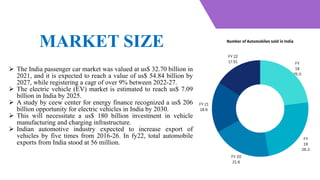
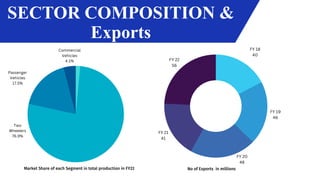
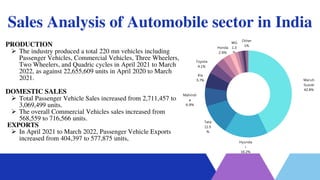
The Indian automobile sector produced approximately 22.93 million vehicles from April 2021 to March 2022 and is projected to become the world's third-largest automotive market by 2030, significantly driven by electric vehicle growth. The industry contributes 7.1% to India's GDP and is crucial for exports, with expectations of a five-fold increase in vehicle exports by 2026. Investments in manufacturing and charging infrastructure are forecast to reach $180 billion by 2030 to support the growth of the EV market, which is anticipated to create 50 million jobs.