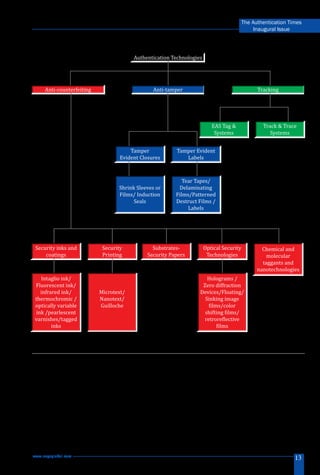
The document discusses the importance of authentication technologies in combating counterfeiting and fraud, highlighting three main areas: anti-counterfeiting, anti-tampering, and track and trace. It categorizes authentication methods into overt, covert, forensic, and digital technologies, explaining their roles and applications across different industries. The article emphasizes that a comprehensive brand protection strategy should involve a combination of technologies and adherence to standards like ISO:12931.