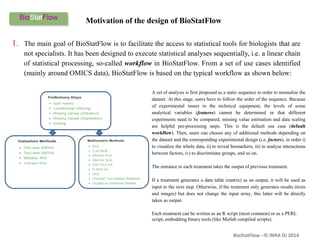
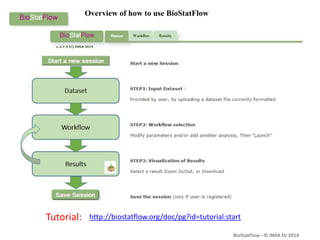
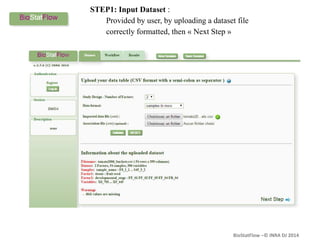
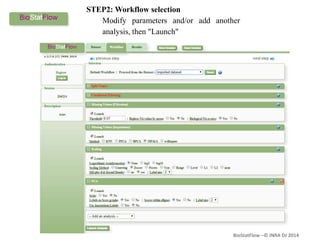
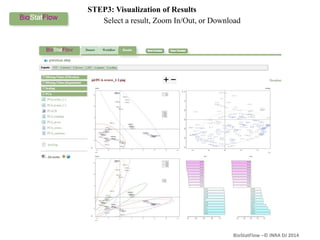
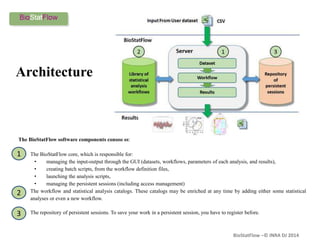
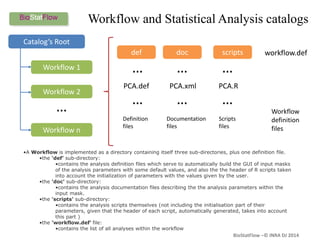
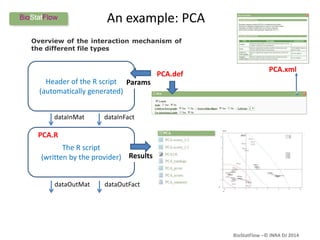
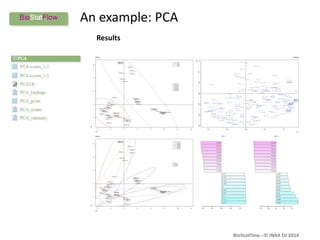
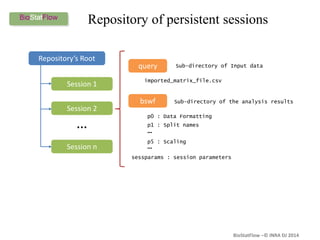
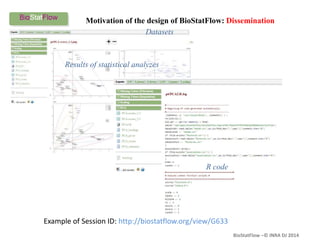
Biostatflow is a web application developed for biologists to analyze 'omics' data using statistical methods, facilitating access to tools for those not specialized in statistics. The platform allows for sequential statistical analyses and supports integration of new methods and workflows, while also enabling the dissemination of results through persistent sessions. Users can upload datasets, follow prescribed workflows, and visualize outcomes, thereby streamlining the analysis of complex biological data.