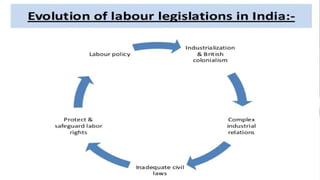
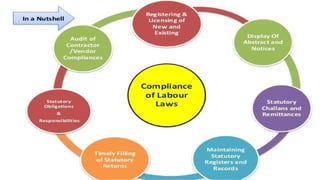
The document discusses the evolution, importance, and objectives of labor laws in India, which originated during the industrial revolution and aim to protect workers' rights. Key aspects include improving employee-employer relations, ensuring fair wages, job security, and social justice. The document also outlines the classification of labor laws based on purpose, legislature, and period of enactment.