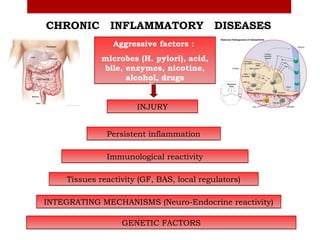
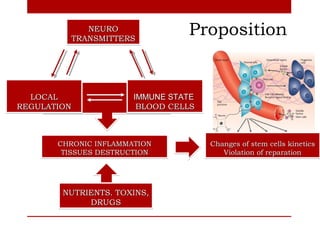
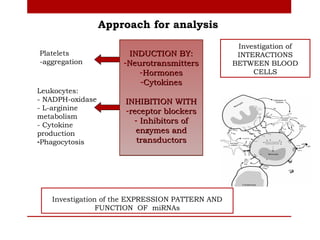
This document outlines a proposed study on chronic inflammatory diseases between several partner organizations. The study would examine over 1,000 patients with conditions like chronic gastritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and irritable bowel disease using clinical exams, imaging, molecular genetics analysis, and other methods. It aims to identify common genetic and organ-specific factors involved, understand immune response regulation mechanisms, and estimate microRNA expression and roles to inform new diagnostics and immunomodulation therapies.