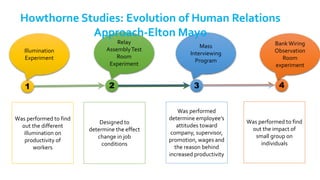
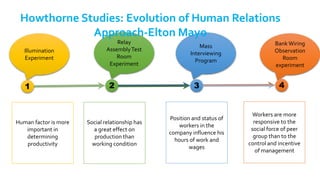
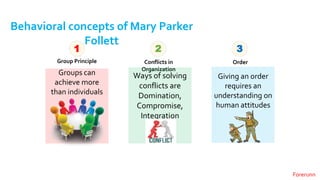
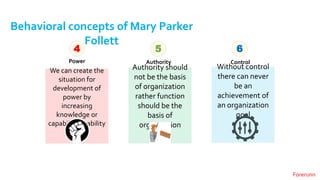
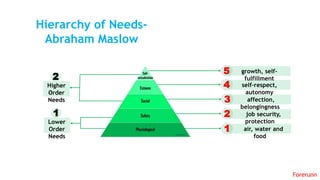
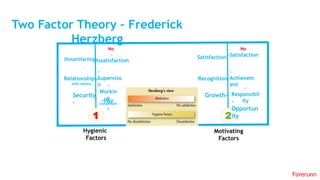
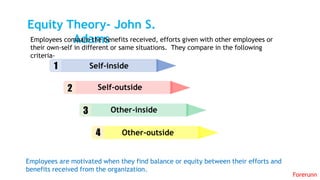
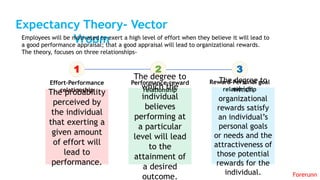
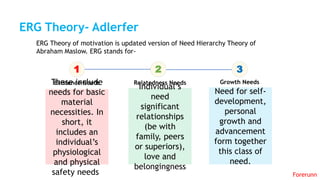
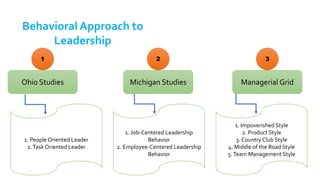
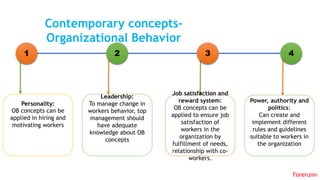
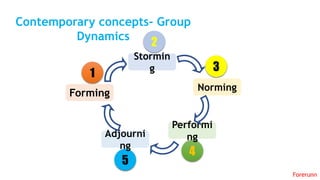
The document provides an overview of the behavioral school of management thought and its key contributors. It discusses several important forerunners such as Mary Parker Follett, Elton Mayo, Abraham Maslow, Douglas McGregor, and Frederick Herzberg. It summarizes their major works and contributions, including Follett's concepts of group principle and integration, Mayo's Hawthorne Studies, Maslow's hierarchy of needs, McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y, and Herzberg's two-factor theory. The document also covers several theories of motivation developed by researchers such as Vroom, McClelland, Adams, Locke, and Adlerfer. It analyzes concepts from the Ohio and Michigan studies on leadership styles