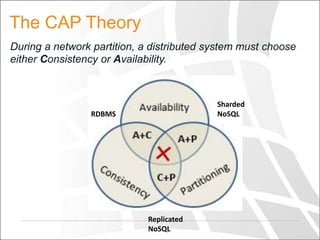
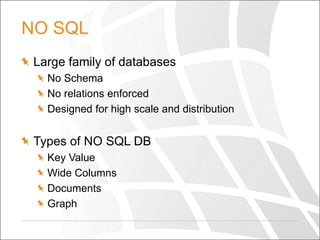
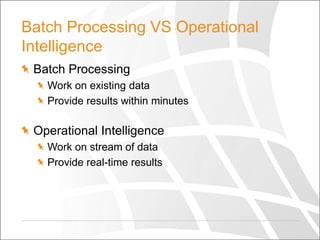
The document discusses the cloud, big data, and NoSQL, emphasizing the importance of analyzing large-scale data using cloud solutions. It outlines the limitations of traditional relational databases in handling diverse data types and introduces various NoSQL databases designed for scalability. The document also highlights the need for parallel processing and cloud-based big data analytics, encouraging readers to identify their specific use cases for optimal data solutions.