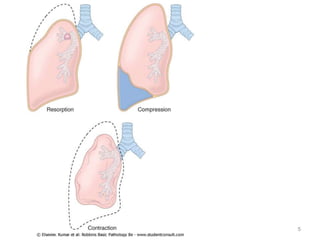
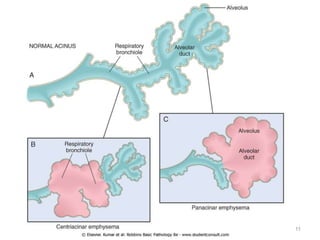
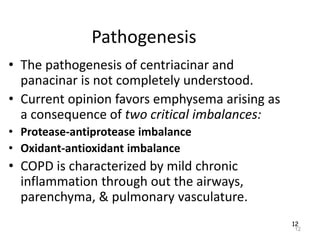
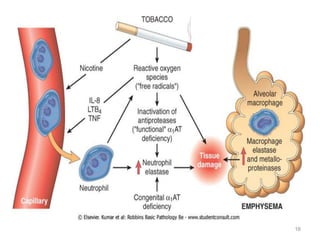
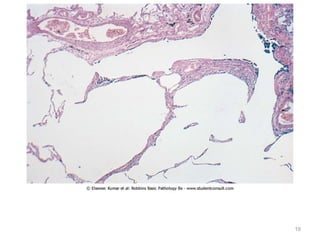
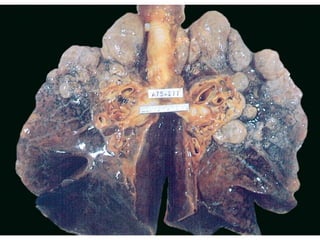
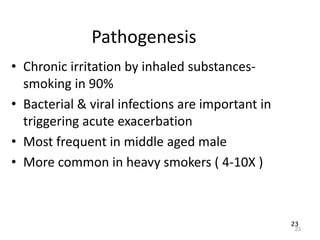
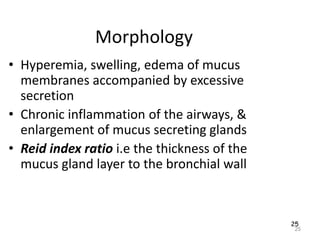
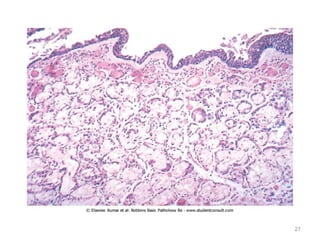
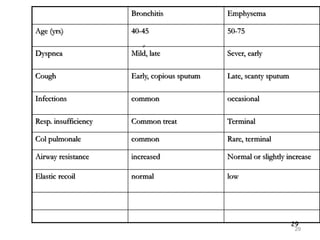
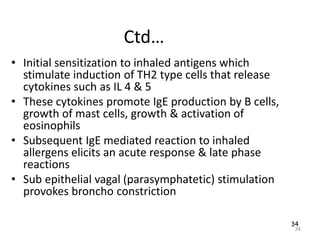
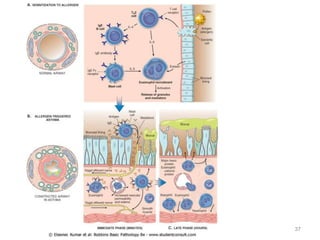
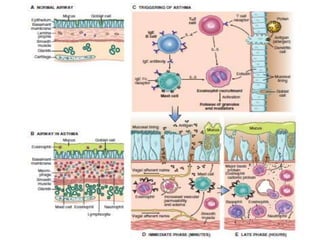
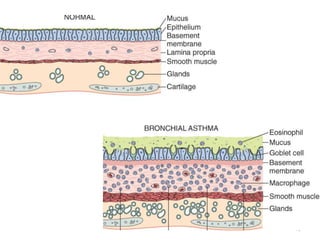
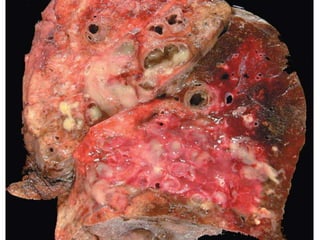
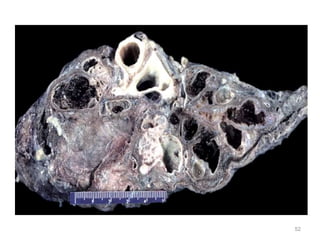
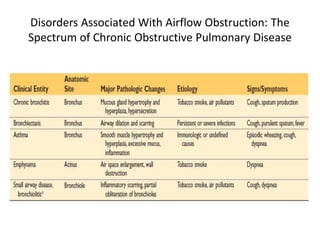
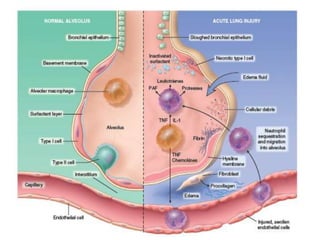
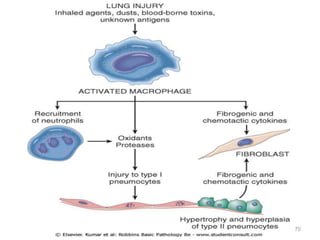
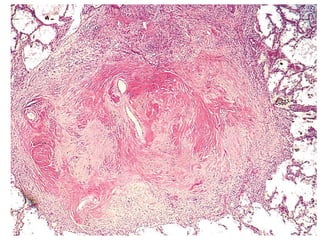
Atelectasis is the collapse of lung tissue caused by inadequate expansion of air spaces. It is classified into three forms: resorption, compression, and contraction atelectasis. Resorption occurs when an obstruction prevents air from reaching distal airways, causing absorption of existing air and alveolar collapse. Compression results from fluid, blood, or air accumulation in the pleural cavity compressing the lung. Contraction occurs when fibrosis affects lung or pleural expansion. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis. Emphysema is characterized by destruction of alveolar walls leading to enlarged air spaces, while chronic bronchitis involves inflammation of the large airways and