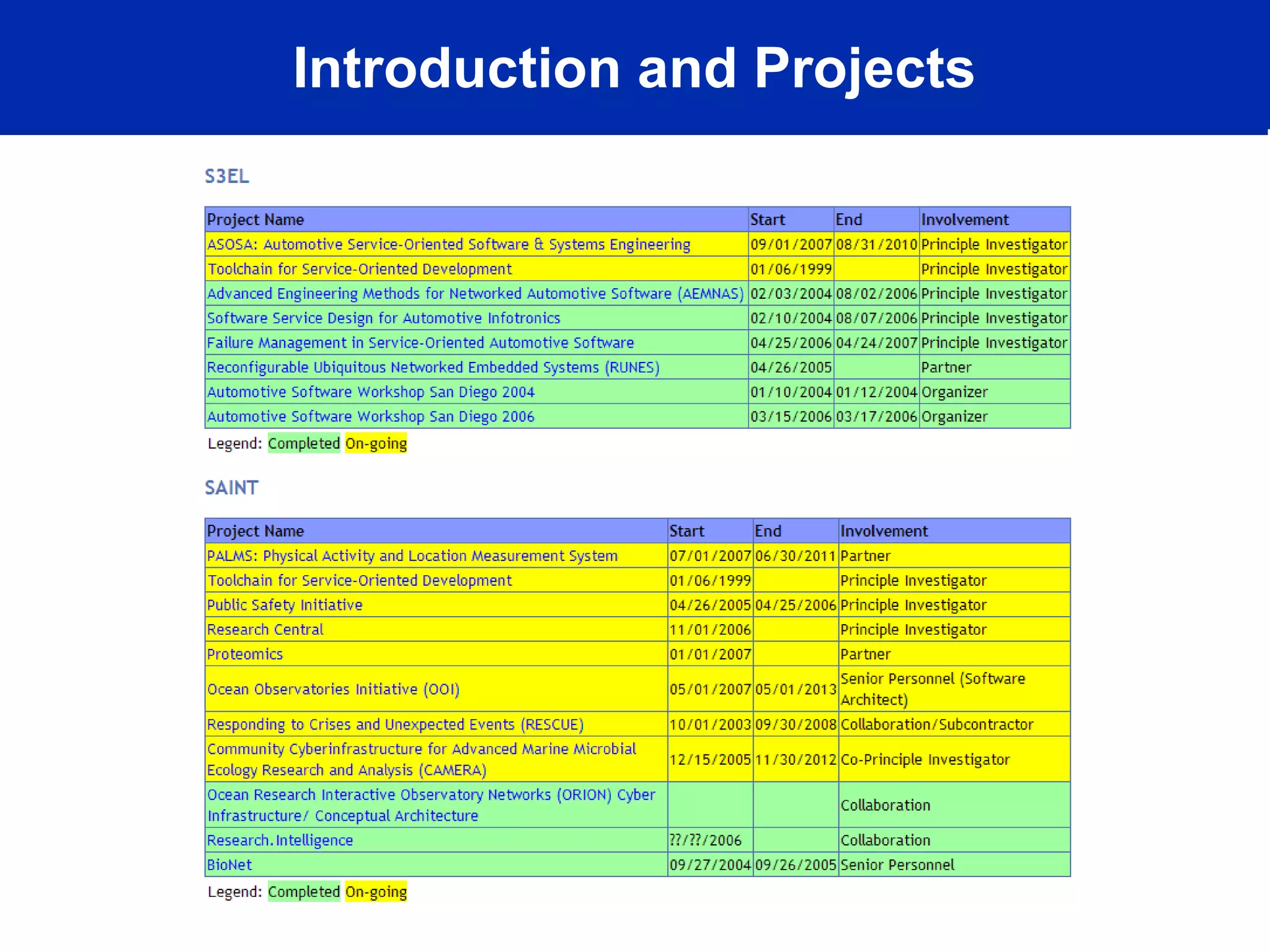
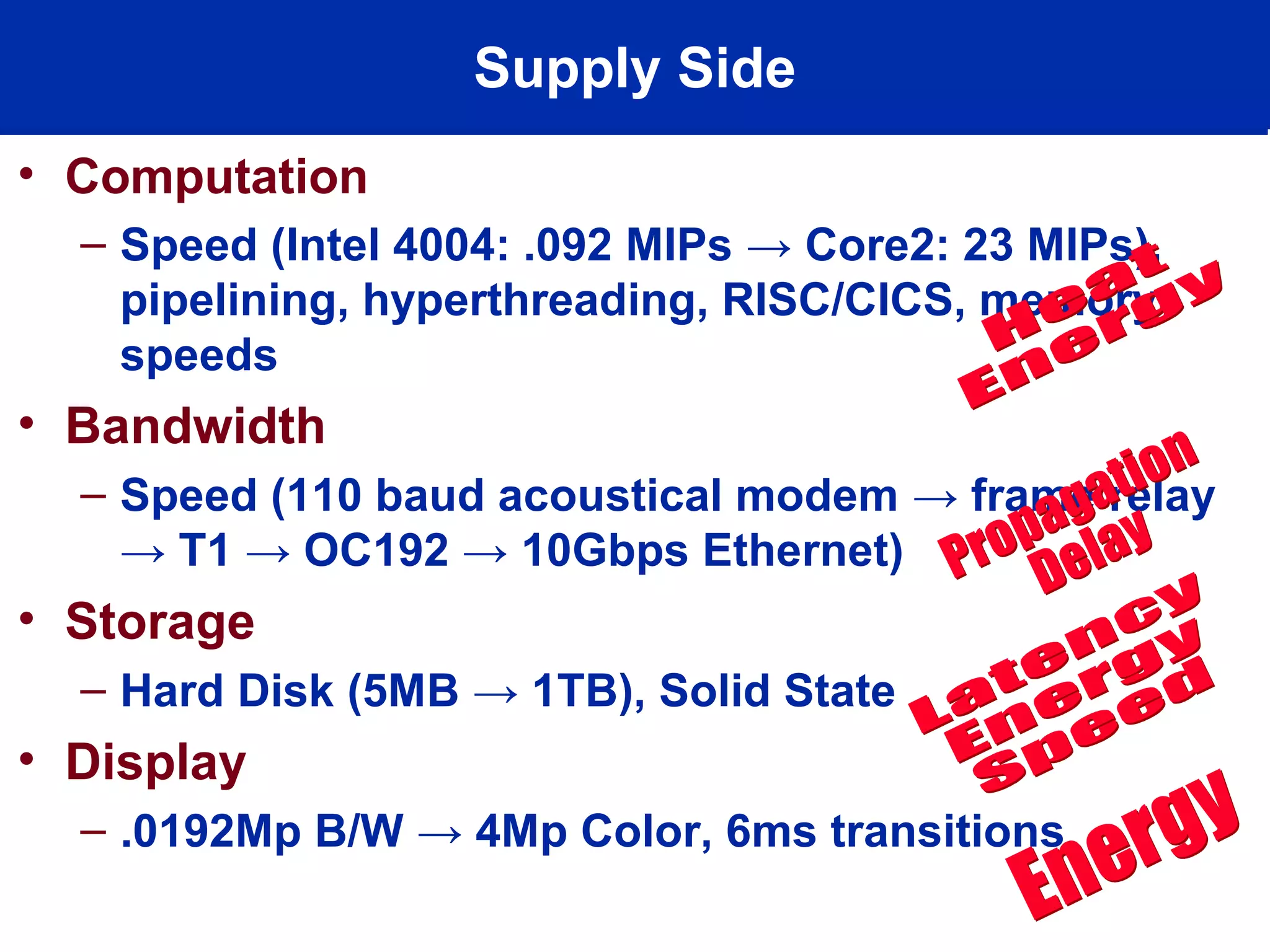
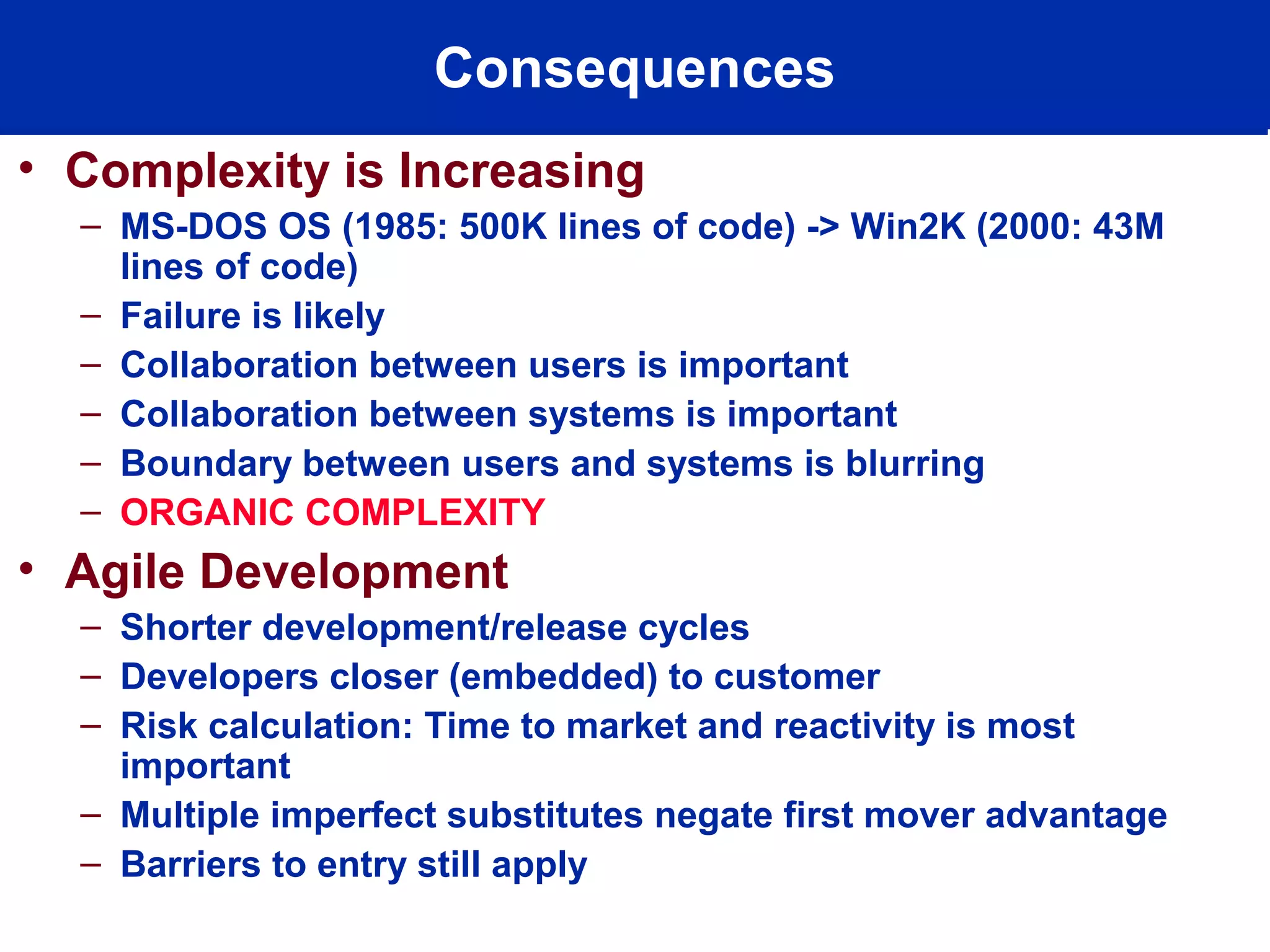
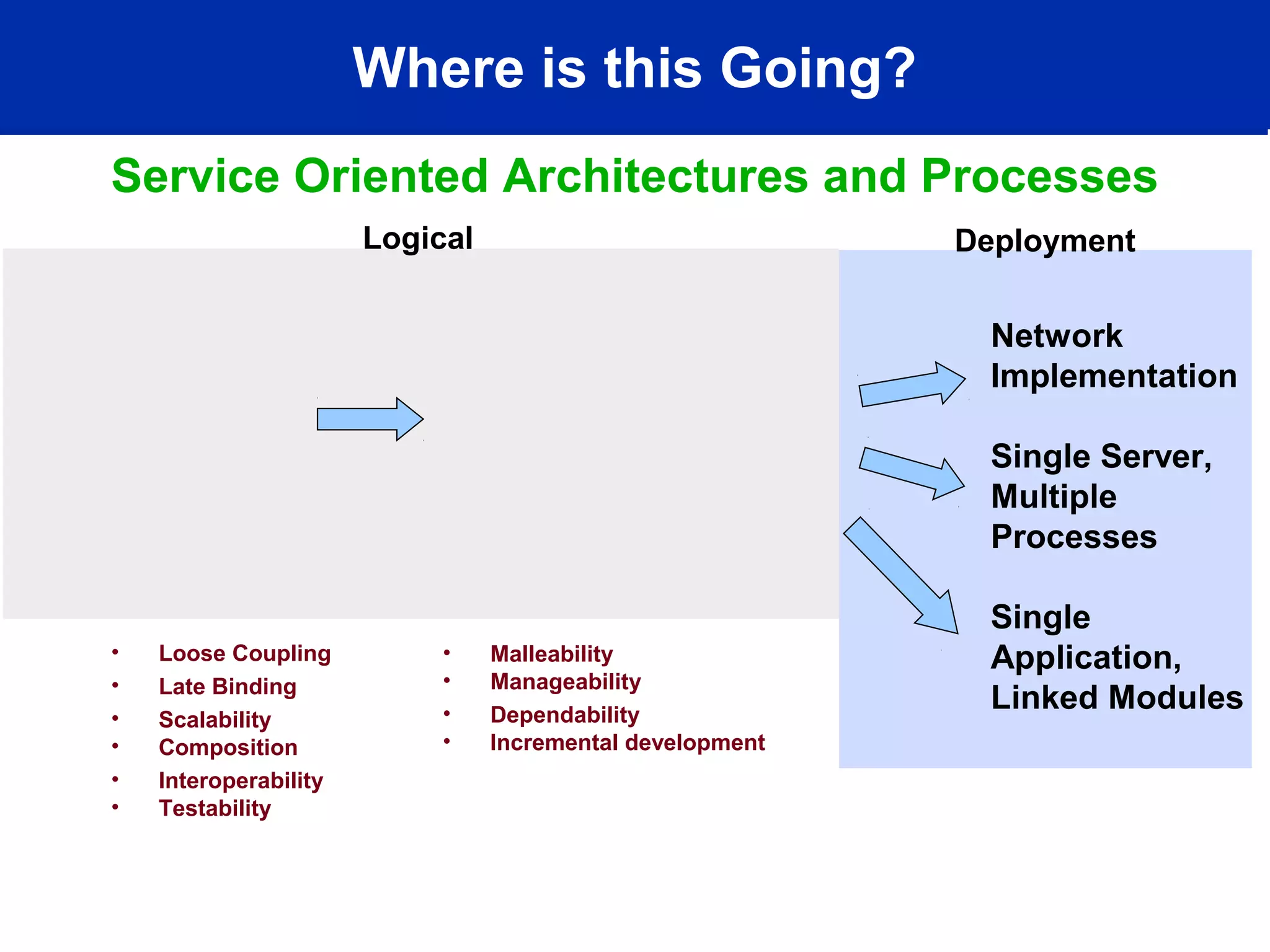
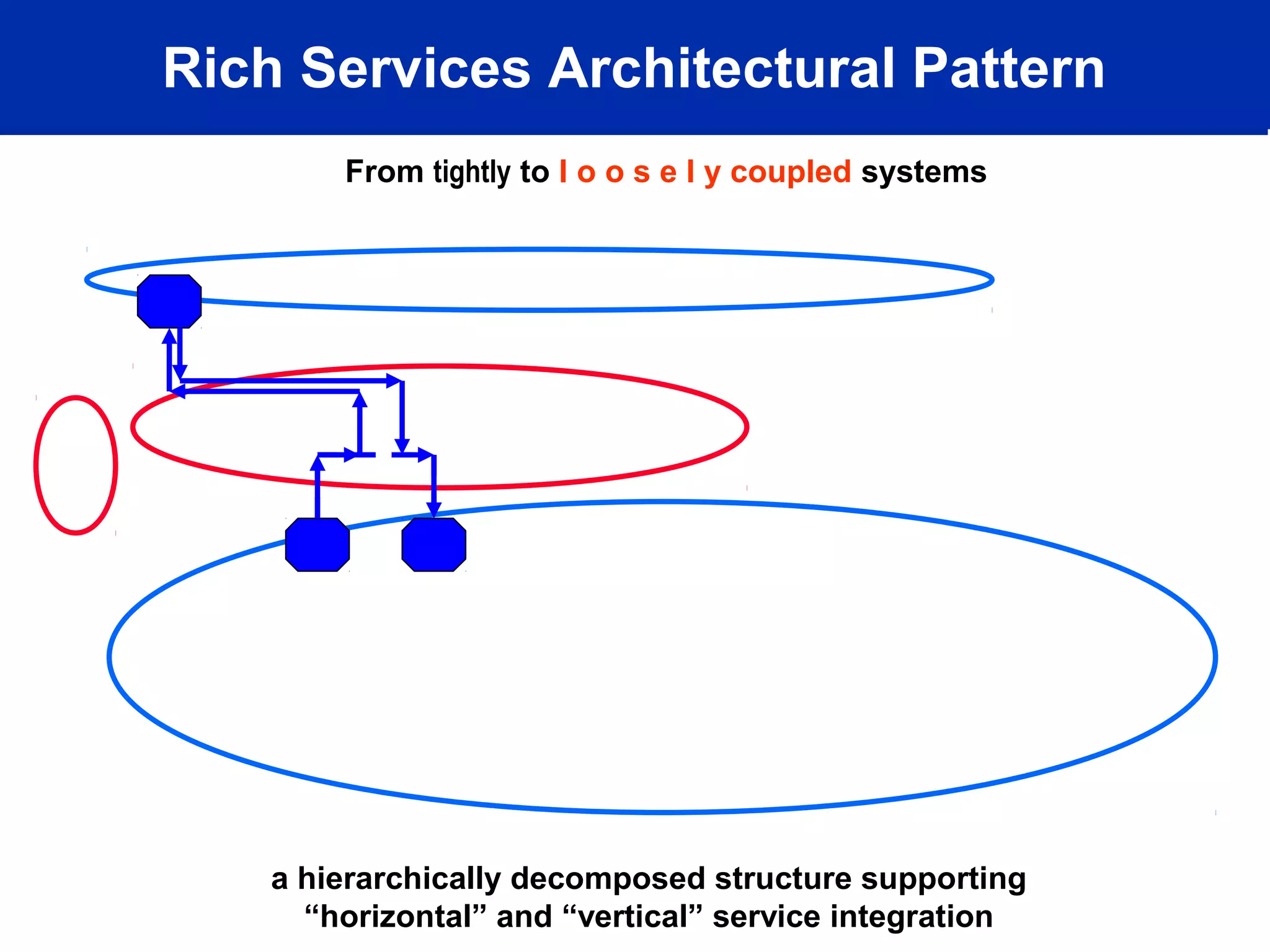
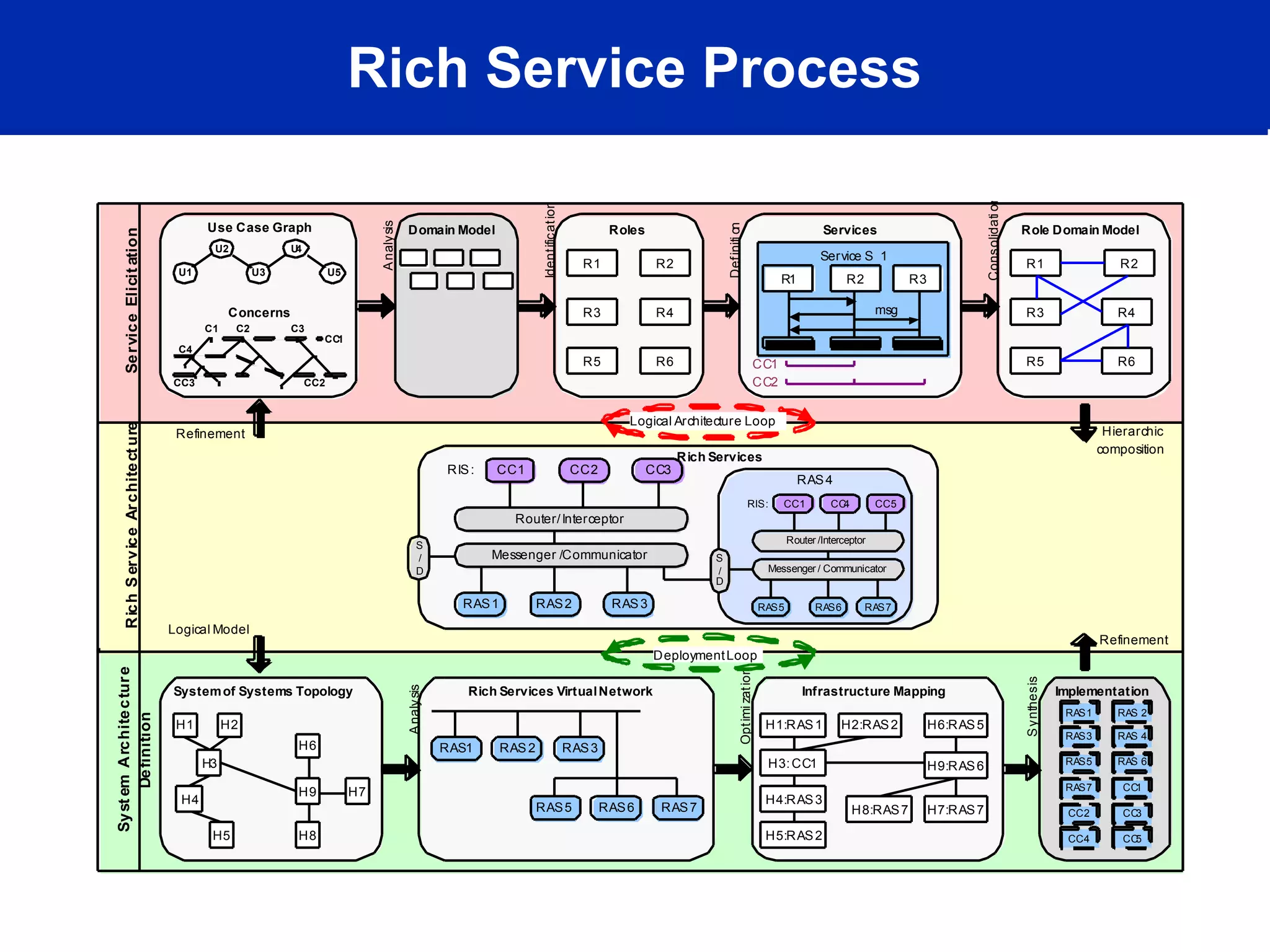
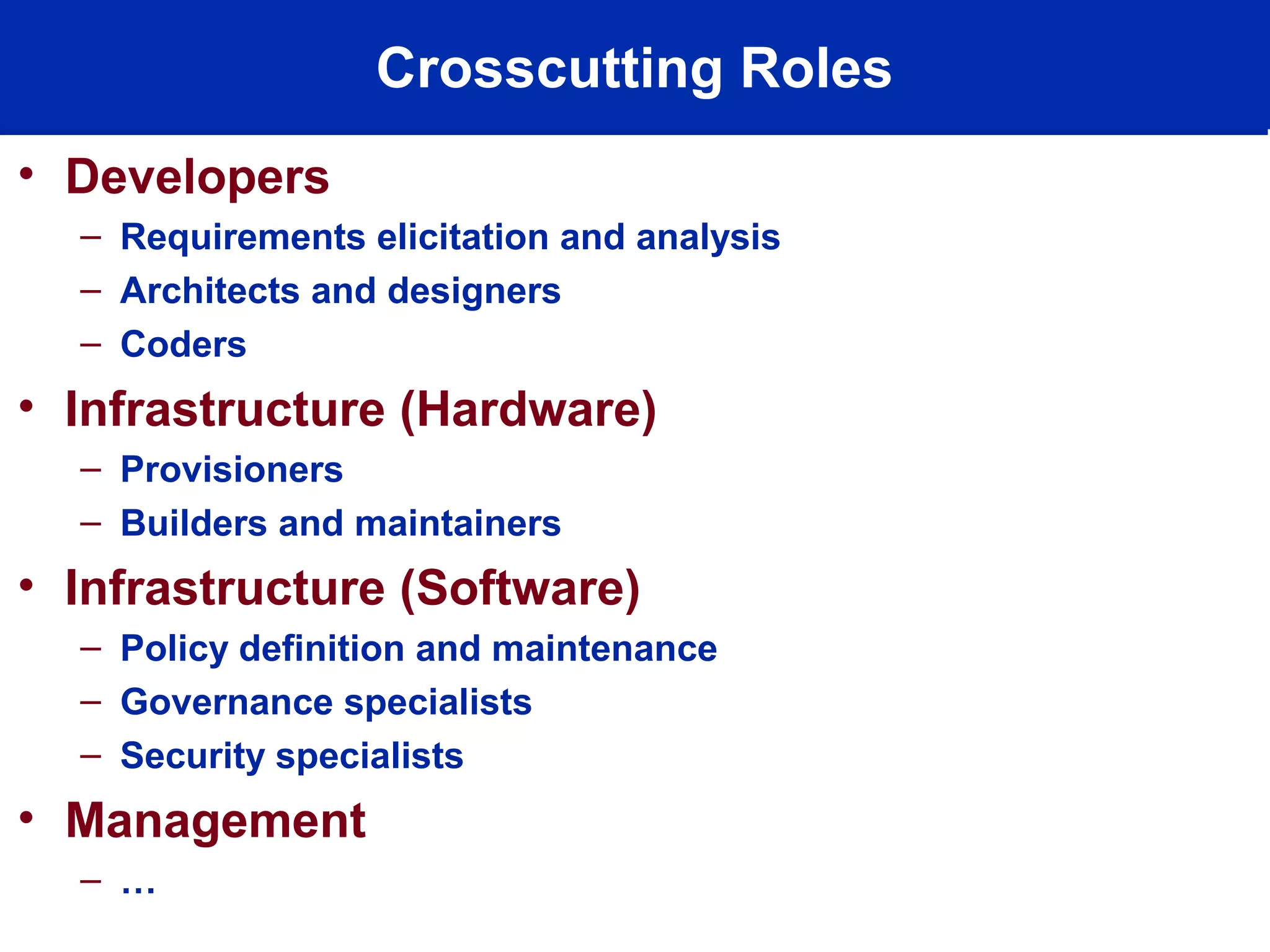
This document discusses technology trends driving changes in systems architecture. It notes rapid growth in computation, bandwidth, storage, and display capabilities (supply), creating demand from various stakeholders including corporations, individuals, and mobile users. This is making systems more complex, distributed, and community-oriented. It advocates for loosely coupled, service-oriented architectures and agile development processes to build scalable, interoperable, and manageable systems. Key roles discussed include web developers, utility providers, software providers, and virtual communities.