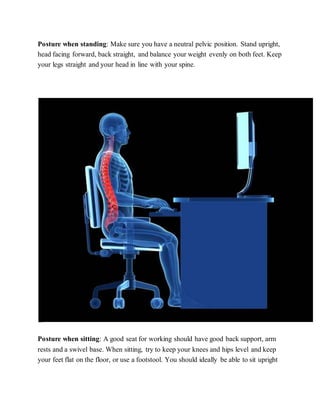
Back pain is a common and debilitating condition that can arise from various causes, including injury, medical conditions, and poor posture. It can manifest as acute or chronic pain, often requiring different treatment approaches such as medication, physical therapy, or in rare cases, surgery. To prevent back pain, maintaining good posture, regular exercise, and addressing risk factors like weight and smoking are essential.