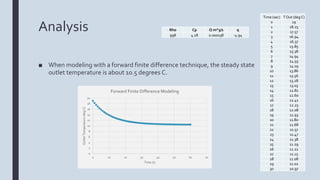
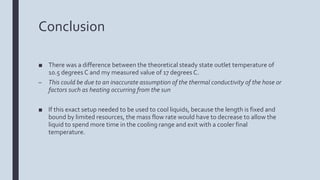
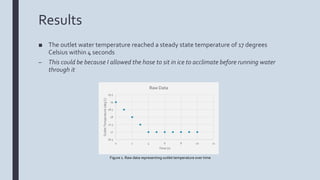
The document describes an experiment to model a pipe heat exchanger that cools water as it passes through a tub of ice. The student measured the inlet and outlet temperatures of water running through a garden hose submerged in an ice bath. The outlet temperature reached a steady state of 17 degrees Celsius within 4 seconds. Modeling with finite differences predicted a steady state of 10.5 degrees Celsius, showing a difference from the experimental results. Decreasing the mass flow rate through the pipe could achieve lower outlet temperatures by allowing more time for heat transfer. Suggestions for improving the experiment included not pre-cooling the hose and using software to better model heat transfer.







![Results
■ Holding all other things constant, mass flow rate can be decreased to achieve different
desired outlet temperatures
0.000
0.050
0.100
0.150
0.200
0.250
0 5 10 15 20
MassFlowRate[kg/s]
Outlet Temperature (deg C)
Required Mass Flow Rates to Reach
DesiredTemperatures
InletTemperature (deg C) Desired OutletTemperature (deg C) Mass Flow Rate Required (kg/s)
19 18 0.235
19 17 0.117
19 16 0.078
19 15 0.059
19 14 0.047
19 13 0.039
19 12 0.034
19 11 0.029
19 10 0.026
19 9 0.023
19 8 0.021
19 7 0.020
19 6 0.018
19 5 0.017
19 4 0.016
Figure 2. Mass Flow Rate vs.Temperature
Table 1. Mass flow rates required for desired outlet temperatures](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/be4120presentation-201112214202/85/Be-4120-presentation-9-320.jpg)