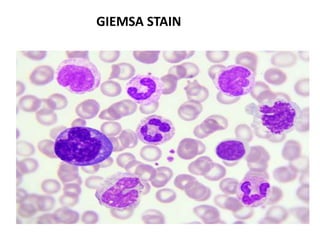
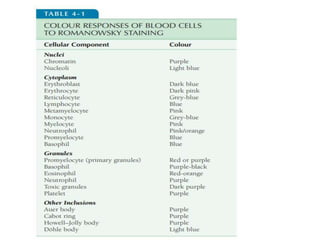
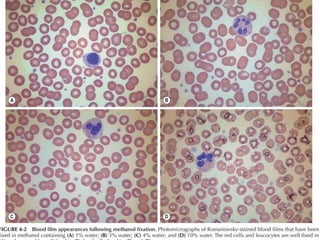
This document discusses various staining techniques used in hematology, including Romanowsky stains, Leishman stain, Giemsa stain, and the May-Grünwald-Giemsa stain. It provides details on the components and preparation of the stains as well as staining methods for blood films. The stains are used to visualize cellular components and identify different blood cell types by selectively binding to proteins, DNA, and other structures.