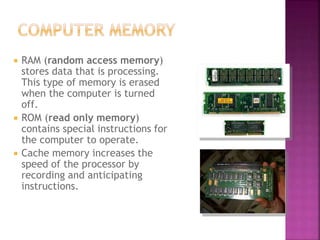
This document defines and describes the key components of a computer system. It discusses computer hardware, software, input/output devices, memory types like RAM, ROM, and cache. Storage devices like hard drives are explained. Peripherals that connect externally are defined. Local and wide area networks are introduced. Finally, multimedia software programs are listed.