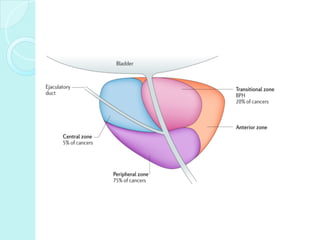
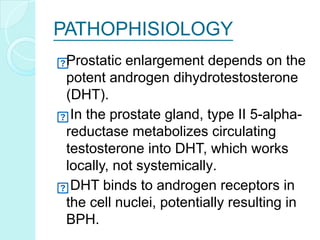
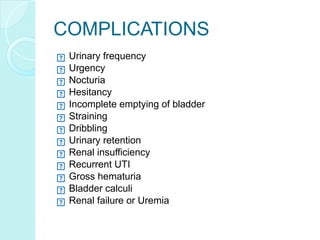
Benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH) is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland that is common in aging men. As men get older, changes in hormone levels can cause the prostate to grow larger and compress the urethra. This compression of the urethra by the enlarged prostate leads to urinary symptoms like frequent urination, urgency, and weak urine flow. Diagnosis involves a digital rectal exam, PSA test, urinalysis and other tests to evaluate urinary symptoms and rule out other conditions. Treatment options include medications to shrink the prostate or relieve symptoms, combination drug therapy, or surgery to remove part of the enlarged prostate for severe cases.