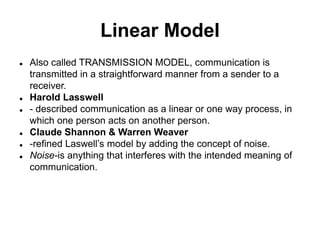
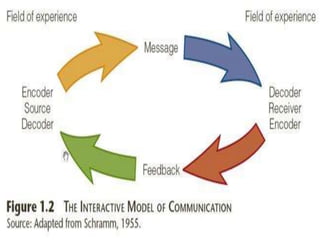
This document discusses three basic models of communication: linear, interactive, and transactional. The linear model describes a one-way transmission of communication from sender to receiver. The interactive model involves the two-way exchange of ideas and messages between sender and receiver. The transactional model depicts communication as an exchange where the roles of sender and receiver reverse as they take turns sending and receiving messages.