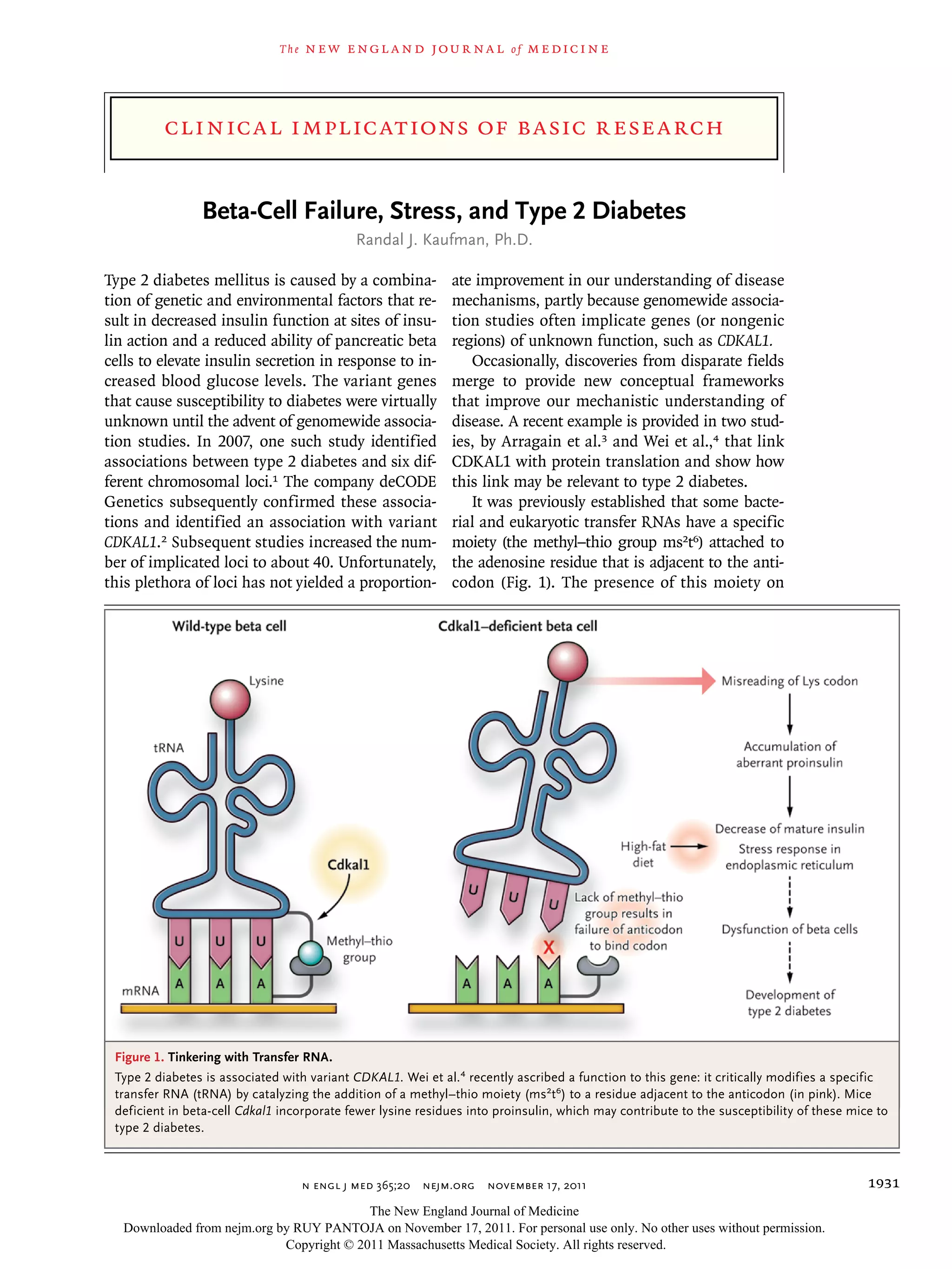
Variant CDKAL1 is associated with type 2 diabetes. Two recent studies link CDKAL1 to the modification of a transfer RNA (tRNA) involved in protein translation. CDKAL1 adds a chemical group to tRNA that incorporates the amino acid lysine during protein synthesis. Mice deficient in CDKAL1 have reduced lysine in proinsulin, impairing its processing into insulin. This provides insight into how CDKAL1 variants may increase susceptibility to type 2 diabetes by disrupting insulin production.
![clinical implications of basic research
tein synthesis (i.e., during translation from mes- sight into how variant CDKAL1 may cause sus-
senger RNA to protein) (Fig. 2). In other words, ceptibility to type 2 diabetes. Several questions
CDKAL1 seems to have a global effect on pro- may be addressed through future study. The au-
tein production by ensuring faithful translation thors propose that a failure to incorporate lysine
of the AAA codon (encoding lysine) through its results in the misfolding of proinsulin and pre-
mediation of a highly specific event (the modi- vents proteolytic processing. Is this indeed the
fication of a specific amino acid residue of case, and if it is, what amino acids (if any) re-
tRNALys[UUU]). The investigators went on to ab- place lysine? If a general deficiency of lysine in-
rogate Cdkal1 in the beta cells of mice and ob- corporation into protein causes protein misfold-
served a diminished insulin response to an intra- ing, perhaps the cellular response to protein
peritoneal injection of glucose. These events misfolding affects the production of insulin.
were exacerbated in mice that were fed a high- There are now a number of examples in which
fat diet for several weeks. protein misfolding in the beta cell prevents pro-
How does an abrogation of Cdkal1 in the beta insulin processing and appropriate trafficking
cell result in a feeble insulin response? One of between the endoplasmic reticulum and the
the most attractive hypotheses is the apparent Golgi apparatus, thus causing stress and a dis-
failure of the mutant beta cell to process the ruption in mitochondrial structure. Because
proinsulin protein into insulin. The authors CDKAL1 is strongly expressed in the endoplas-
found that proinsulin in the mutant cells had a mic reticulum, its own misfolding (assuming
lower lysine content than proinsulin in wild-type that such occurs) may affect other folding, pro-
cells. They also found that levels of C-peptide (a cessing, or quality-control events that may cause
by-product of proinsulin processing) were low- an accumulation of unfolded protein and beta-
er in the islets and serum of the mutant mice. cell death. In a broader aspect, there are now
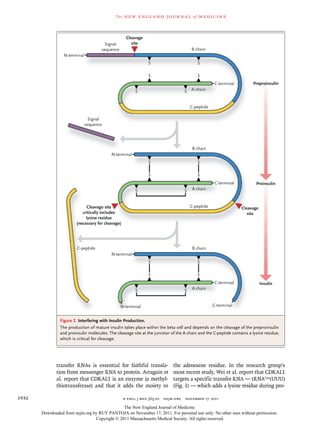
Linking these two observations is the fact that many associations between oxidative stress and
lysine makes up the cleavage site between C-pep- beta-cell failure. It is interesting to consider that
tide and the A chain of insulin (Fig. 2). Thus, a CDKAL1, owing to its composition, may be ex-
deficiency of lysine content in proinsulin would quisitely sensitive to oxidation. As the molecular
be predicted to result in a molecule that is re- mechanisms of CDKAL1 are revealed, researchers
sistant to cleavage at the junction between the may consider small-molecule mediators to pre-
C-peptide and the A chain. vent the progression of type 2 diabetes in pa-
However, it is clear that the general health of tients who carry CDKAL1 risk variants.
the mutant beta cell is also compromised. For ex- Disclosure forms provided by the author are available with the
full text of this article at NEJM.org.
ample, the authors observed an increase in expres-
sion of stress molecules in the endoplasmic re- From the Center for Neuroscience, Aging, and Stem Cell Research,
ticulum. Such stress is likely to be caused by an Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute, La Jolla, CA.
increased number of proteins (including insulin) 1. Sladek R, Rocheleau G, Rung J, et al. A genome-wide asso-
that are misfolded because they are deficient in ciation study identifies novel risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Nature
lysine. Moreover, there is scanty cell-surface ex- 2007;445:881-5.
2. Steinthorsdottir V, Thorleifsson G, Reynisdottir I, et al.
pression of the Glut2 receptor on the mutant A variant in CDKAL1 influences insulin response and risk of
beta cell. (Glut2 transports extracellular glucose type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet 2007;39:770-5.
into the cell, which sets off a chain of events 3. Arragain S, Handelman SK, Forouhar F, et al. Identification
of eukaryotic and prokaryotic methylthiotransferase for biosyn-
that culminate in the mobilization of insulin- thesis of 2-methylthio-N6-threonylcarbamoyladenosine in tRNA.
containing granules.) All, some, or none of these J Biol Chem 2010;285:28425-33.
events may be pivotal to the diabetic phenotype 4. Wei FY, Suzuki T, Watanabe S, et al. Deficit of tRNA(Lys)
modification by Cdkal1 causes the development of type 2 diabe-
of the mutant mice. tes in mice. J Clin Invest 2011;121:3598-608.
The authors have provided much-needed in- Copyright © 2011 Massachusetts Medical Society.
n engl j med 365;20 nejm.org november 17, 2011 1933
The New England Journal of Medicine
Downloaded from nejm.org by RUY PANTOJA on November 17, 2011. For personal use only. No other uses without permission.
Copyright © 2011 Massachusetts Medical Society. All rights reserved.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/betacellfailurestressanddm2-111117100745-phpapp02/85/Beta-cell-failure-stress-and-dm2-3-320.jpg)