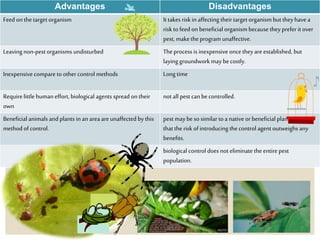
Biological control is a component of integrated pest management that involves using natural enemies like predators, parasitoids, and pathogens to reduce pest populations. It typically requires active human involvement. Biological control can be used against insect pests, weeds, and plant diseases. While it has advantages like being selective and inexpensive, it also has disadvantages like taking a long time to become established and not eliminating pest populations entirely.