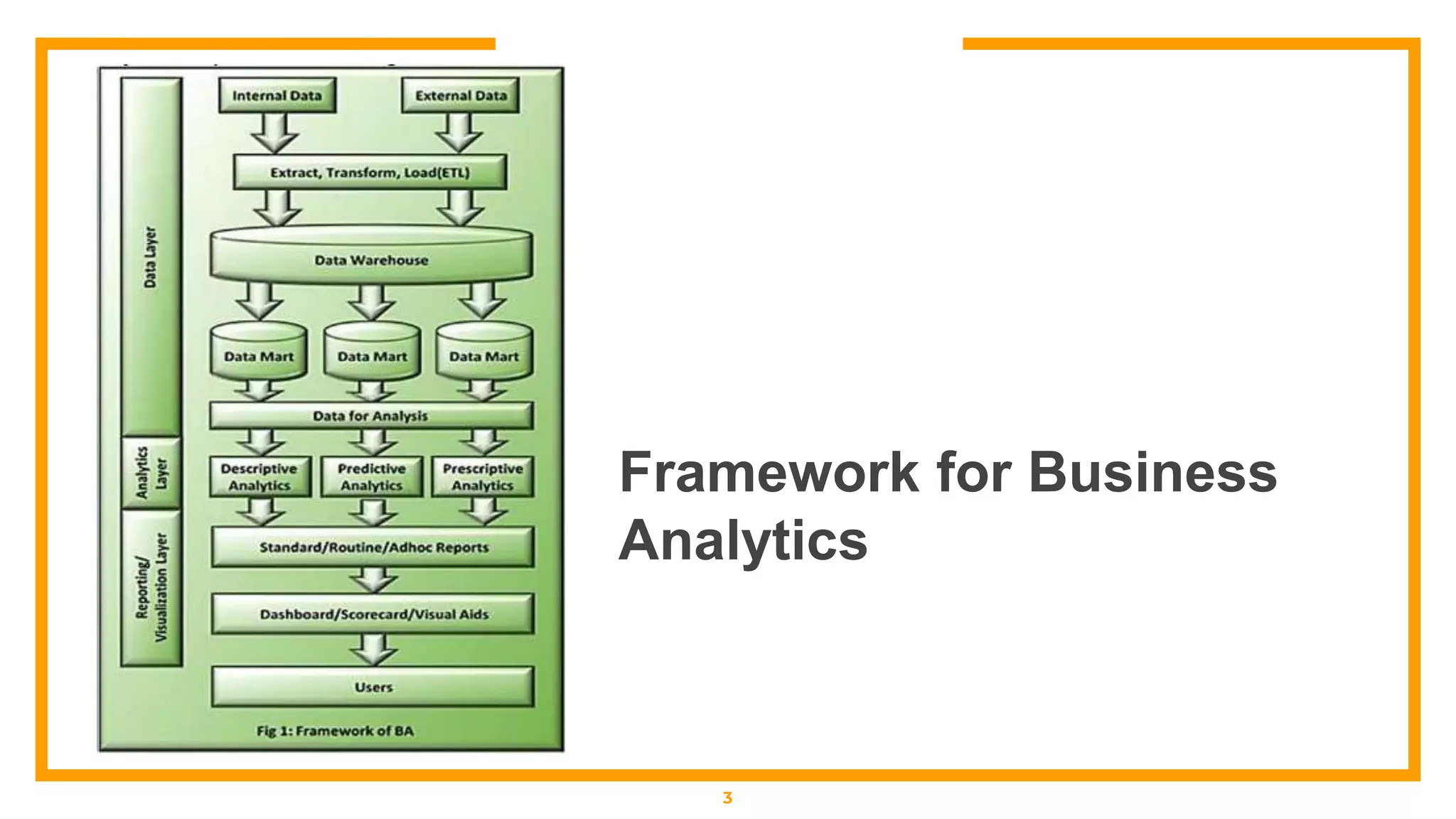
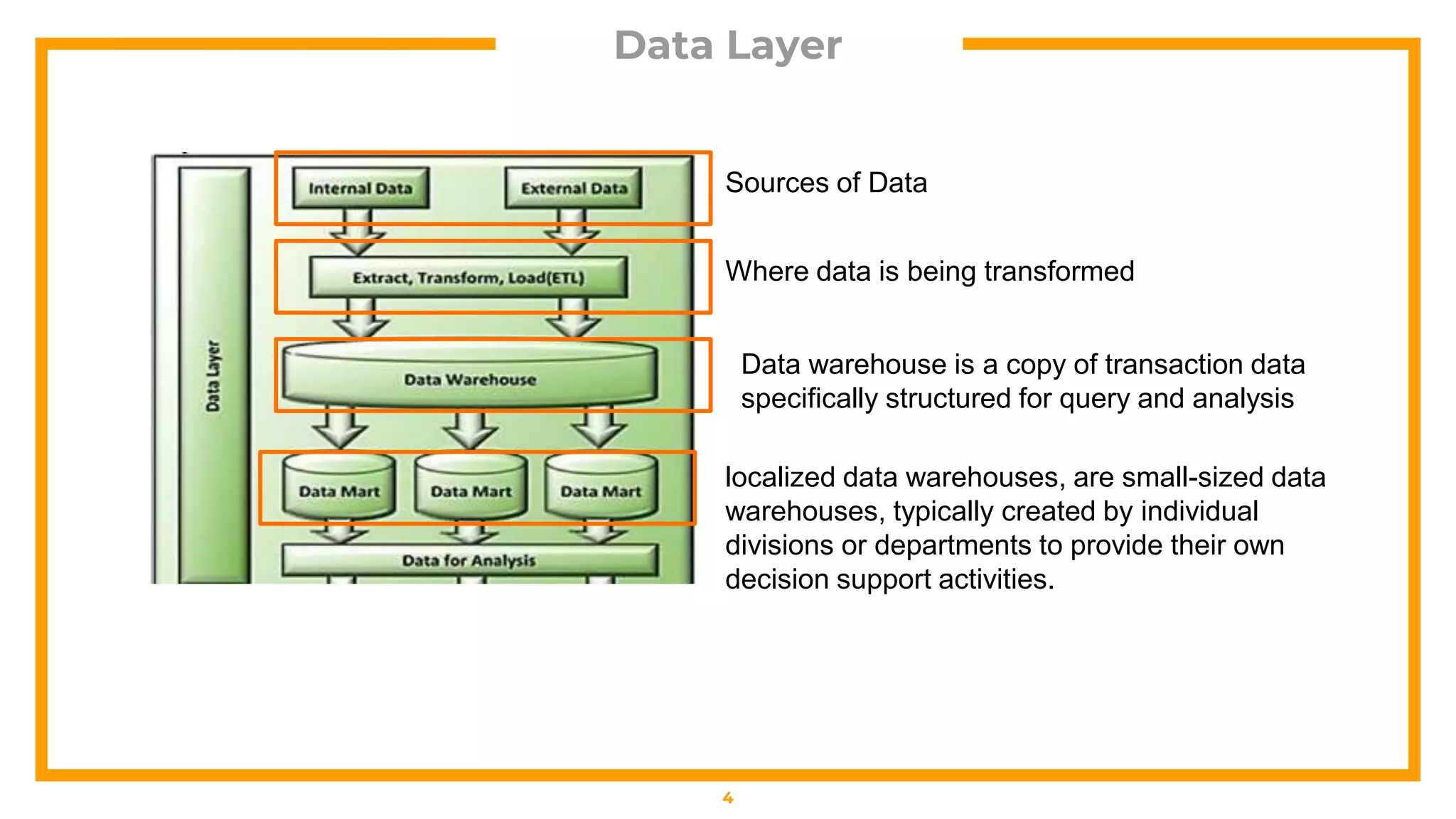
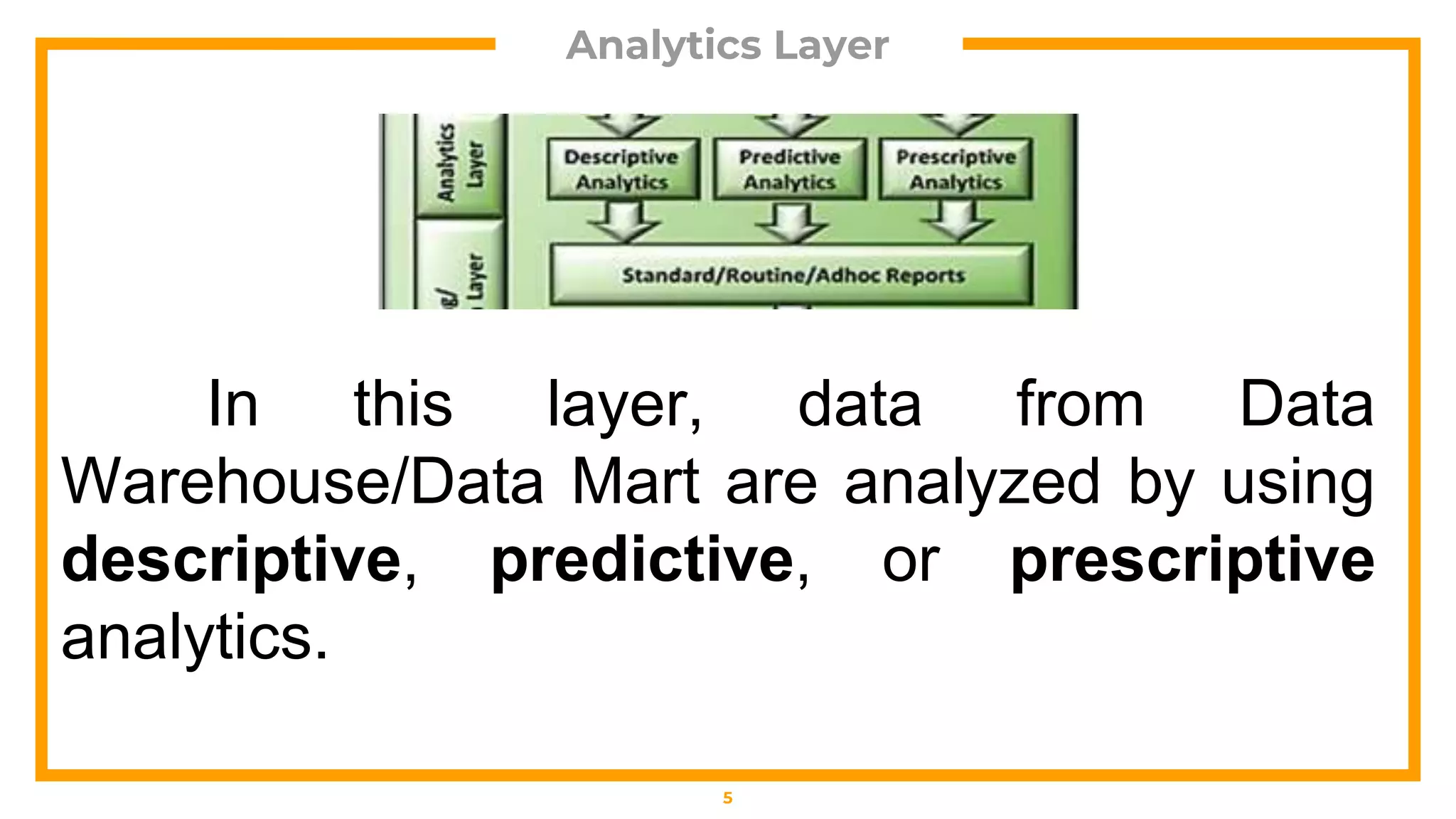
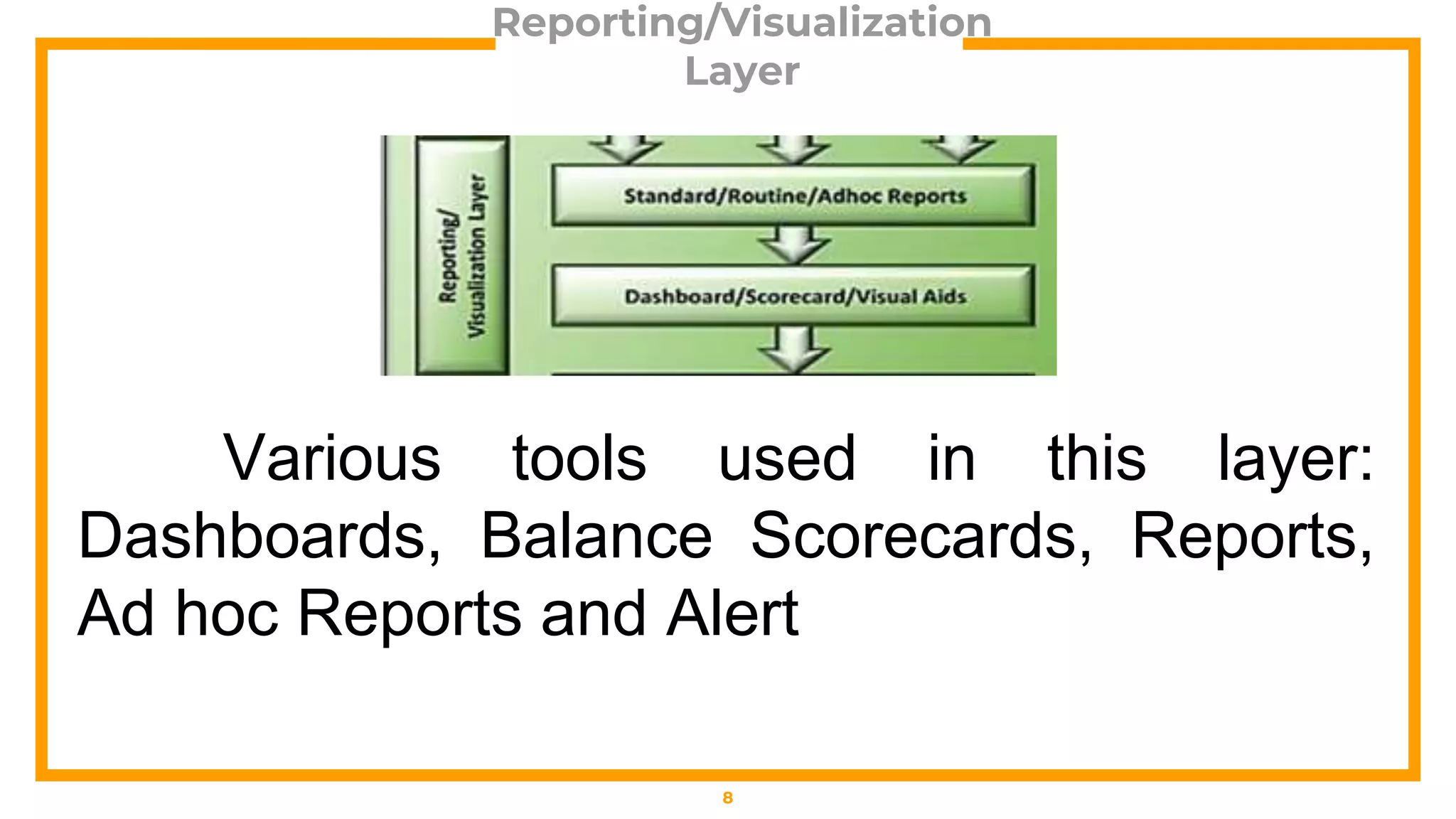
This document outlines a business analytics framework with 4 layers: 1) Data Layer which sources and transforms data, 2) Analytics Layer which analyzes data using descriptive, predictive, or prescriptive techniques like data mining and multidimensional analysis, 3) Reporting/Visualization Layer which uses tools like dashboards and reports, and 4) Access Layer. It also describes 4 types of analytics: descriptive (explains what happened), diagnostic (explains why it happened), predictive (forecasts what may happen), and prescriptive (recommends actions based on forecasts).