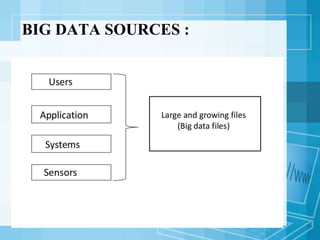
This document discusses big data, providing definitions and outlining its key characteristics of volume, velocity, and variety. It describes processes involved like integrating disparate data stores and employing Hadoop MapReduce. Sources of big data are identified as mobile devices, sensors, social media, etc. Tools used include distributed servers, storage, and databases. Statistics on data generated by companies like Facebook and Twitter are provided. Applications of big data include improving science, healthcare, finance, and security. Advantages include access to vast information, while disadvantages include costs and privacy issues.