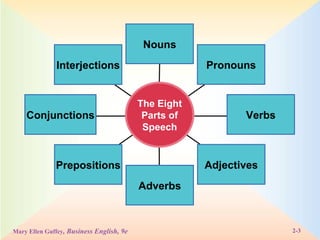
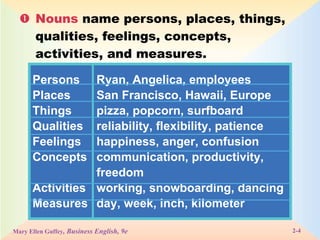
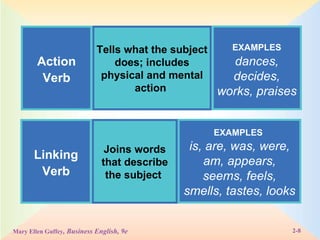
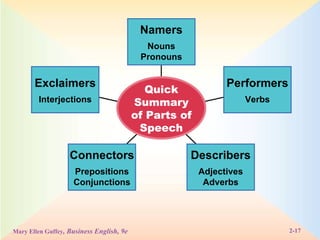
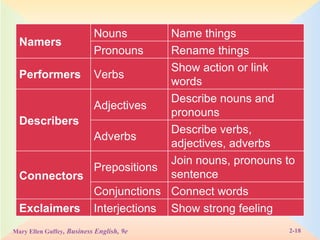
The document defines and provides examples of the eight parts of speech: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. It explains the function of each part of speech and provides tips and exercises for identifying parts of speech in sentences.