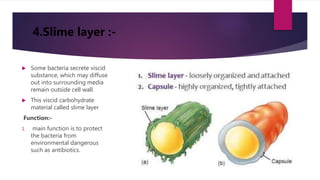
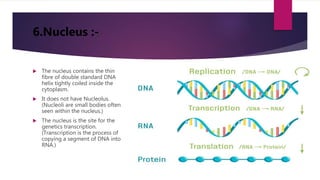
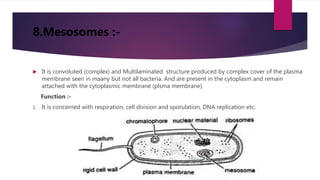
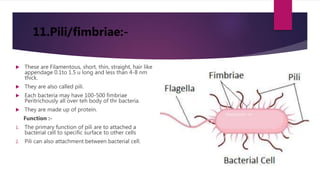
Microbes are tiny living organisms too small to be seen with the naked eye. They include bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa, and algae. Bacteria are single-celled microbes that can be spherical (cocci), rod-shaped (bacilli), or spiral (spirochetes). Bacterial cells contain a cell wall, cytoplasm, DNA, ribosomes, and may have structures like flagella, pili, or a capsule. Flagella and pili help bacteria move and attach to surfaces. Bacteria are classified by their shape, size, and oxygen requirements. The human body contains many beneficial microbes as well as pathogens.