Binary Search Tree (BST) - A Complete Description
1. Introduction to BST
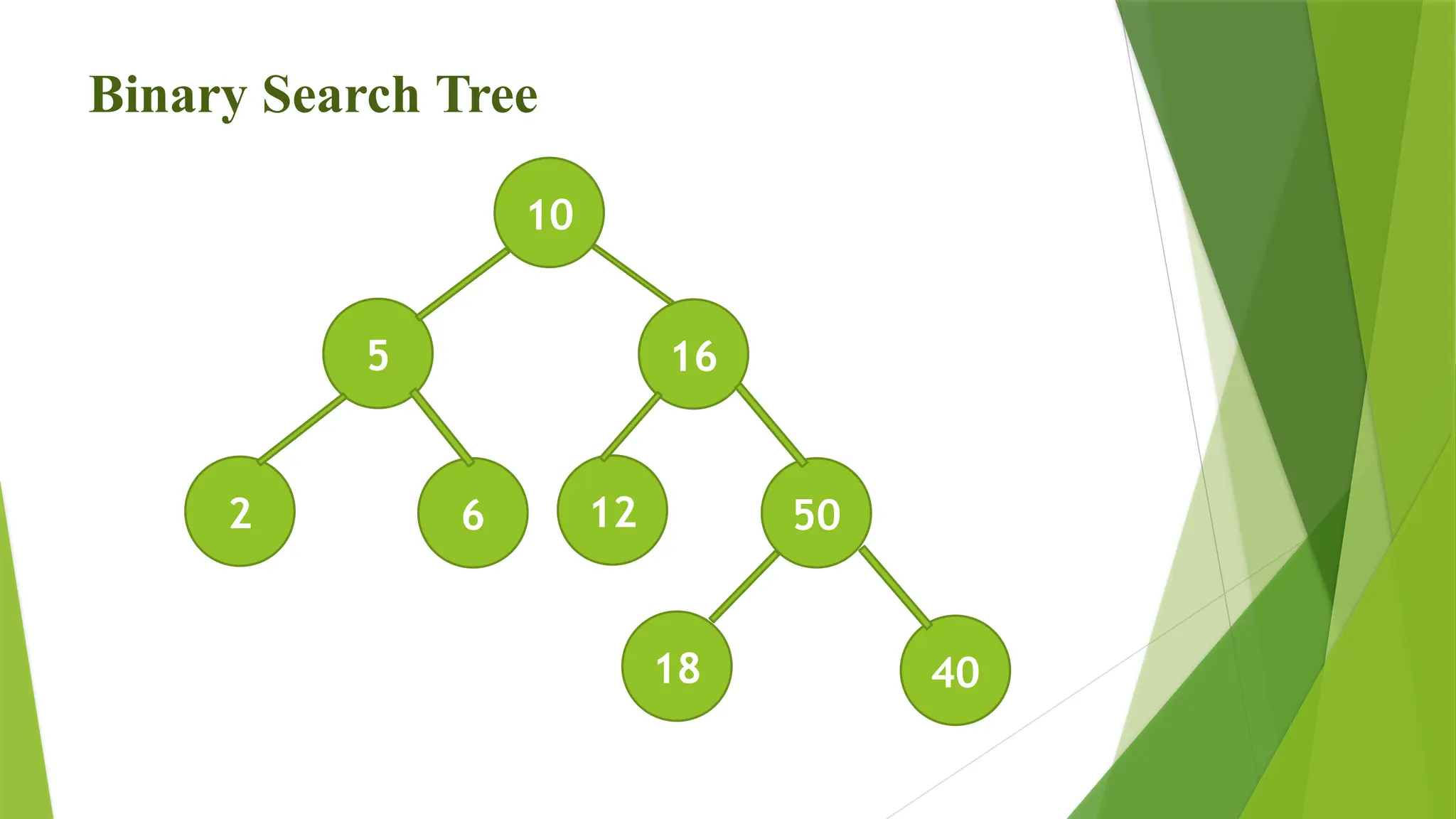
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is a special type of binary tree that maintains its elements in a sorted manner. It is a hierarchical data structure where each node has at most two children: a left child and a right child. The key characteristic of a BST is the following property:
For every node in the tree:
All elements in the left subtree are less than the node.
All elements in the right subtree are greater than the node.
This structure makes searching, insertion, and deletion operations much more efficient compared to linear data structures like arrays and linked lists.
Why Use BST?
BSTs are useful in scenarios where fast data retrieval, insertion, and deletion are important. They provide:
Faster search (on average, O(log n) time).
Dynamic memory usage (no need to allocate a fixed size).
Ordered data storage (can be used for sorting and searching simultaneously).
2. Basic Terminologies
Before diving deeper, it's important to understand some basic terminologies related to trees:
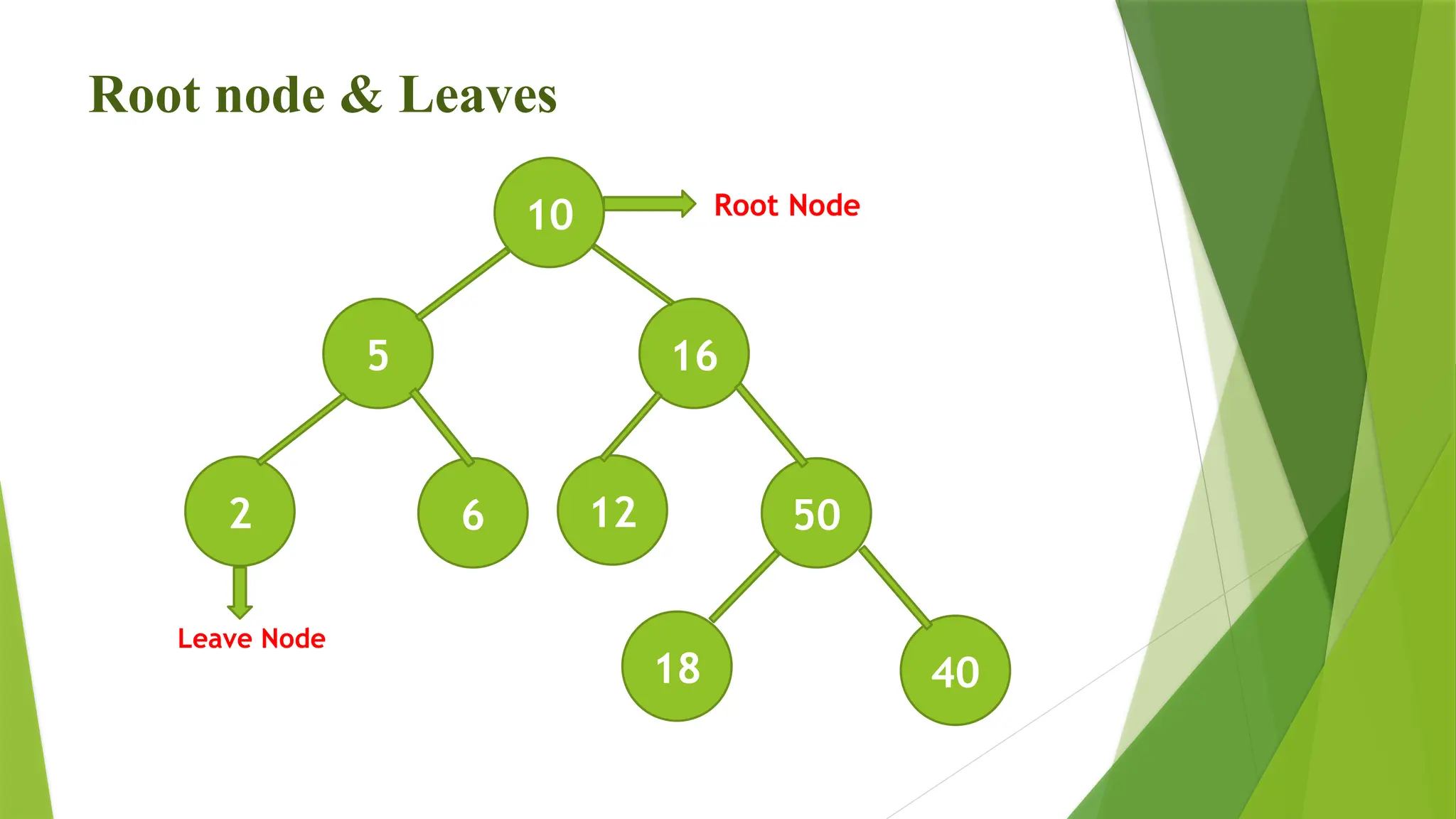
Node: Each element in the tree.
Root: The topmost node in the tree.
Parent: A node that has one or more child nodes.
Child: A node that descends from another node.
Leaf: A node with no children.
Subtree: A tree entirely contained within another tree.
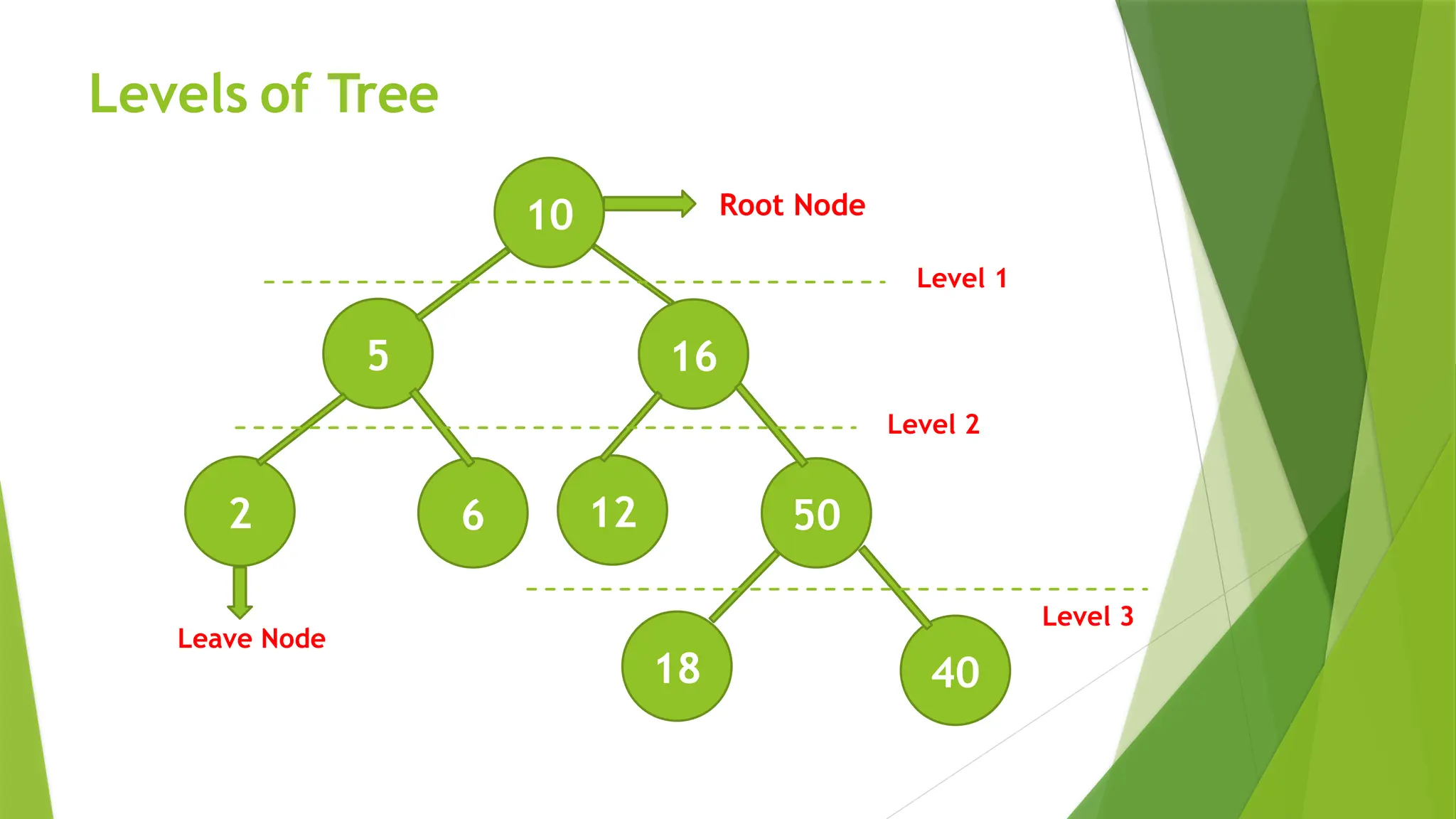
Height: The number of edges on the longest path from a node to a leaf.
Depth: The number of edges from the root to a particular node.
4. BST Operations
a) Insertion
To insert a new node:
Compare it with the root.
If smaller, go to the left subtree.
If larger, go to the right subtree.
Repeat until a null position is found, and insert the node there.
Example:
Insert 50, 30, 70, 20, 40, 60, 80
Resulting BST:
markdown
Copy
Edit
50
/ \
30 70
/ \ / \
20 40 60 80
b) Searching
Search operation follows the same rule as insertion:
Start at root.
If the key equals the node value, found.
If the key is less, go left.
If the key is more, go right.
c) Deletion
Deleting a node in BST has three cases:
Leaf node: Just delete it.
One child: Replace the node with its child.
Two children: Find the inorder successor (smallest value in right subtree), copy its value to the node, then delete the successor.
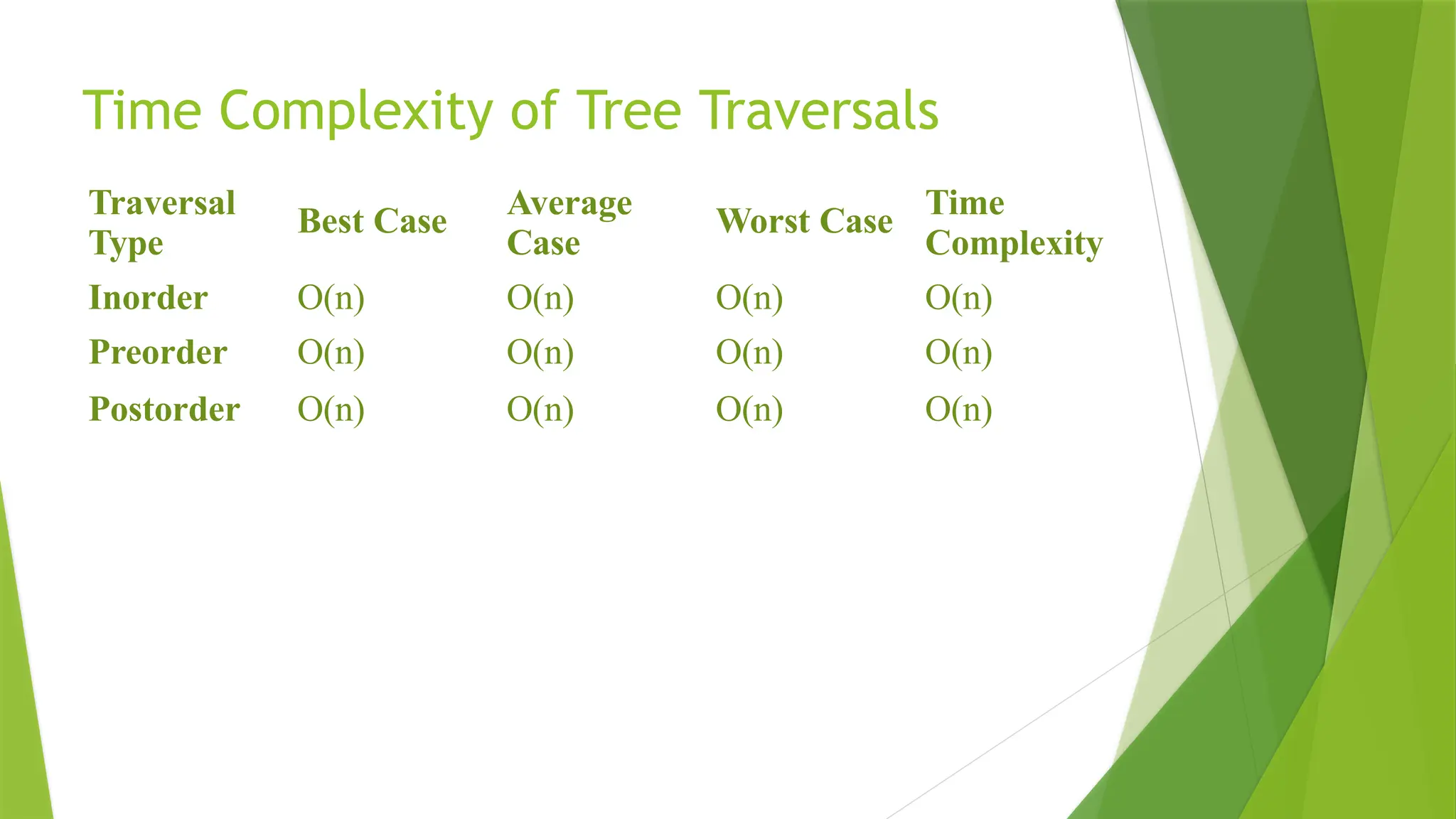
5. BST Traversals
Tree traversal is the process of visiting all the nodes in some order.
a) Inorder Traversal (Left - Root - Right)
This traversal returns values in sorted order for BST.
Example:
cpp
Copy
Edit
void inorder(Node* root) {
if (root != nullptr) {
inorder(root->left);
cout << root->data << " ";
inorder(root->right);
}
}
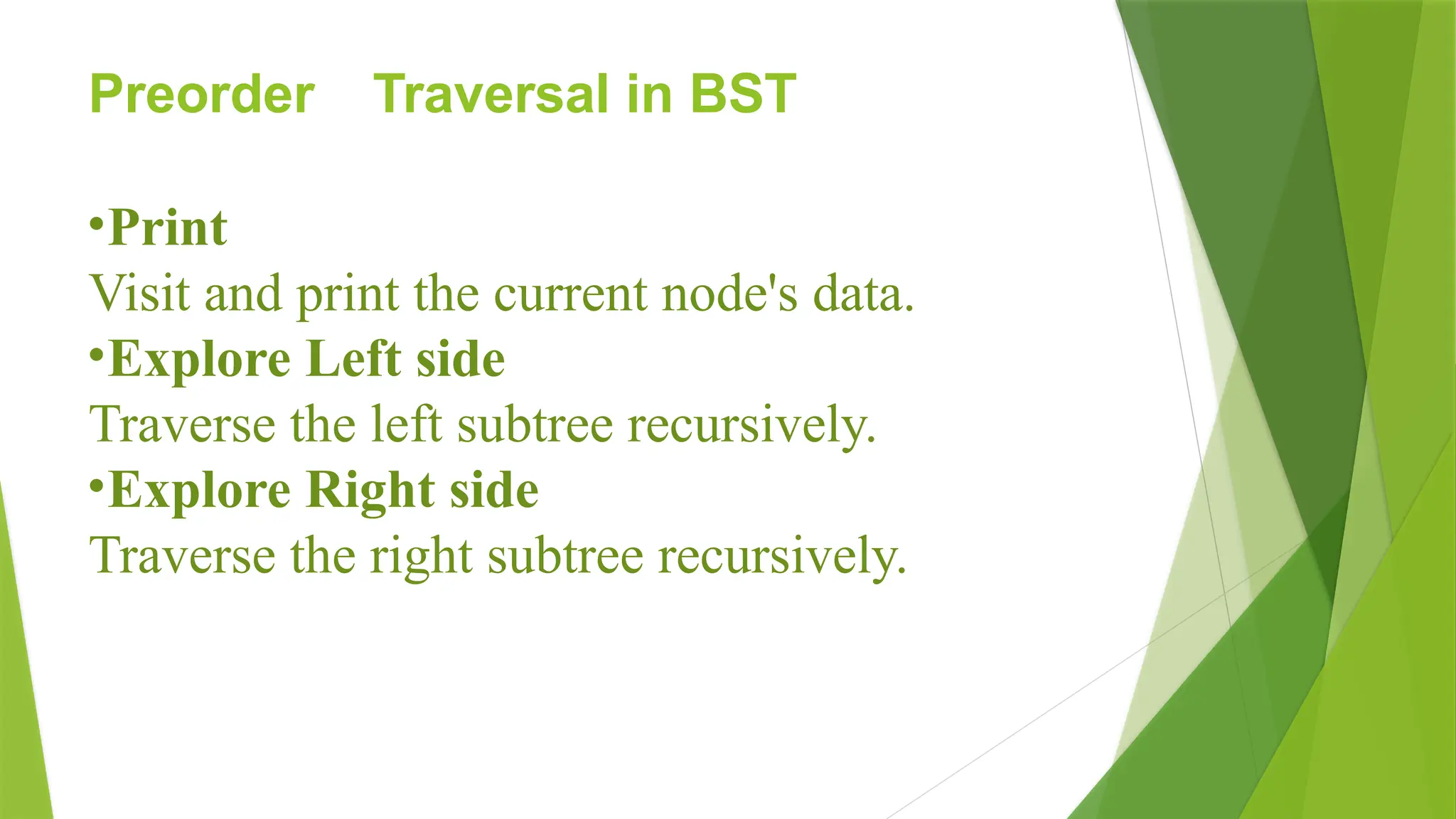
b) Preorder Traversal (Root - Left - Right)
Useful for copying the tree or expression trees.
c) Postorder Traversal (Left - Right - Root)
Used for deleting the tree or evaluating expressions.
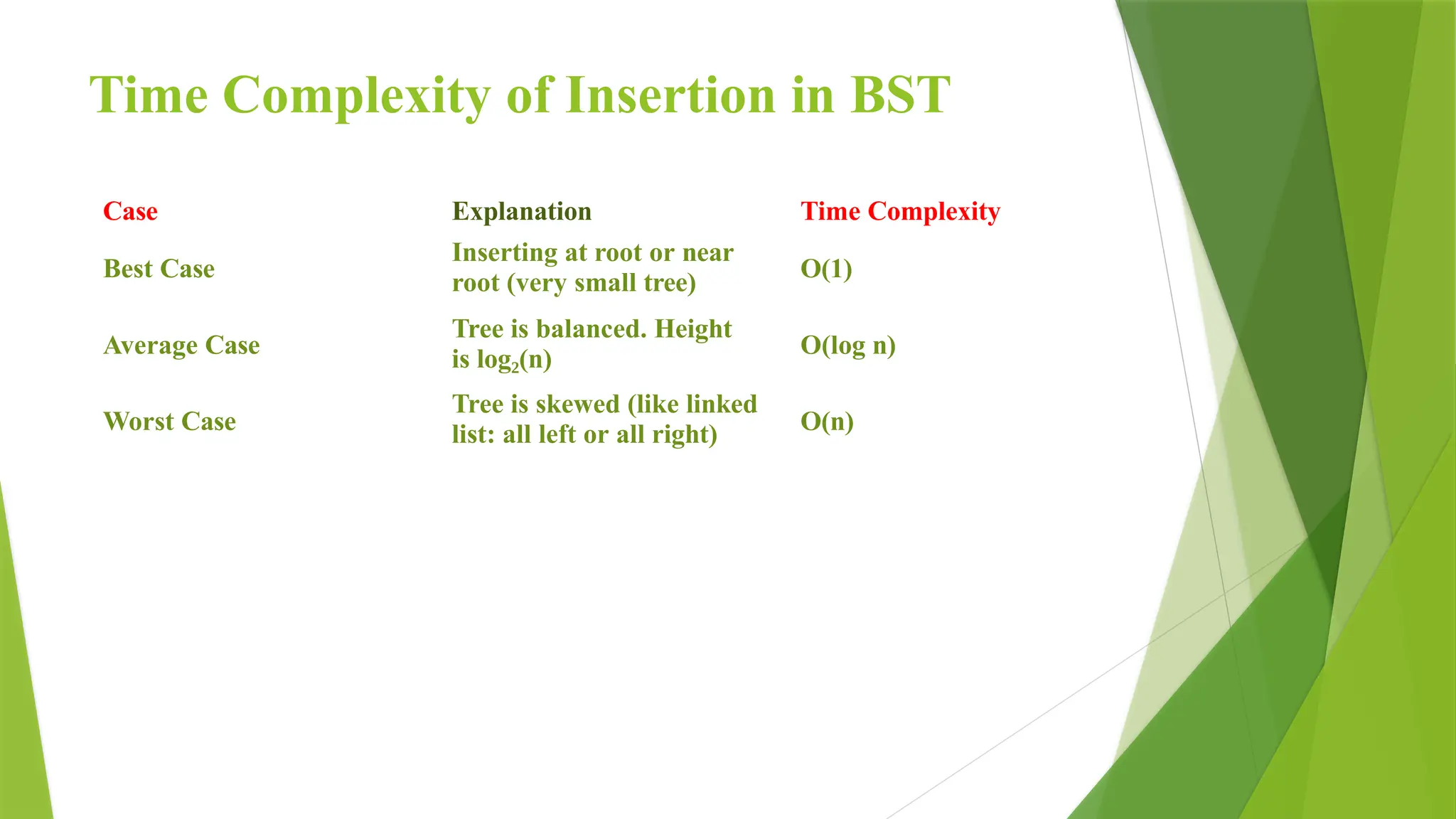
6. Time Complexity of BST Operations
Operation Best Case Average Case Worst Case
Search O(log n) O(log n) O(n)
Insertion O(log n) O(log n)