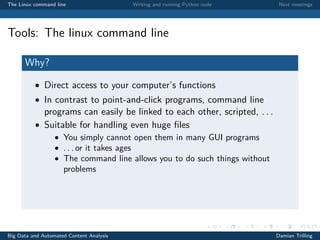
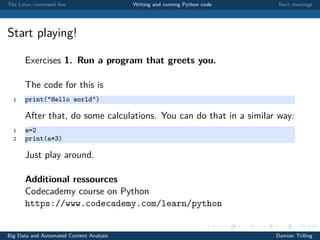
The document outlines an introduction to using the Linux command line and Python for big data and automated content analysis. It emphasizes the importance of using open-source tools and provides an overview of how to write and run Python code, including the use of interactive modes and IDEs. Additionally, it includes instructions for basic Python exercises and information about upcoming meetings related to the course.