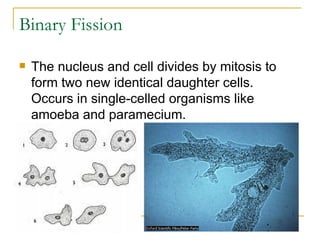
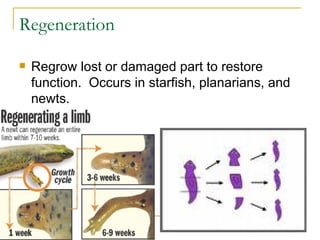
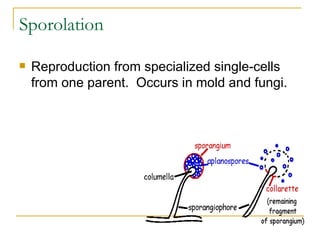
Asexual reproduction allows for reproduction with only one parent where the offspring are genetically identical clones of the parent. There are several types of asexual reproduction including binary fission in single-celled organisms, budding in hydra and yeast where one cell remains attached, and vegetative propagation where new plants grow from roots or stems of the parent plant.