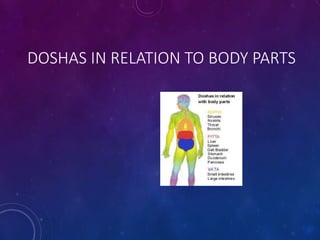
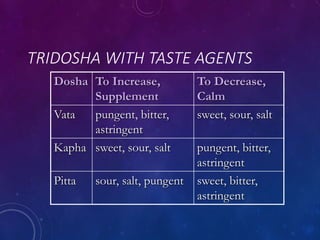
Ayurveda is an ancient holistic system of medicine that aims to promote health and prevent disease. It focuses on three doshas or biological energies - vata, pitta, and kapha - that must remain balanced for health. The eight branches of Ayurveda cover internal medicine, pediatrics, surgery, eye/ear treatments, psychiatry, toxicology, rejuvenation therapies, and aphrodisiacs. Basic principles include the five elements, three doshas, biological fire or digestion, and applying Ayurvedic fundamentals to improve life.