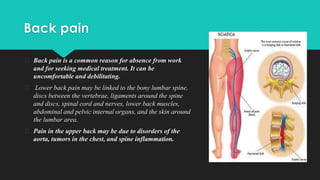
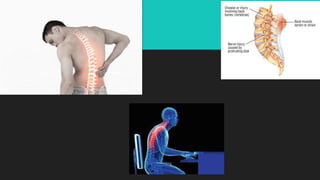
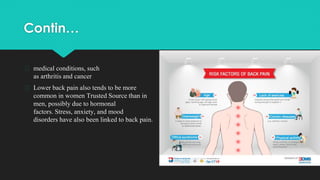
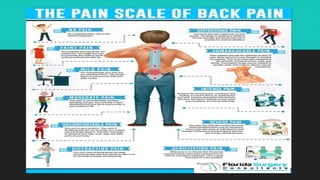
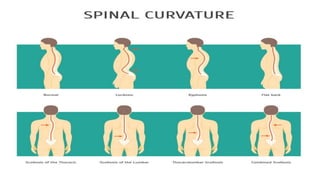
Back pain is a prevalent issue related to various anatomical and lifestyle factors, often caused by strain, injury, structural problems, or medical conditions. It can manifest as acute or chronic pain, with symptoms ranging from discomfort to sharp pain radiating through the legs. Treatment typically includes home remedies and medication, but may progress to physical therapy, injections, or alternative methods if pain persists.