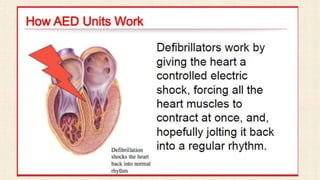
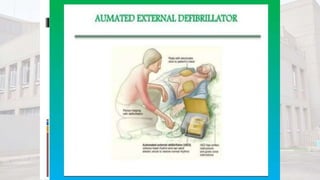
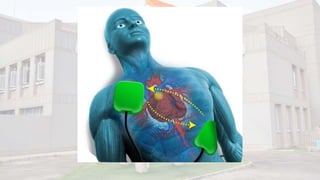
The document outlines the steps for using an automated external defibrillator (AED) to treat cardiac arrest. It begins by listing the indications for AED use as cardiac arrest from sudden disruption of the heart's normal rhythm. Contraindications include non-cardiac arrest, children under 1 year old, and wet/moist environments. The 10 steps for using an AED are then described, beginning with assessing the situation and activating emergency services, and ending with assisting emergency personnel upon their arrival. Basic AED parts are also identified.