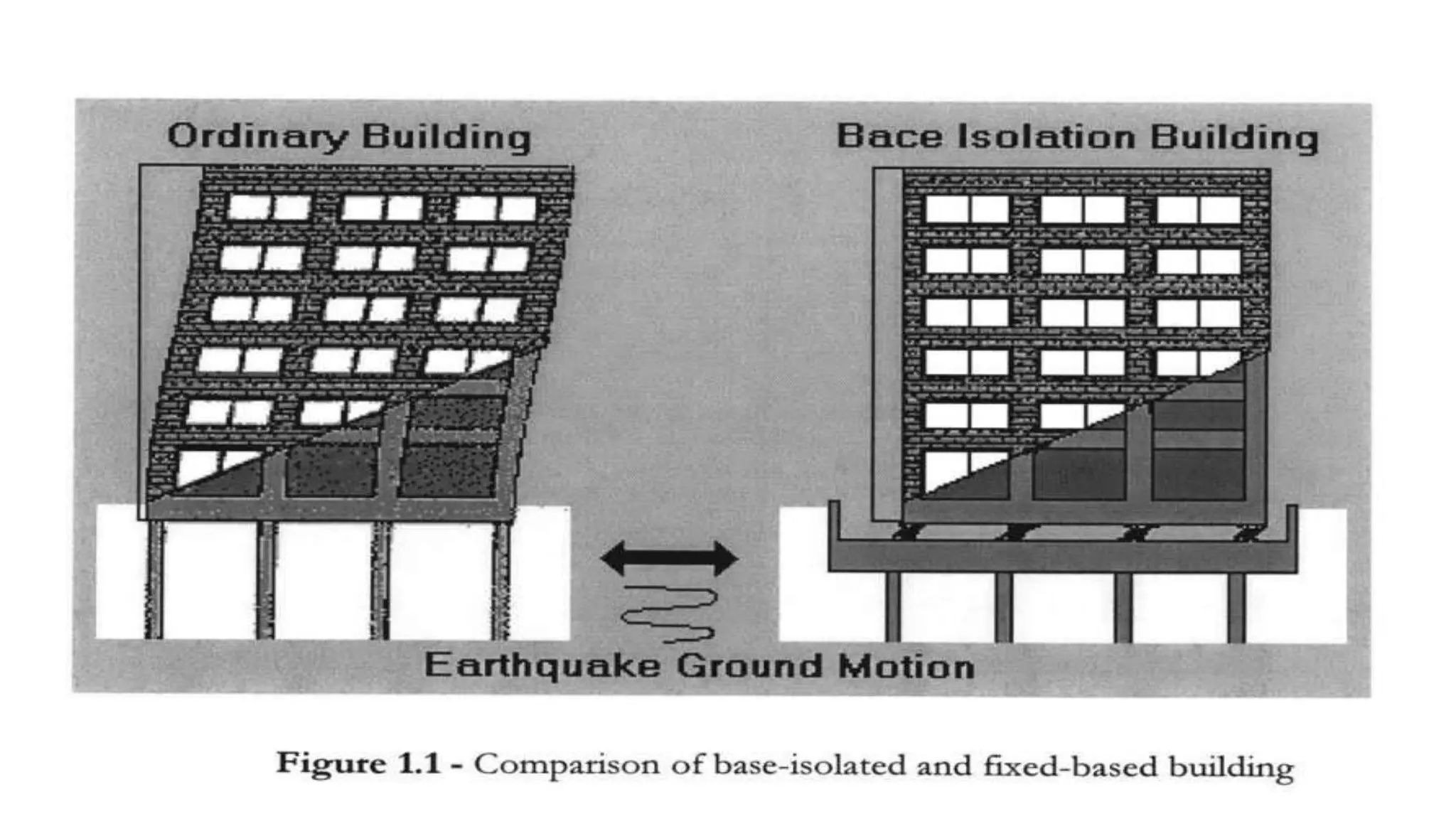
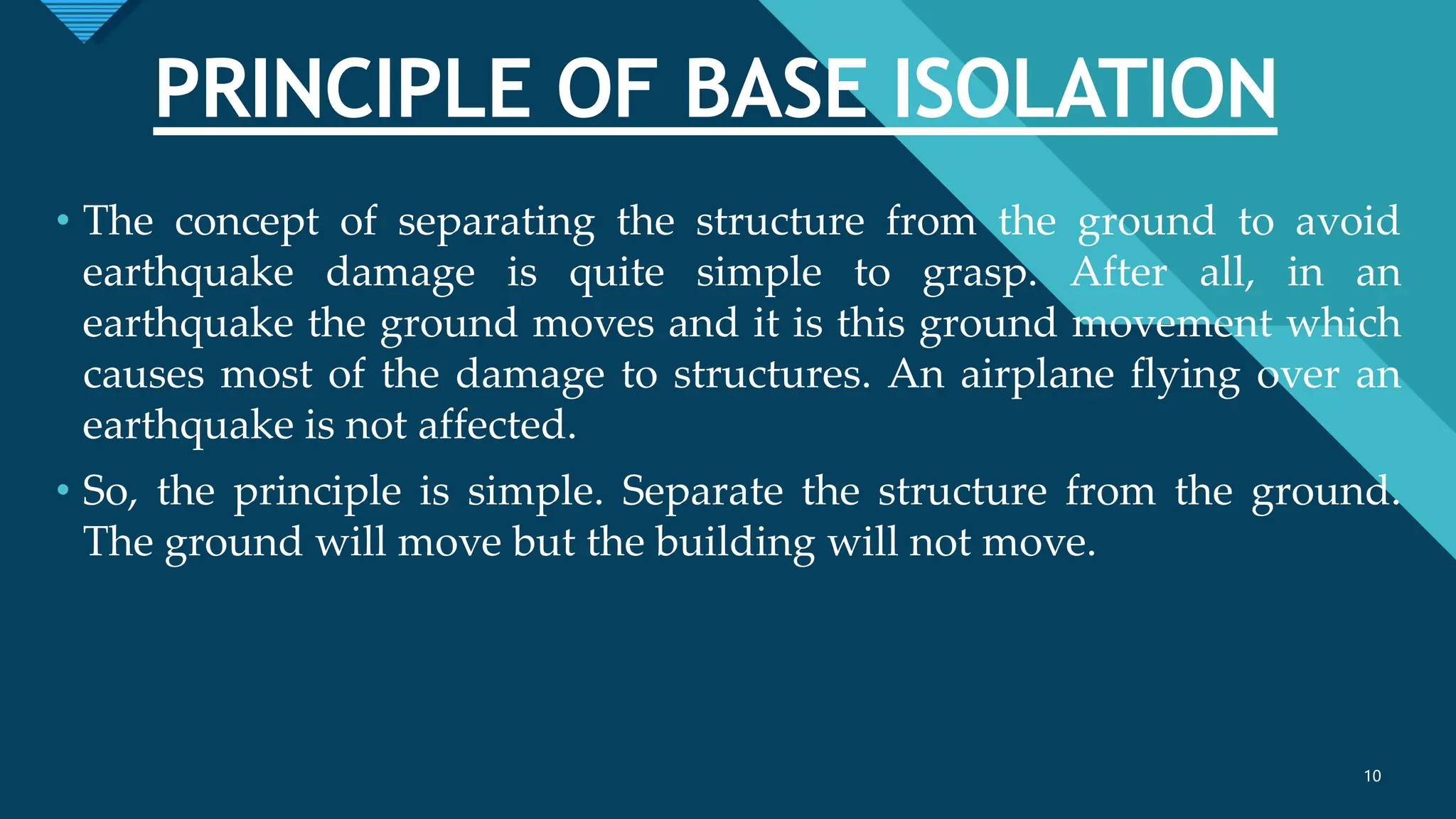
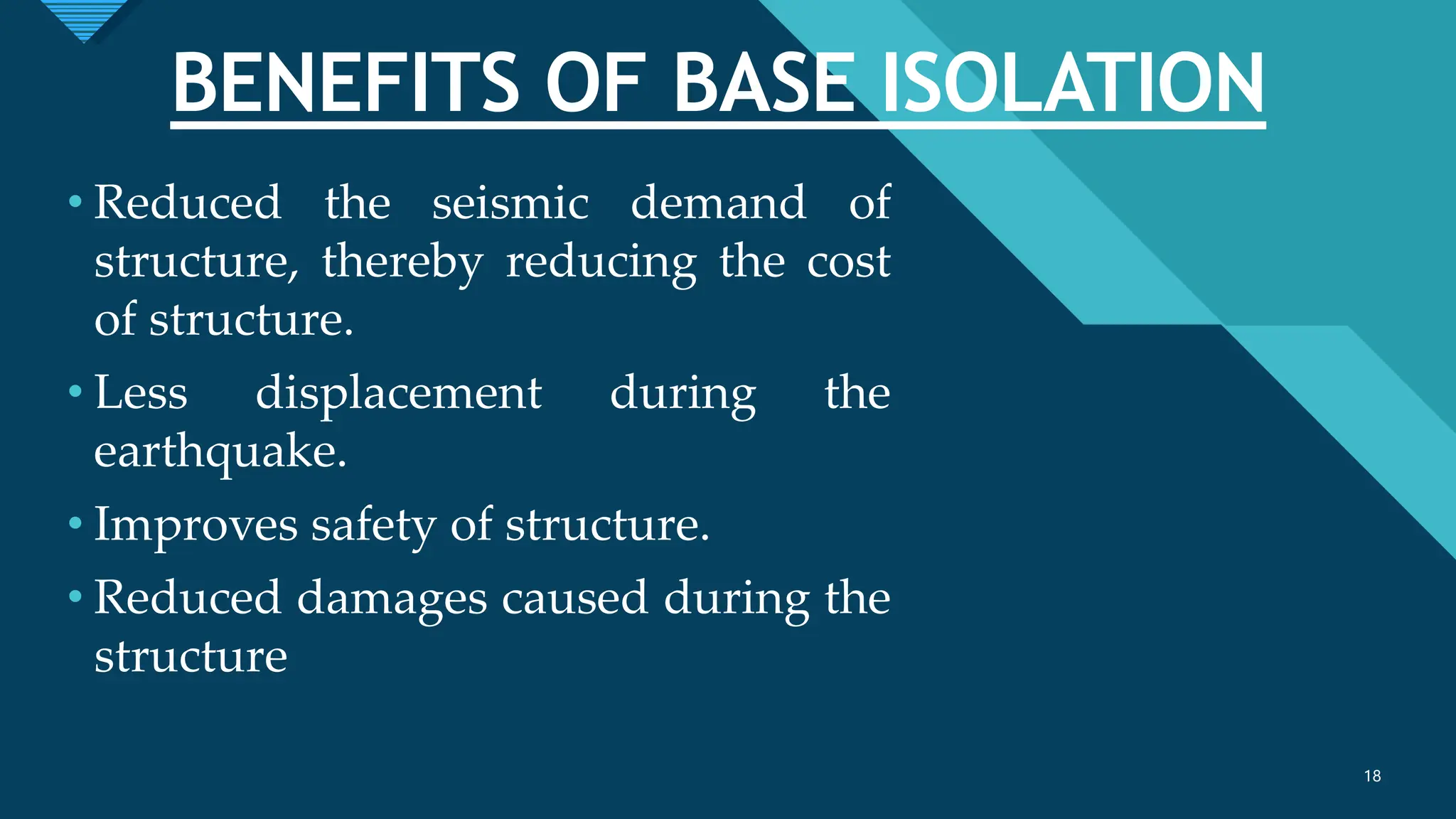
The document discusses the concept and implementation of base isolation as a seismic protection system for buildings, highlighting its effectiveness in reducing earthquake damage by decoupling structures from ground motion. It acknowledges the contributions of supervisors, the university, and personal support while outlining various types of base isolation techniques, their benefits, and real-life applications. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of appropriate materials and design in constructing earthquake-resistant buildings to ensure safety.