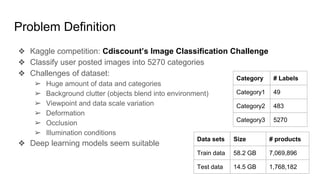
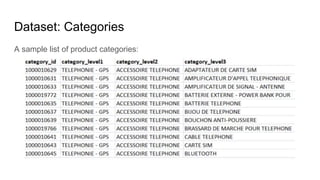
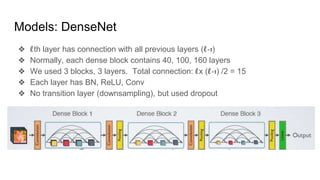
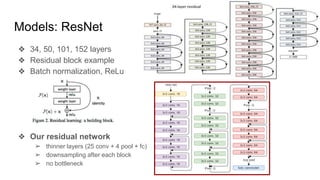
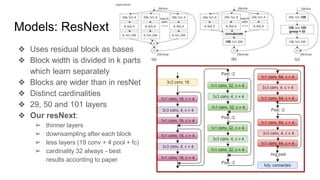
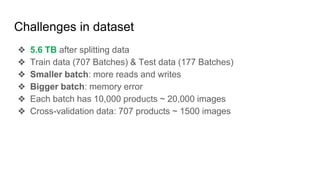
This document summarizes research on using deep convolutional networks for multi-class image classification on a large dataset from a product image classification Kaggle competition. The dataset contains over 5 million images across 5270 categories. Several deep learning models were tested including CNNs, DenseNet, ResNet, ResNext, and WideResNet. WideResNet achieved the best results with over 40% accuracy, while ResNext was the slowest. Training the models required significant computing resources and time due to the large dataset size. Future work includes submitting results to the Kaggle competition after more training epochs.