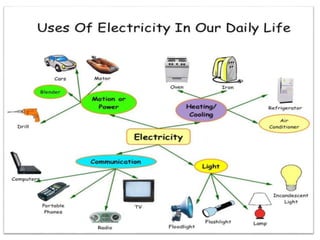
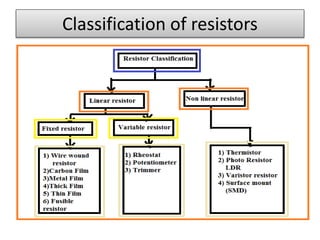
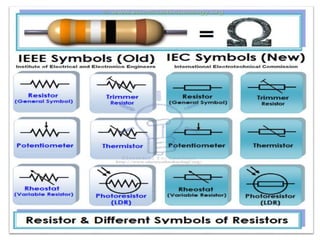
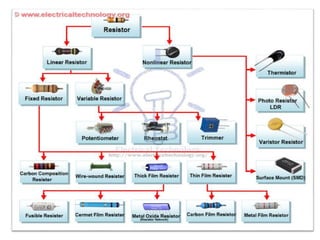
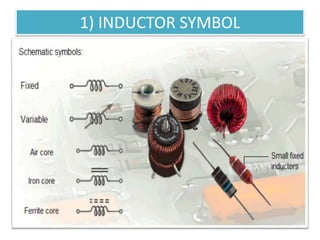
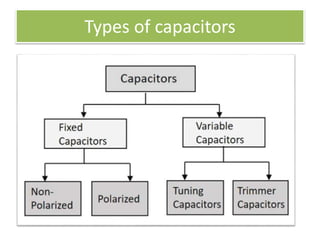
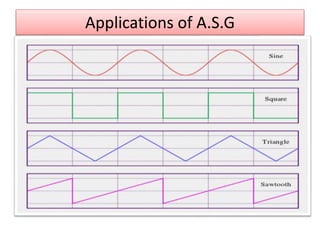
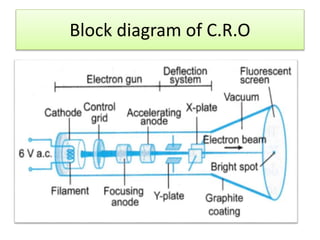
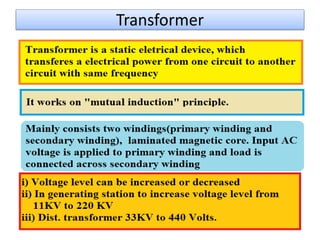
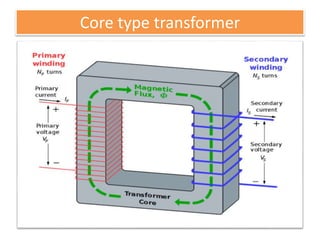
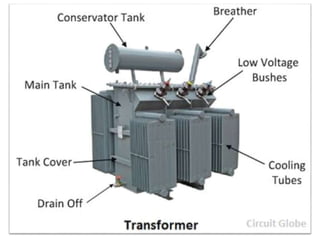
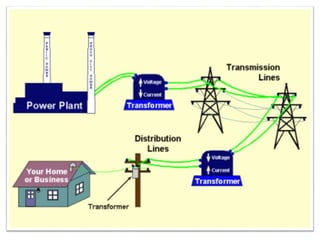
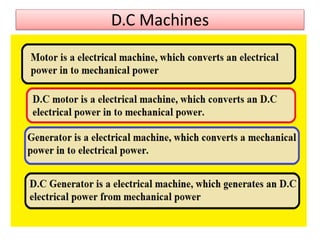
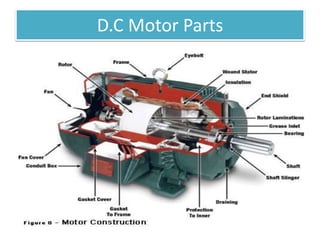
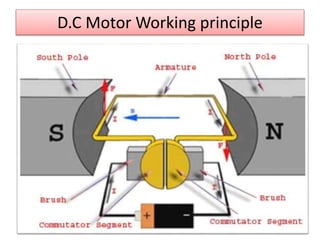
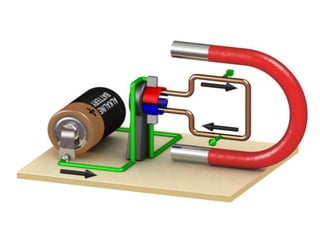
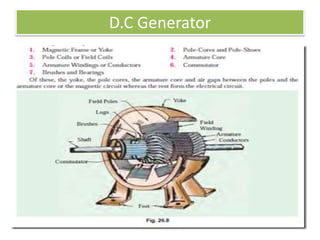
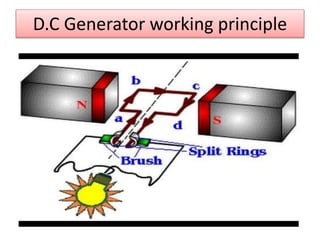
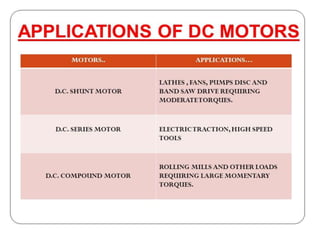
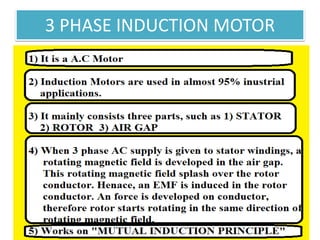
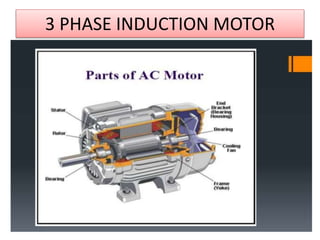
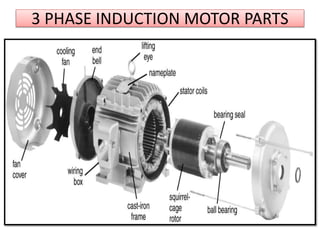
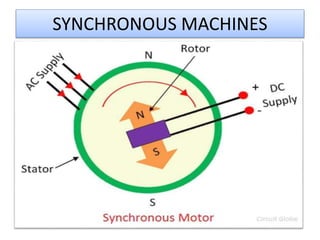
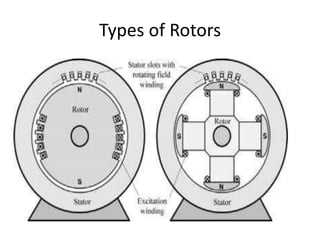
The document covers fundamental components and concepts in electrical and electronics engineering, including resistors, inductors, capacitors, diodes, transistors, transformers, and electrical machines. It elaborates on their functions, classifications, and applications, highlighting tools like multimeters and audio signal generators for testing and troubleshooting. Additionally, it addresses safety precautions in electrical work.