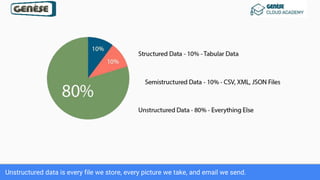
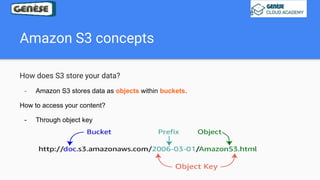
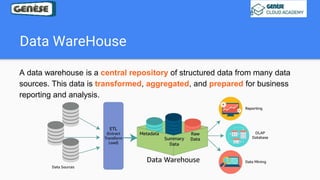
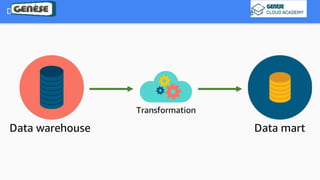
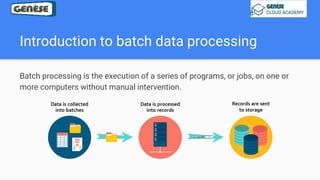
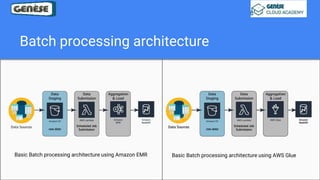
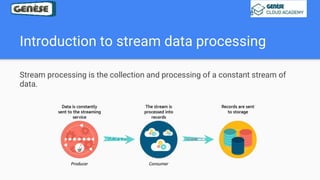
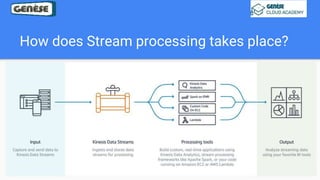
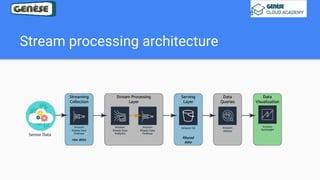
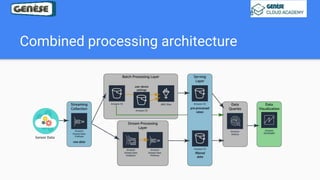
1. The document discusses various data analysis, storage, and processing solutions including data analysis, data analytics, data lakes, data warehouses, data marts, batch processing, and stream processing.
2. It describes challenges of data analytics including volume, velocity, and variety and recommends solutions like Amazon S3, Redshift, EMR, and Kinesis to address these challenges at scale.
3. The key aspects covered are data storage methods like data lakes, data warehouses, and data marts and data processing methods including batch processing using EMR and stream processing using Kinesis.



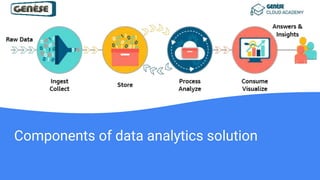
![Steps of a data analysis solution
1. Get the data [Collect, Store]: Know where your data comes
from.
2. Discover and analyze your data[Analyze/Process]: Know the
options for processing your data
3. Visualize and learn from your data[Consume/Visualize]: Know
what you need to learn from data](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontodataanalysisstorageprocessingsolutions-210929093006/85/Introduction-to-Data-Analysis-Storage-Processing-Solutions-5-320.jpg)