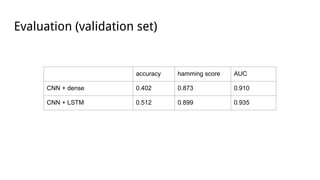
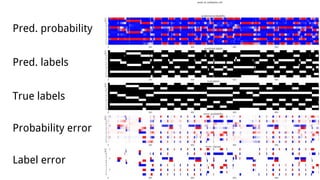
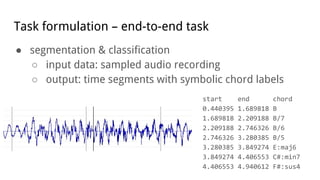
This document discusses using deep neural networks for audio chord recognition from music recordings. It describes the task of identifying chord labels for time segments of audio. The model uses convolutional and recurrent layers with chromagram features extracted from the audio as input. Evaluation shows the CNN+LSTM model achieves over 50% accuracy on a dataset of 180 annotated songs. Future work ideas include improving segmentation and exploring additional neural network architectures.


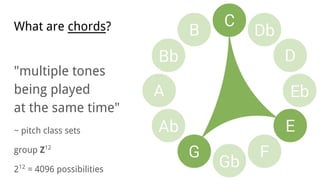

![Representation ● symbolic names
● pitch class sets (unique tones)
[1, 3, 5] [1, 4, 6] [2, 5, 7]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/audiochordrecognition-usingdeepneuralnetworks-160919205844/85/Audio-chord-recognition-using-deep-neural-networks-6-320.jpg)








![model = Sequential()
model.add(TimeDistributed(Convolution1D(32, 3, activation='relu'), input_shape=(max_seq_size, feature_count, 1)))
model.add(TimeDistributed(Convolution1D(32, 3, activation='relu')))
model.add(TimeDistributed(MaxPooling1D(2, 2)))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(TimeDistributed(Convolution1D(64, 3, activation='relu')))
model.add(TimeDistributed(Convolution1D(64, 3, activation='relu')))
model.add(TimeDistributed(MaxPooling1D(2, 2)))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(TimeDistributed(Convolution1D(64, 3, activation='relu')))
model.add(TimeDistributed(Convolution1D(64, 3, activation='relu')))
model.add(TimeDistributed(MaxPooling1D(2, 2)))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(TimeDistributed(Flatten()))
model.add(BatchNormalization())
model.add(LSTM(64, return_sequences=True))
model.add(LSTM(64, return_sequences=True))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(TimeDistributed(Dense(12, activation='sigmoid')))
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(X_train, Y_train, validation_data=(X_valid, Y_valid), nb_epoch=10, batch_size=32)
implemented in Python
using Keras on top of
Theano/TensorFlow
6x convolutions
2x recurrent
1x classifier](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/audiochordrecognition-usingdeepneuralnetworks-160919205844/85/Audio-chord-recognition-using-deep-neural-networks-18-320.jpg)