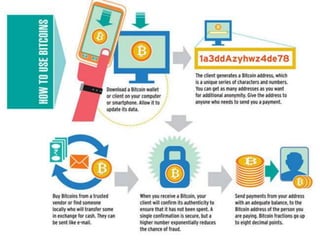
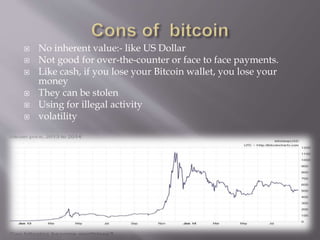
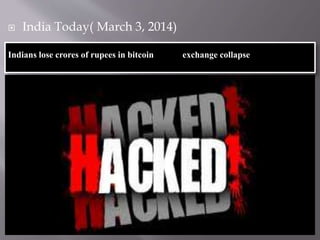
This document discusses Bitcoin, a digital currency. It provides information on what Bitcoin is, how it works, and its key characteristics such as being decentralized, having a limited supply, and being pseudonymous. The document also discusses the legal status of Bitcoin in India, noting that the Reserve Bank of India does not recognize or regulate it as a currency. Finally, some risks of Bitcoin are mentioned such as volatility, risk of theft, and lack of consumer protection if exchanges collapse.