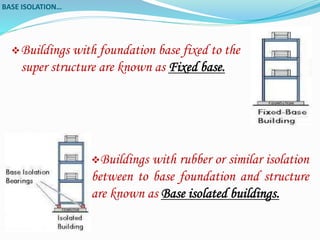
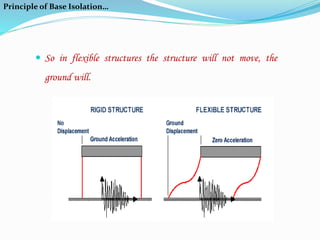
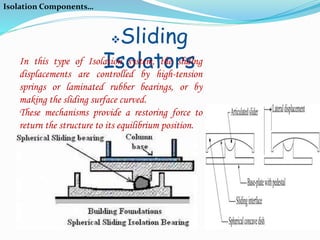
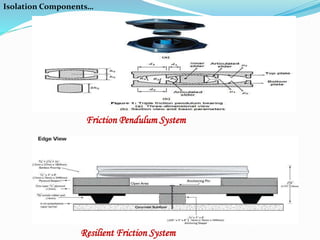
This document discusses base isolation as a seismic protection system for buildings. It defines base isolation as reducing the interaction between a structure and the ground by incorporating seismic isolation at the base. It describes the principles of base isolation, including allowing the ground to move without transmitting motions to the structure. It also outlines different isolation components like elastomeric isolators and sliding isolators. Examples of base isolation being used in real buildings in India are provided. The document concludes that base isolation is a reliable earthquake resistant design method when properly planned and developed isolation systems are used.