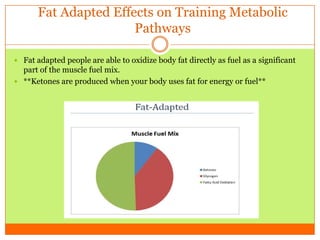
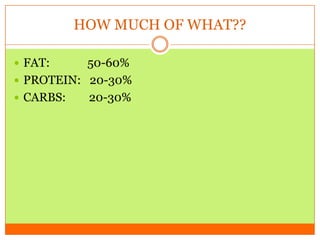
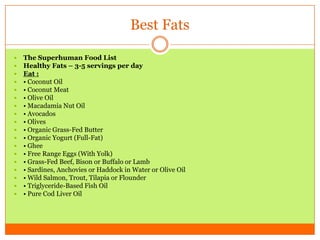
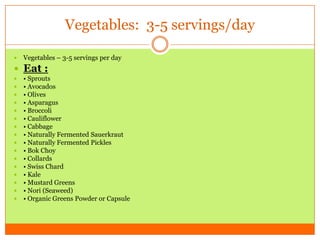
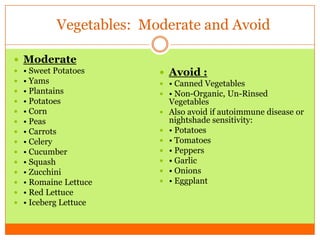
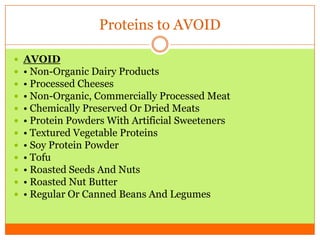
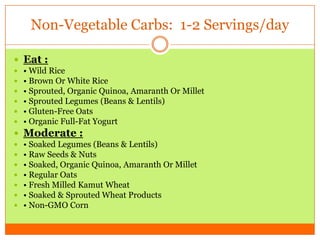
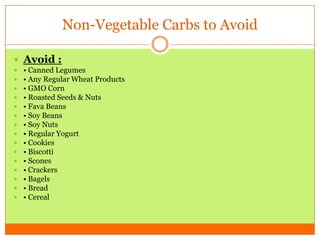
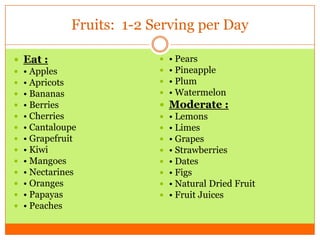
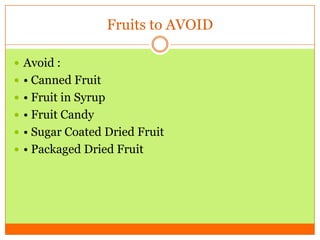
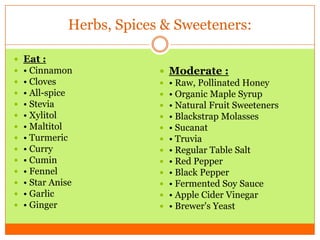
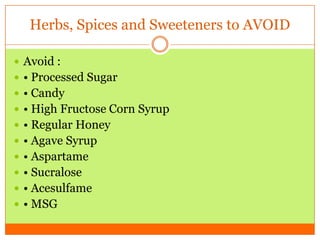
The document outlines the concept of becoming a fat-adapted athlete, which refers to training the body to utilize fatty acids rather than sugars for energy. Benefits include improved health, performance, and easier weight loss, while the document provides guidance on dietary adjustments and the importance of fat versus carbohydrates. It also highlights a new food pyramid model that prioritizes healthy fats and reduces carbohydrate intake for optimal athletic performance.