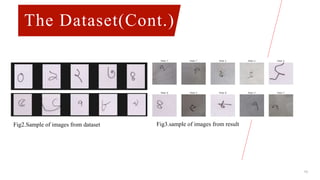
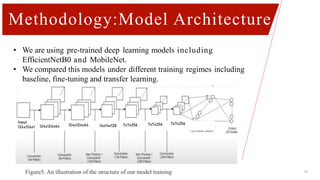
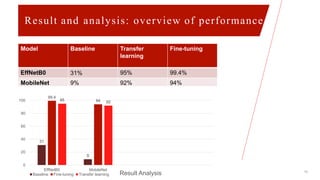
This document describes a project on Bangla handwritten digit recognition using deep learning models. It discusses preprocessing a dataset of 2500 training and 500 testing Bangla handwritten digit images. Two models - EfficientNetB0 and MobileNet - were trained using baseline, transfer learning, and fine-tuning methods. Fine-tuning achieved the best results, with 99.4% and 94% accuracy for EfficientNetB0 and MobileNet respectively. Limitations and future work are discussed to improve dataset quality and model performance.