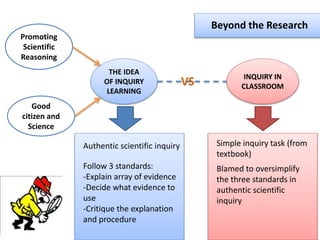
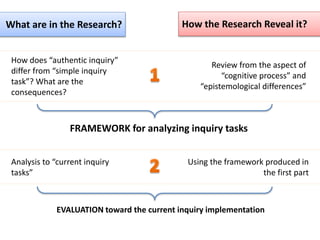
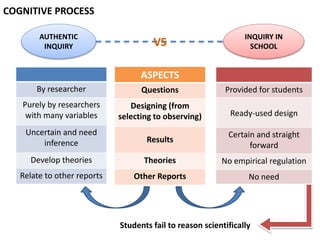
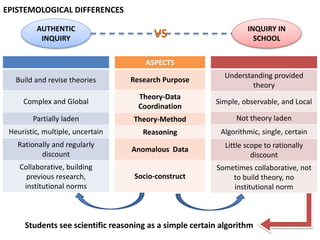
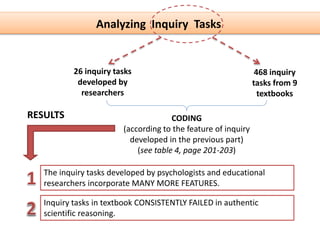
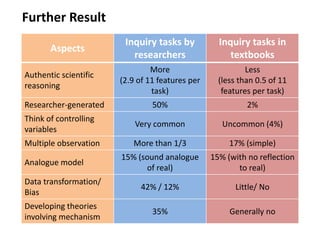
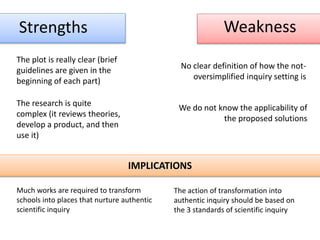
This document presents a theoretical framework for evaluating inquiry tasks based on the differences between authentic scientific inquiry and simple inquiry tasks from textbooks. It defines three standards for authentic inquiry: explaining evidence, deciding what evidence to use, and critiquing explanations and procedures. The framework analyzes inquiry tasks based on their cognitive processes and epistemological aspects. An analysis of 468 textbook inquiry tasks found they consistently failed at authentic reasoning, featuring less than half the aspects of researcher-generated tasks. The implications are that transforming schools to nurture authentic inquiry requires significant work and should be based on the three standards of scientific inquiry.