Recommended
PDF
Building Information Modeling (BIM) Research Paper
PPTX
BIM_Introduction_Designed_PPT_common_presentation
PPTX
Building Information modeling Presentation.pptx
PDF
Building Information Modeling (BIM) Transforming the Construction Industry.pdf
PPTX
BIM_Presentation_BUILDING INFORMATION MODELING
PPTX
PDF
An overview of of bim by assist. prof. a. j. niazi
PPTX
Navigating the Future BIM Services and the AEC Industry Trends
PPTX
BIM_in_Construction building information modelling
PPTX
BIM_in_Construction. information modelling
PDF
buildinginformationmodelling-171125085704.pdf
PPTX
Building information modelling
PPTX
PPTX
Introduction to Building Information Modeling
PDF
Contribution Of Building Information Modeling (BIM) To Solve Problems In Arch...
PPTX
Introduction to Building Information Modeling
PDF
Building Information Modeling (BIM)
PPTX
4 Statistics Proving BIM means Business for AEC.pptx
PPTX
Key BIM Insights & Trends for the Global AEC Industry.pptx
PPTX
BIM - Building Information Model
PDF
BIM-Era of digital construction
PPTX
BIM for Construction, BPMs and Owners
PPTX
Building Information Modelling ppt.pptx
PPTX
introdução ao BIM Building Information Modeling_Impactos e benefícios nos esc...
PPTX
Building information modeling (bim)
PPTX
PPTX
BIM Method for best resourcefull on MYPES
PDF
buildinginformationmodeling-161107172241.pdf
PDF
Nilesh Mathur NID_Thesis 2025 ( Machphysolutions: Insulinsure_IIT Delhi )
PPTX
Understanding the Role of Mobile Apps Today
More Related Content
PDF
Building Information Modeling (BIM) Research Paper
PPTX
BIM_Introduction_Designed_PPT_common_presentation
PPTX
Building Information modeling Presentation.pptx
PDF
Building Information Modeling (BIM) Transforming the Construction Industry.pdf
PPTX
BIM_Presentation_BUILDING INFORMATION MODELING
PPTX
PDF
An overview of of bim by assist. prof. a. j. niazi
PPTX
Navigating the Future BIM Services and the AEC Industry Trends
Similar to BIM_Introduction_Presentation_common_presentation
PPTX
BIM_in_Construction building information modelling
PPTX
BIM_in_Construction. information modelling
PDF
buildinginformationmodelling-171125085704.pdf
PPTX
Building information modelling
PPTX
PPTX
Introduction to Building Information Modeling
PDF
Contribution Of Building Information Modeling (BIM) To Solve Problems In Arch...
PPTX
Introduction to Building Information Modeling
PDF
Building Information Modeling (BIM)
PPTX
4 Statistics Proving BIM means Business for AEC.pptx
PPTX
Key BIM Insights & Trends for the Global AEC Industry.pptx
PPTX
BIM - Building Information Model
PDF
BIM-Era of digital construction
PPTX
BIM for Construction, BPMs and Owners
PPTX
Building Information Modelling ppt.pptx
PPTX
introdução ao BIM Building Information Modeling_Impactos e benefícios nos esc...
PPTX
Building information modeling (bim)
PPTX
PPTX
BIM Method for best resourcefull on MYPES
PDF
buildinginformationmodeling-161107172241.pdf
Recently uploaded
PDF
Nilesh Mathur NID_Thesis 2025 ( Machphysolutions: Insulinsure_IIT Delhi )
PPTX
Understanding the Role of Mobile Apps Today
PPTX
How to Create Modern Scandinavian Décor at Home.pptx
PPTX
Session 04:�Ethical Behaviours in Leadership
PPTX
Career Pathways in Textile Quality Assurance.pptx
PDF
The Future of Cross-Platform Development.pdf
PPT
74676371-Coagulation-and-Flocculation[1].ppt
PDF
Introduction to System histolog-1.pdf lctr 1
PDF
LAYOUT dapur mbg sesuai dengan juklak dan juknis
PDF
Gamification Concept in UX Design with Proven Examples (2026).pdf
PDF
Buy Facebook Ads Accounts_ the Backbone of Social Advertising in 2025.pdf
PPTX
Jewel Tones: Bringing Bold Color Back into Your Home
PPTX
3 Phase Alternators in basic electric and electronic devices.pptx
PDF
Daniella Atterano Junior Graphic Design Portfolio.pdf
PPTX
TYPES OF AGRICULTURE -Diverse Farming Methods
PDF
literature case study of museo do amanha
PPTX
GATE-ALL-AROUND Tunneling Field Effect Transistor .pptx
PPTX
Doors and Windows in Building Construction
PDF
How to Shortlist the Right App Development Partner.pdf
PDF
VS-Unit 1, vastu shastra, spatial design according vastupdf
BIM_Introduction_Presentation_common_presentation 1. 2. What is BIM?
• • BIM stands for Building Information
Modeling
• • A digital representation of physical and
functional characteristics of a facility
• • Serves as a shared knowledge resource for
information about a facility
3. Why BIM?
• • Improved collaboration
• • Better visualization
• • Accurate documentation
• • Clash detection
• • Cost & time savings
4. BIM vs Traditional Methods
• • Traditional CAD: 2D drawings, manual
updates
• • BIM: 3D intelligent models, automatic
updates
• • Enhanced accuracy and coordination
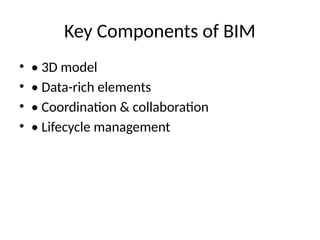
5. Key Components of BIM
• • 3D model
• • Data-rich elements
• • Coordination & collaboration
• • Lifecycle management
6. BIM Levels (0 to 3+)
• • Level 0: Paper-based, unmanaged CAD
• • Level 1: Managed CAD in 2D/3D
• • Level 2: Collaborative BIM using common
data environment
• • Level 3: Full integration, cloud-based
7. BIM Uses & Applications
• • Design visualization
• • Construction planning
• • Facility management
• • Cost estimation
• • Sustainability analysis
8. BIM Tools & Software
• • Revit – Architectural modeling
• • Navisworks – Clash detection
• • ArchiCAD – Design
• • Tekla – Structural modeling
• • AutoCAD – Drafting
9. Challenges in BIM Adoption
• • High initial cost
• • Need for training
• • Resistance to change
• • Interoperability issues
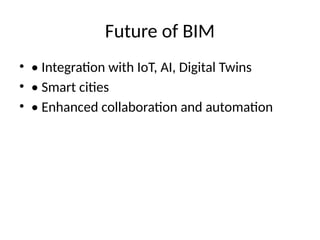
10. Future of BIM
• • Integration with IoT, AI, Digital Twins
• • Smart cities
• • Enhanced collaboration and automation