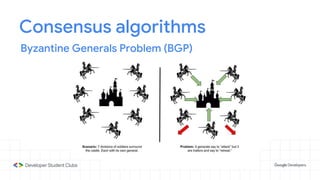
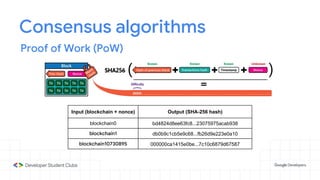
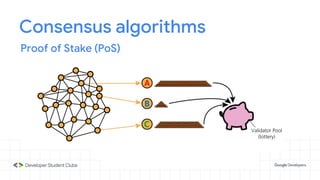
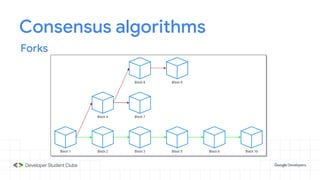
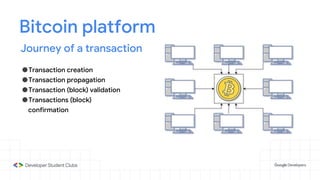
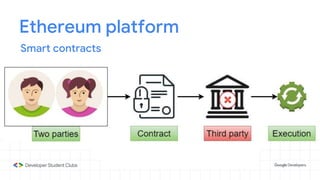
This document provides an introduction to blockchain technology. It discusses what blockchain is, how it is implemented in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, and some of its other applications. Blockchain uses a distributed ledger that records transactions in a decentralized way. The document contrasts public versus private blockchains and explains the history and structure of the Bitcoin platform, including transactions, blocks, nodes, and how consensus is reached through proof-of-work algorithms. It also briefly introduces Ethereum and smart contracts.