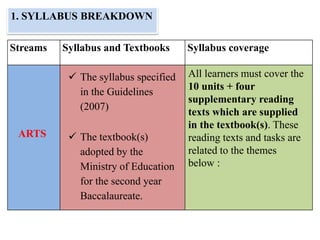
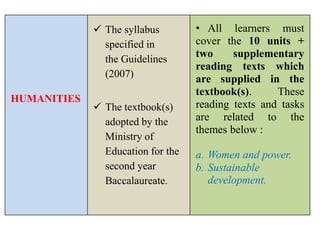
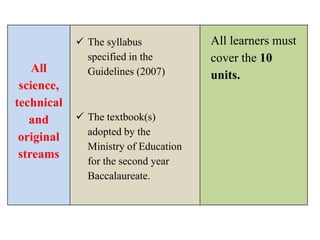
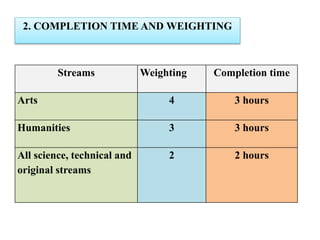
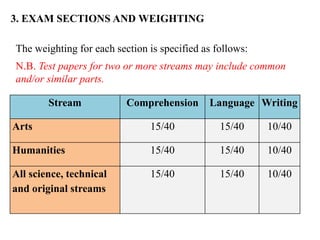
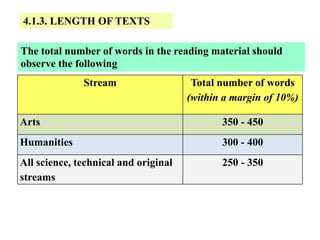
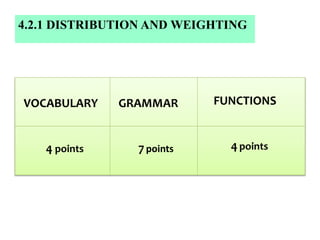
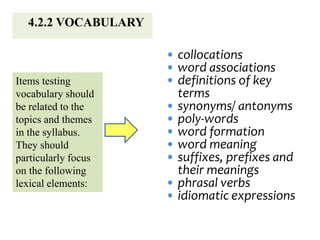
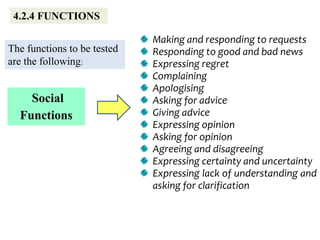
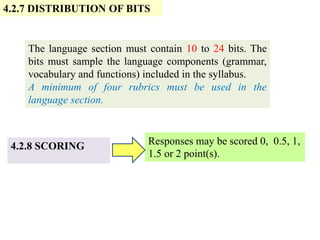
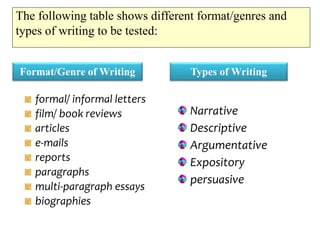
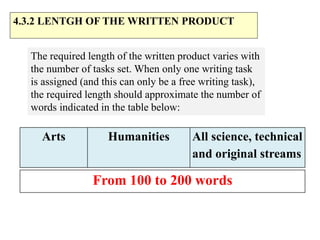
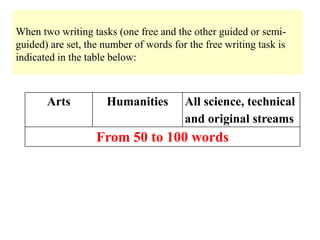
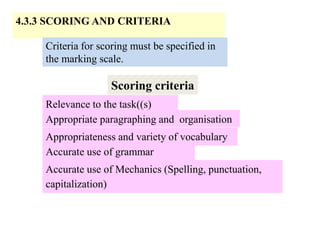
The document outlines the specifications for the 2014 Moroccan national baccalaureate exam in English, detailing the content structure and assessment criteria for various educational streams, including arts and sciences. It specifies the exam's focus on reading comprehension, language accuracy, and writing skills, including the number of units and themes that must be covered in the curriculum. The document also includes guidelines on scoring, test techniques, and the required length for writing tasks.