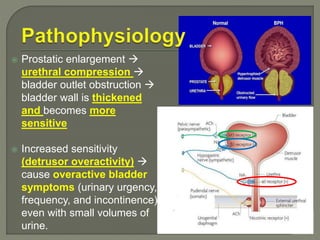
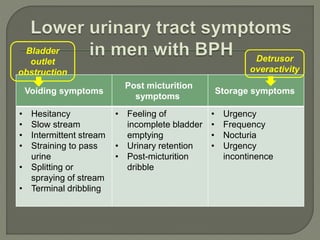
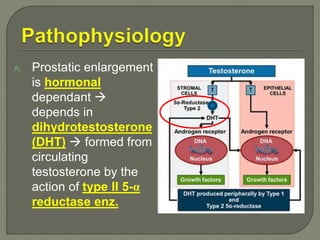
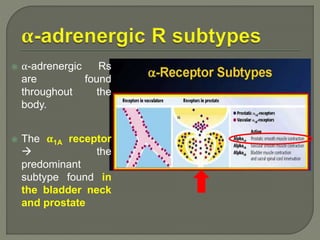
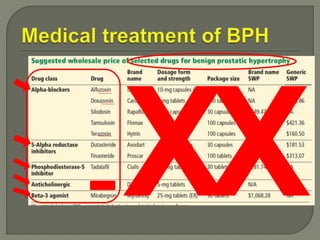
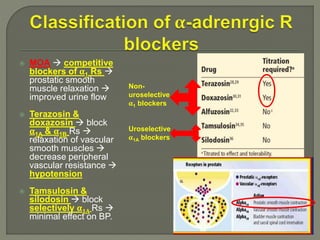
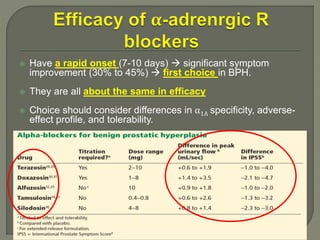
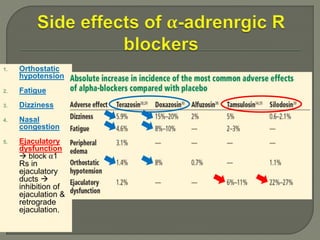
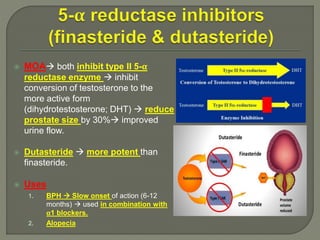
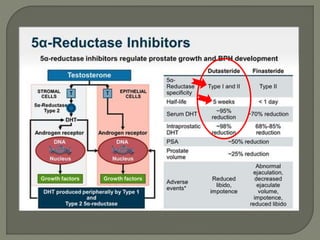
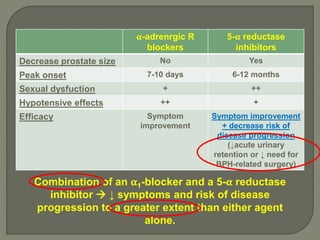
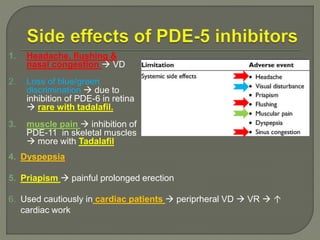
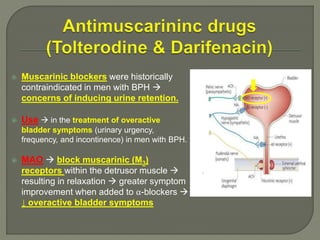
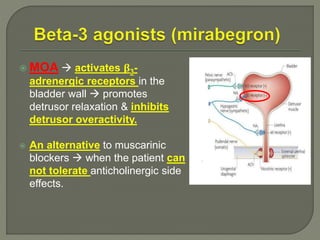
This document discusses the pathophysiology and treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). BPH causes bladder outlet obstruction which leads to bladder wall thickening and overactivity. Common treatments include alpha-1 blockers, 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors, and anticholinergics. Each class of drugs has different mechanisms of action and side effect profiles for treating lower urinary tract symptoms from BPH. Combination therapy may provide greater relief of symptoms than single agents alone.